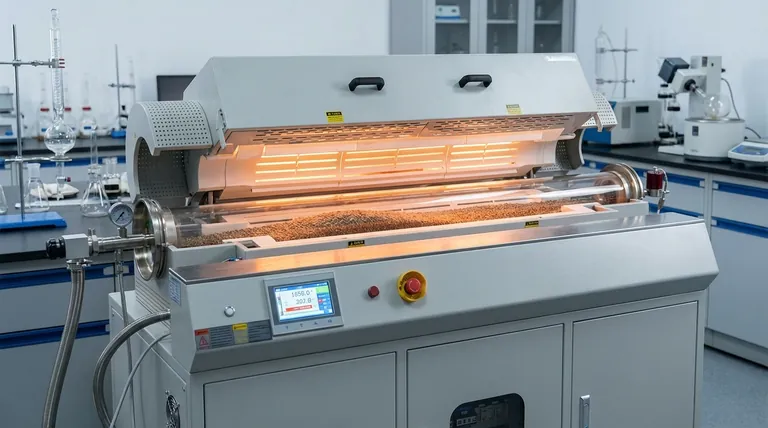
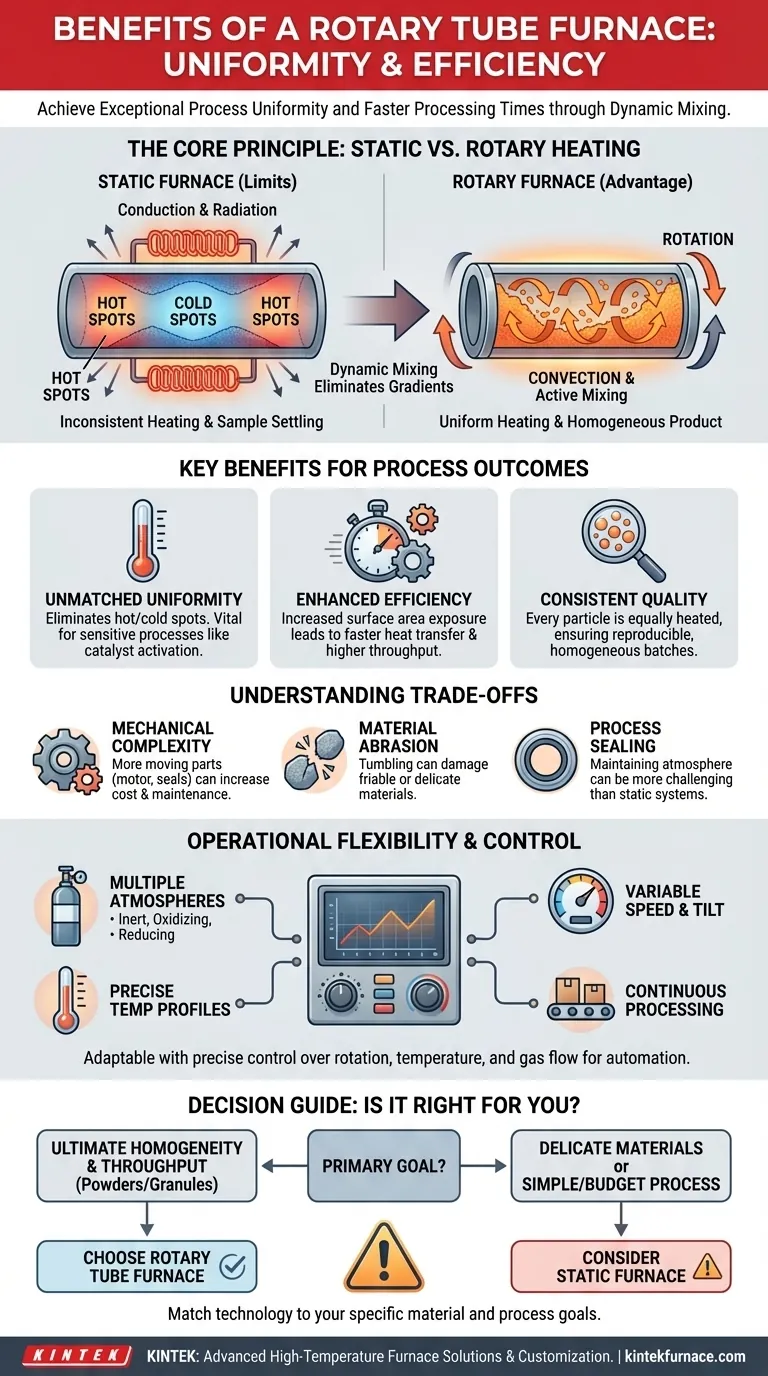
At its core, the primary benefit of a rotary tube furnace is its ability to achieve exceptional process uniformity and efficiency. By continuously tumbling materials within a heated tube, it solves the fundamental problems of inconsistent heating and sample settling found in static furnaces, resulting in a higher quality product and faster processing times.
