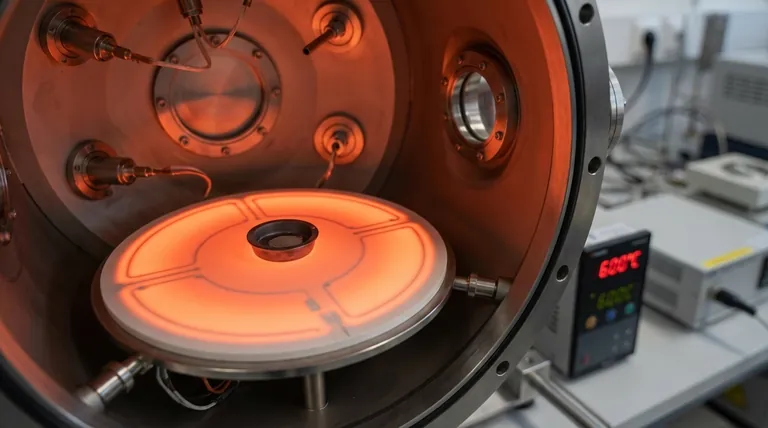
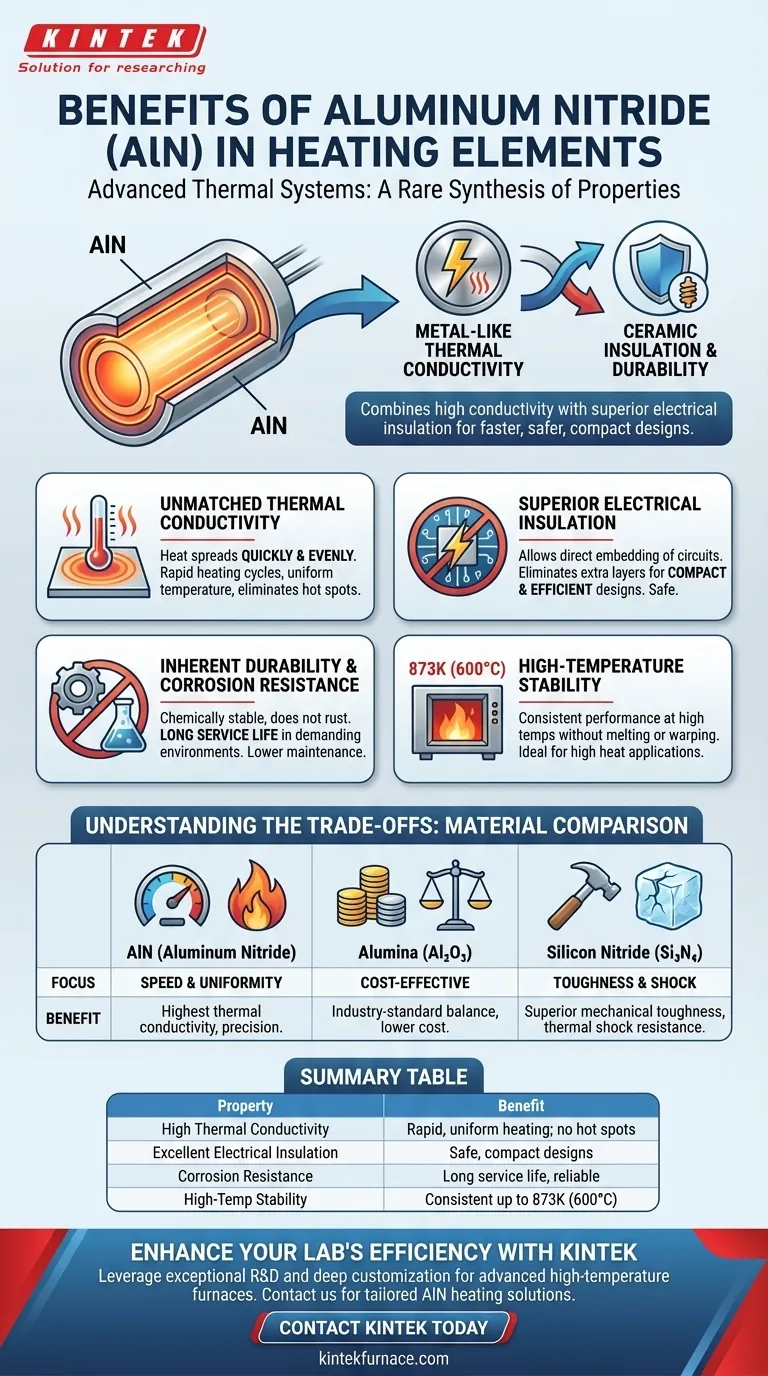
In advanced thermal systems, aluminum nitride (AlN) provides a unique combination of properties that distinguish it from other ceramic materials. Its primary benefits for heating elements are exceptionally high thermal conductivity, which allows for very rapid and uniform heating, combined with excellent electrical insulation and resistance to corrosion.
