At its core, the continuous movement of the sample in a rotary tube furnace is a mechanism for achieving unparalleled process consistency. This dynamic action ensures every particle of the material is exposed to identical thermal and atmospheric conditions, leading to superior product homogeneity, enhanced reaction efficiency, and faster processing times compared to static furnace designs.
The fundamental advantage is not just mixing; it is the systematic elimination of variables. By constantly turning the material, a rotary furnace guarantees that no single particle is shielded from heat or the controlled atmosphere, solving the common problems of hot spots, cold spots, and uneven chemical reactions.
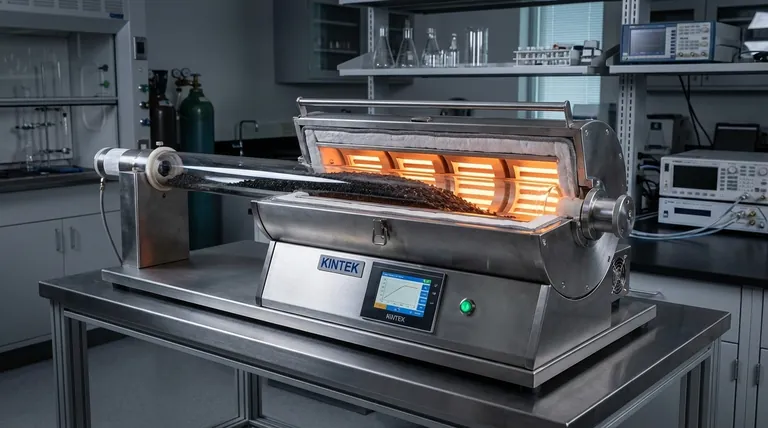

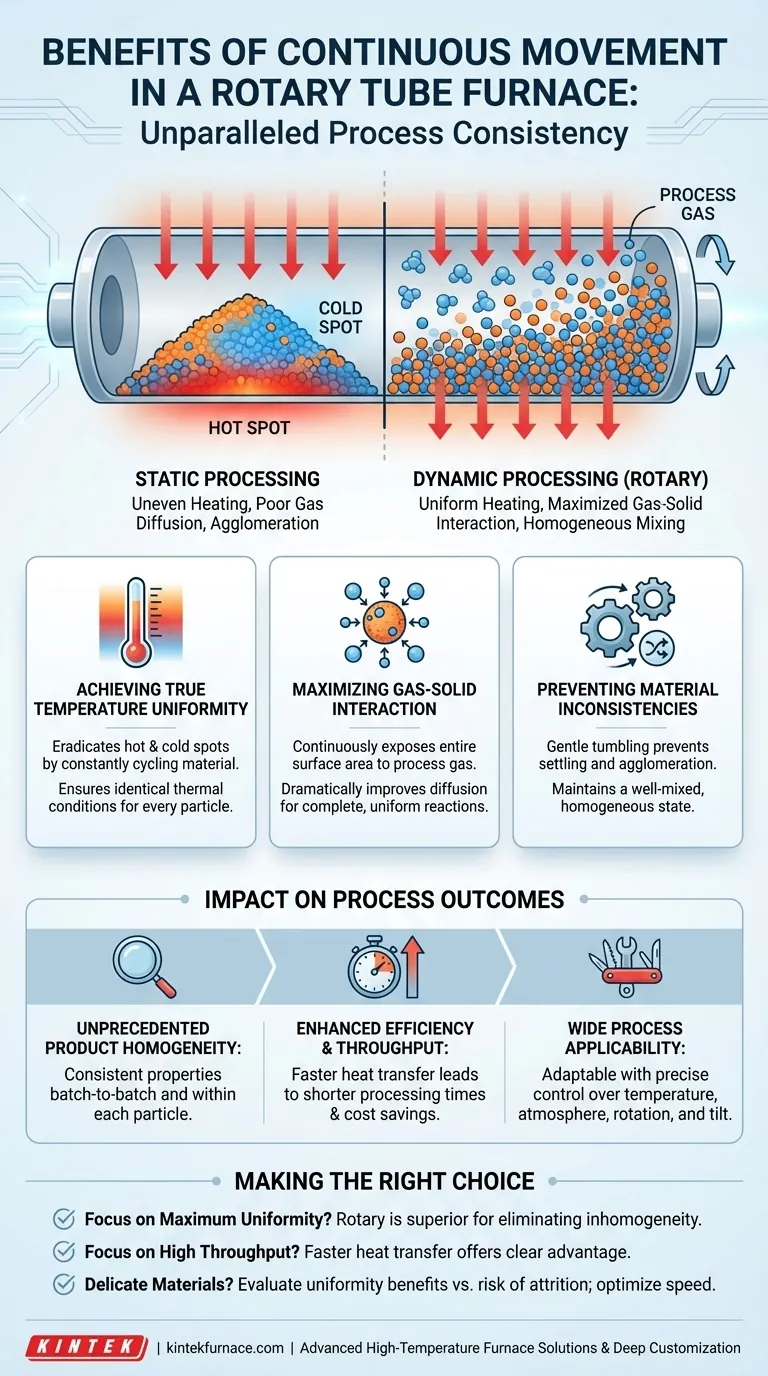
The Principle: From Static to Dynamic Processing
The shift from a stationary sample to one in continuous motion fundamentally changes the physics of heat treatment. It transforms the process from a passive one, reliant on slow thermal conduction and gas diffusion, to an active, forced-convection system.
