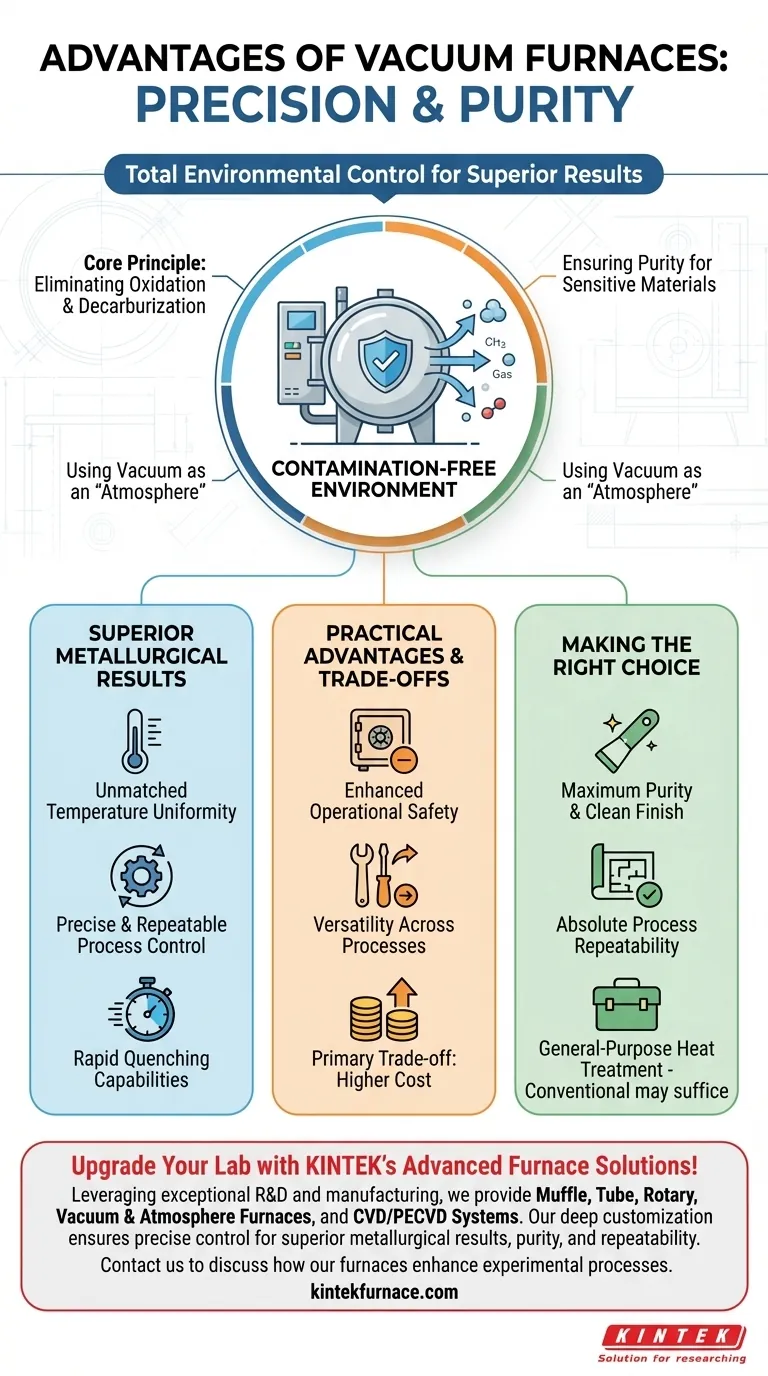
At their core, the advantages of a vacuum furnace stem from one fundamental capability: total environmental control. By removing air and other gases, these furnaces create a pristine, chemically inert environment that prevents unwanted reactions like oxidation, ensures part cleanliness, and allows for extremely precise and repeatable thermal processing. This control is what delivers superior metallurgical properties that are often unattainable with conventional furnaces.
A vacuum furnace isn't just a tool for heating metal; it's a precision instrument for manipulating material properties in a perfectly controlled environment. Its primary advantage is not heat, but the elimination of atmospheric interference, leading to higher purity, strength, and consistency.

The Core Principle: Creating a Contamination-Free Environment
The defining feature of a vacuum furnace is its ability to operate without the reactive gases found in normal air. This single factor is the source of its most significant benefits.