While conventional static furnaces often produce inconsistent results due to hot spots and poor heat distribution, a rotary tube furnace’s dynamic mixing action guarantees that every particle is heated uniformly. This principle is the key to achieving superior product homogeneity, process efficiency, and repeatable outcomes.

The Core Principle: Dynamic vs. Static Heating
To understand the benefits of a rotary furnace, we must first compare it to its static counterpart. The fundamental difference lies in how heat is transferred to the material being processed.
The Limits of a Static Furnace
In a standard, non-rotating tube furnace, the sample material remains stationary. Heat is transferred primarily through conduction and radiation.
This static approach often leads to significant temperature gradients. The material touching the furnace walls gets much hotter than the material in the center, creating hot spots and cold spots.
Furthermore, different components of a powder mixture can settle or separate due to density differences, resulting in a non-uniform final product.
The Rotary Advantage: Active Mixing
A rotary tube furnace introduces a third, more effective mode of heat transfer: convection. As the tube rotates, the material inside is continuously lifted and tumbled.
This constant mixing eliminates temperature gradients, ensuring every particle is exposed to the heat source and the surrounding atmosphere equally. It also prevents the sample from settling or agglomerating.
The result is exceptionally uniform heating and a far more homogeneous end product.
Key Benefits for Process Outcomes
The dynamic heating principle translates directly into tangible advantages for scientific and industrial processes.
Unmatched Temperature Uniformity
The elimination of hot and cold spots is the most critical benefit. This is vital for sensitive processes like catalyst activation or sintering, where precise temperature control dictates the material's final properties.
Enhanced Heat Transfer Efficiency
The tumbling action dramatically increases the surface area of the material exposed to heat at any given moment. This enhanced heat transfer leads to faster processing times and higher throughput.
Consistent and Homogeneous Product Quality
Because every particle undergoes the same thermal experience, the final product is highly consistent from batch to batch. This prevents a mix of under-processed and over-processed material, which is a common issue in static systems.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No technology is without its considerations. An objective evaluation requires acknowledging the potential downsides.
Mechanical Complexity
The addition of a motor, seals, and a rotation mechanism makes a rotary furnace mechanically more complex than a static one. This can translate to higher initial costs and potentially more maintenance over its lifespan.
Material Abrasion
The continuous tumbling action is not suitable for all materials. Friable or delicate materials can be broken down or worn away by the abrasive motion inside the tube, a process known as attrition.
Process Sealing
Maintaining a perfectly controlled, sealed atmosphere can be more challenging in a rotary system due to the rotating seals at the ends of the tube, especially when compared to a completely sealed static furnace.
Operational Flexibility and Control
Modern rotary furnaces offer a high degree of control, making them adaptable to a wide range of applications.
Adaptable to Multiple Atmospheres
Like static tube furnaces, rotary systems can be designed to operate with specific gas environments. This allows for processes in inert (Nitrogen, Argon), oxidizing (Air), or reducing (Hydrogen) atmospheres.
Precise Control Over Process Variables
Operators can precisely adjust key parameters to optimize their process. These variables include rotation speed, tube tilt angle, temperature profile, and gas flow rate.
Suitability for Continuous Processing
The design of a rotary furnace is inherently well-suited for continuous or semi-continuous material processing. Integrated feeders and collection systems allow for automated, high-throughput production with minimal manual intervention.
Is a Rotary Tube Furnace Right for Your Process?
Choosing the correct furnace requires matching the technology's strengths to your primary goal.
- If your primary focus is ultimate product homogeneity: The rotary tube furnace is the superior choice, as its mixing action is purpose-built to eliminate inconsistency.
- If your primary focus is maximizing throughput for powders or granules: The faster heat transfer and continuous processing capability of a rotary furnace make it highly efficient.
- If you are processing delicate, friable, or oddly shaped materials: Carefully consider the risk of mechanical damage from tumbling; a static furnace may be a safer option.
- If your primary focus is a simple thermal treatment on a limited budget: A standard static tube furnace offers a more cost-effective solution with less mechanical complexity.
Ultimately, selecting the right furnace is about understanding how heat transfer impacts your specific material and process goals.
Summary Table:
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Uniform Heating | Eliminates hot/cold spots through continuous tumbling for consistent temperature distribution. |
| Enhanced Efficiency | Faster heat transfer reduces processing times and increases throughput. |
| Product Homogeneity | Ensures every particle is equally processed for repeatable, high-quality results. |
| Operational Flexibility | Adaptable to various atmospheres (inert, oxidizing, reducing) with precise control over parameters. |
Ready to enhance your lab's performance with a custom rotary tube furnace? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can deliver superior uniformity, efficiency, and reliability for your processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the basic construction of a rotary tube furnace? Key Components for Uniform Heating
- What are the common approaches to mixing in rotary furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Efficiency in Thermal Processing
- What are the main structural components of a rotary furnace? Explore Key Parts for Efficient Material Processing
- What supplementary features can enhance rotary tube furnace performance? Boost Efficiency with Precision Control
- What materials can be used to make the rotating tube assembly of these furnaces? Choose the Best for Your High-Temp Needs



