Achieving True Temperature Uniformity
A stationary pile of material inevitably develops a temperature gradient. The outer layers get hotter faster, while the core remains cooler, leading to an inconsistent final product.
Continuous rotation solves this by constantly bringing cooler material from the core to the surface to be heated, while cycling hotter material back into the bulk. This action eradicates hot and cold spots, ensuring a highly uniform radial temperature profile throughout the entire sample bed.
Maximizing Gas-Solid Interaction
In many thermal processes, such as calcination or reactions under specific atmospheres (inert, oxidizing, or reducing), interaction with the process gas is critical.
Rotation continuously exposes the entire surface area of the sample material to the surrounding gas. This dramatically improves gas diffusion into the material, ensuring reactions are complete and uniform while often reducing the total volume of expensive process gas required.
Preventing Material Inconsistencies
In a static furnace, finer particles can settle, and certain materials can sinter or agglomerate into clumps. This segregation leads to a non-uniform product.
The gentle tumbling action of a rotary furnace prevents settling and agglomeration. It maintains a well-mixed, homogeneous state, which is critical for processes like catalyst manufacturing where every particle must have identical properties.
The Impact on Process Outcomes
These underlying principles translate directly into measurable improvements in efficiency, quality, and operational flexibility.
Unprecedented Product Homogeneity
The primary outcome of uniform heating and gas exposure is a final product with exceptional consistency. Whether roasting, sintering, or drying, the properties of the material will be uniform from batch to batch and throughout each particle.
Enhanced Efficiency and Throughput
By actively moving material, a rotary furnace enhances heat transfer efficiency. The sample heats up faster and more evenly, leading to shorter processing times and increased throughput. This, combined with more efficient gas usage, results in significant energy and cost savings.
Wide Process Applicability
The ability to precisely control the environment (temperature, atmosphere, rotation speed, tilt angle) makes rotary tube furnaces highly versatile. They are adaptable to a wide range of materials and processes, from gentle drying to high-temperature sintering.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, the mechanical nature of a rotary furnace introduces factors that must be considered for any application.
Mechanical Complexity
Unlike a simple static tube furnace, a rotary system has moving parts, including seals, motors, and drive mechanisms. This introduces points of potential failure and requires a more rigorous maintenance schedule to ensure long-term reliability.
Material Attrition
The tumbling action, while gentle, can cause attrition or breakdown of very fragile or friable materials. For delicate powders or crystals, the rotation speed must be carefully optimized to balance the need for uniformity against the risk of damaging the sample.
Added Process Variables
Introducing rotation and tilt adds powerful control levers, but they are also variables that must be managed. Dialing in the optimal rotation speed and tube angle for a specific material and process requires careful experimentation and characterization.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right furnace depends entirely on your process requirements and desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is maximum product uniformity and consistency: A rotary tube furnace is the superior choice, as it is purpose-built to eliminate the variables that cause inhomogeneity.
- If your primary focus is high-throughput processing and efficiency: The faster heat transfer and reduced cycle times of a rotary furnace offer a clear advantage over static systems.
- If you are working with extremely delicate materials prone to breaking: You must carefully evaluate if the benefits of uniformity outweigh the risk of attrition, potentially opting for a very slow rotation speed or a different furnace type.
Ultimately, embracing continuous movement is a commitment to controlling every aspect of your thermal process for a more reliable and efficient result.
Summary Table:
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Homogeneity | Ensures uniform material properties by eliminating hot/cold spots and preventing agglomeration. |
| Enhanced Efficiency | Reduces processing times and energy costs through improved heat transfer and gas diffusion. |
| Process Versatility | Adaptable to various materials and applications with precise control over rotation and atmosphere. |
| Consistency | Delivers reliable, batch-to-batch uniformity for high-quality outcomes in thermal treatments. |
Ready to elevate your lab's thermal processing with a custom rotary tube furnace? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Rotary Furnaces, Muffle, Tube, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we can precisely meet your unique experimental requirements for superior uniformity and efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can benefit your specific applications!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- How do rotary tube furnaces achieve precise temperature control? Master Uniform Heating for Dynamic Processes
- What is the purpose of the rotation mechanism in a rotary tube furnace? Achieve Uniform Heating and Enhanced Process Control
- What supplementary features can enhance rotary tube furnace performance? Boost Efficiency with Precision Control
- What types of materials can be processed in a rotary tube furnace? Discover Ideal Materials for High-Temp Processing
- What are the common approaches to mixing in rotary furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Efficiency in Thermal Processing



