Eliminating Oxidation and Decarburization
By removing oxygen, a vacuum furnace prevents the formation of oxides on a material's surface during high-temperature processing. This results in bright, clean parts that often require no subsequent surface cleaning.
This same principle prevents decarburization, the loss of carbon from the surface of steel, which preserves the material's intended hardness and structural integrity.
Ensuring Purity for Sensitive Materials
High-performance materials like superalloys, titanium, and advanced ceramics are highly reactive with oxygen and nitrogen at elevated temperatures. A vacuum environment is essential to process these materials without introducing impurities that would degrade their mechanical properties.
Using the Vacuum as an "Atmosphere"
For many heat-treating processes, such as hardening and annealing, the vacuum itself is the ideal "atmosphere." It is perfectly non-reactive, eliminating the cost and complexity of sourcing, managing, and introducing specialized process gases.
Achieving Superior Metallurgical Results
The controlled environment enables a level of precision that directly translates into higher-quality and more consistent outcomes.
Unmatched Temperature Uniformity
Vacuum furnaces are engineered for exceptional temperature uniformity, often maintaining a consistent temperature across the entire workload. This ensures that every part, regardless of its position in the furnace, receives the exact same thermal treatment.
Precise and Repeatable Process Control
Modern vacuum furnaces are computer-controlled, allowing for the programming of highly specific and complex heating, soaking, and cooling cycles. This automation ensures that every batch is processed with metallurgical repeatability, a critical requirement for industries like aerospace and medical manufacturing.
Rapid Quenching Capabilities
After heating, the vacuum environment facilitates extremely rapid and controlled cooling, known as quenching. By backfilling the chamber with high-pressure inert gas, the furnace can cool parts at precise rates to achieve specific microstructures, hardness, and material strengths.
Understanding the Practical Advantages and Trade-offs
Beyond metallurgical quality, vacuum furnaces offer distinct operational benefits but also come with important considerations.
Enhanced Operational Safety
Unlike conventional furnaces that operate under positive pressure, vacuum furnaces operate at negative pressure. This inherently eliminates the risk of an explosion. Furthermore, the low-oxygen environment dramatically reduces the risk of fire.
Versatility Across Processes
A single vacuum furnace can often be used for a wide range of processes, including hardening, annealing, tempering, brazing, and sintering. This versatility can make it a valuable asset in a manufacturing environment.
The Primary Trade-off: Cost
The primary disadvantage of vacuum furnaces is their higher initial investment and operational cost compared to traditional atmosphere furnaces. Their sophisticated systems and robust construction contribute to a higher price point. The necessity of a vacuum furnace must be weighed against the specific requirements of the material and the end-product.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Deciding whether to use a vacuum furnace depends entirely on your material requirements and quality standards.
- If your primary focus is maximum purity and a clean finish: A vacuum furnace is non-negotiable for reactive materials or when parts must emerge from heat treatment bright and free of oxides.
- If your primary focus is absolute process repeatability: The precise computer control of a vacuum furnace offers unparalleled consistency for high-specification components where failure is not an option.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose heat treatment: For less sensitive materials where some surface oxidation is acceptable and post-processing is planned, a conventional atmosphere furnace may be a more cost-effective solution.
Ultimately, choosing a vacuum furnace is an investment in control, purity, and repeatability.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Contamination-Free Environment | Prevents oxidation and decarburization for clean, bright parts |
| Superior Metallurgical Results | Ensures precise temperature uniformity and repeatable processes |
| Enhanced Safety | Operates at negative pressure, reducing explosion and fire risks |
| Versatility | Supports multiple processes like hardening, brazing, and sintering |
| Rapid Quenching | Allows controlled cooling for specific material properties |
Upgrade your lab's capabilities with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems tailored to your unique needs. Our deep customization ensures precise control for superior metallurgical results, purity, and repeatability. Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can enhance your experimental processes and deliver unmatched performance for industries like aerospace and medical manufacturing!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the general operational features of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Superior Material Purity & Precision
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in TBC post-processing? Enhance Coating Adhesion
- What are the components of a vacuum furnace? Unlock the Secrets of High-Temperature Processing
- Why does heating steel rod bundles in a vacuum furnace eliminate heat transfer paths? Enhance Surface Integrity Today
- How does a vacuum heat treatment furnace influence Ti-6Al-4V microstructure? Optimize Ductility and Fatigue Resistance



