Aluminum Nitride's distinct advantage is not just one feature, but its rare synthesis of properties. It delivers the high thermal conductivity you expect from a metal, but with the superior electrical insulation and durability of an advanced ceramic, enabling faster, safer, and more compact heating element designs.
The Core Properties of AlN Heaters
To understand why AlN is chosen for high-performance applications, we must look at how its fundamental characteristics translate into tangible benefits.
Unmatched Thermal Conductivity
Aluminum Nitride's standout feature is its remarkably high thermal conductivity, far exceeding that of other ceramics like alumina.
This means heat generated within the element spreads out quickly and evenly. The practical results are rapid heating cycles and a uniform temperature across the entire heating surface, eliminating hot spots.
Superior Electrical Insulation
Like other ceramics, AlN is an excellent electrical insulator. This property is non-negotiable for safety and reliability in any electric heater.
By using AlN, the heating circuit can be directly embedded or bonded to the material itself, which serves as both the heat conductor and the insulator. This eliminates the need for extra insulation layers, allowing for more compact and efficient designs.
Inherent Durability and Corrosion Resistance
AlN is a chemically stable material that does not rust or corrode like metal heating elements.
This resistance to chemical attack and high temperatures ensures a long service life, even in demanding industrial environments. The result is lower maintenance costs and greater operational reliability.
High-Temperature Stability
Aluminum nitride heating elements can operate consistently at very high temperatures without melting, warping, or degrading.
References note its capability for rapid heating to 873K (600°C), showcasing its suitability for applications that require both high heat and thermal stability over time.
Understanding the Trade-offs: AlN vs. Other Materials
No material is perfect for every situation. Choosing AlN requires understanding its position relative to other common options.
AlN vs. Alumina (Al₂O₃)
Alumina is a widely used, cost-effective ceramic. The primary trade-off is performance.
Alumina has significantly lower thermal conductivity than AlN. This makes it slower to heat up and less uniform in temperature distribution. AlN is the superior choice when speed and precision are critical.
AlN vs. Silicon Nitride (Si₃N₄)
Silicon Nitride is another advanced ceramic, known for its exceptional mechanical toughness and resistance to thermal shock.
The choice here depends on the primary challenge. If the heater must withstand significant physical stress or rapid, repeated temperature shocks, Silicon Nitride may be preferable. If the highest priority is heat transfer efficiency, AlN is the clear winner.
The Cost-Performance Balance
As a high-performance material, AlN is typically more expensive to produce and process than more common ceramics like Alumina.
The decision to use AlN is therefore an investment in performance. It is justified in applications where its speed, uniformity, and compactness provide a significant competitive or operational advantage.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your material selection should be driven by the primary objective of your design.
- If your primary focus is maximum heating speed and uniformity: Choose Aluminum Nitride (AlN) for its unmatched thermal conductivity in a ceramic.
- If your primary focus is a cost-effective solution for general use: Choose Alumina (Al₂O₃) as the industry-standard balance of good performance and lower cost.
- If your primary focus is extreme durability in harsh mechanical environments: Choose Silicon Nitride (Si₃N₄) for its superior toughness and thermal shock resistance.
Ultimately, choosing the right ceramic heater is about precisely matching the material's unique strengths to your specific performance goals.
Summary Table:
| Property | Benefit |
|---|---|
| High Thermal Conductivity | Rapid, uniform heating; eliminates hot spots |
| Excellent Electrical Insulation | Safe, compact designs; no extra insulation needed |
| Corrosion Resistance | Long service life; reliable in harsh environments |
| High-Temperature Stability | Consistent performance at up to 873K (600°C) |
Ready to enhance your lab's heating efficiency with tailored solutions? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace options like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how our aluminum nitride heating elements can deliver faster, safer, and more compact performance for your specific applications!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of using high purity green silicon carbide powder in heating elements? Boost Efficiency and Lifespan
- What are the properties and capabilities of Silicon Carbide (SiC) as a heating element? Unlock Extreme Heat and Durability
- Why is silicon carbide resistant to chemical reactions in industrial furnaces? Unlock Durable High-Temp Solutions
- What are the properties and applications of silicon carbide (SiC)? Unlock High-Temperature Performance
- What is the maximum temperature silicon carbide heating elements can withstand? Key Factors for Longevity and Performance



















