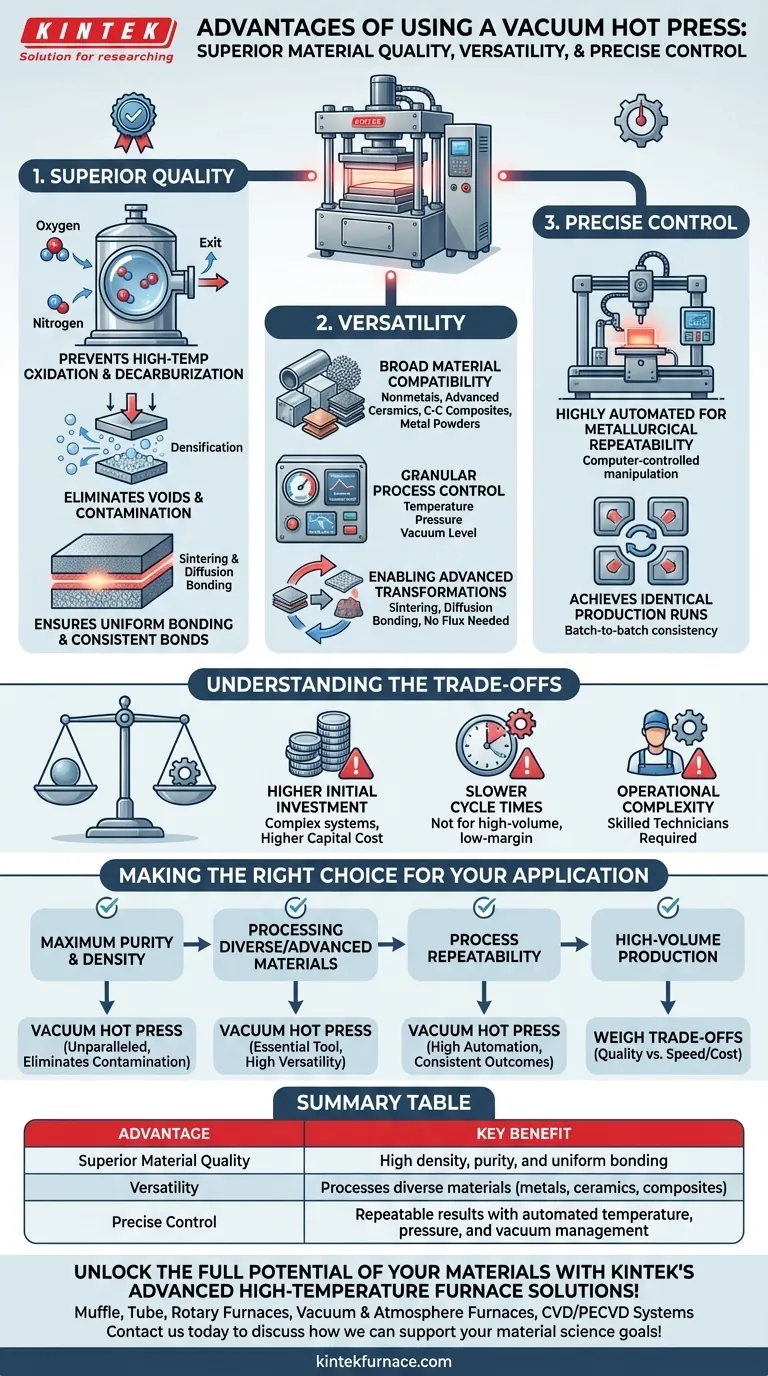
At its core, a vacuum hot press offers three primary advantages: it produces exceptionally high-quality materials, is versatile enough to process a wide range of substances, and provides precise, repeatable control over the manufacturing process. By applying heat and pressure simultaneously within a controlled vacuum, it eliminates the oxidation and contamination that degrade materials in conventional furnaces, resulting in superior density, purity, and bonding.
The fundamental challenge in advanced material fabrication is controlling the processing environment. A vacuum hot press overcomes this by creating a pristine, oxygen-free chamber, unlocking the ability to produce materials with unparalleled uniformity and structural integrity that would be impossible to achieve in open-atmosphere systems.

How a Vacuum Hot Press Delivers Superior Material Quality
The defining feature of this technology is its ability to create a near-perfect environment for material consolidation. This directly translates to higher-quality end products.
The Critical Role of the Vacuum
A vacuum chamber is essential for removing atmospheric gases like oxygen and nitrogen. This prevents high-temperature oxidation and decarburization, which preserves the material's intended chemical composition and results in cleaner surfaces.
Without this protection, many advanced metals and composites would burn or form weak, brittle oxide layers when heated.
Eliminating Voids and Contamination
The combination of pressure and vacuum works to physically squeeze out and evacuate trapped gases and other volatile impurities from within the material.
This process, known as densification, minimizes internal porosity. The result is a final product with significantly higher density, strength, and durability.
Ensuring Uniform Bonding
The system's optimized heating elements and press mechanism work in concert to deliver uniform temperature and pressure across the entire component.
This uniformity is critical for achieving consistent metallurgical bonds, whether sintering powders into a solid block or diffusion bonding two dissimilar materials together. It eliminates weak spots and ensures predictable performance.
The Foundation of Versatility and Precision
Beyond quality, the technology is defined by its adaptability and the granular control it offers engineers and researchers. This makes it a powerful tool for both development and specialized production.
Broad Material Compatibility
Vacuum hot presses are not limited to a single class of material. They are engineered to effectively process a diverse range of substances.
This includes nonmetals, advanced ceramics, carbon-carbon composites, and various metal powders. This flexibility makes them a cornerstone of modern materials science labs and specialized manufacturing facilities.
Granular Process Control
Modern systems are highly automated, allowing for precise, computer-controlled manipulation of the three key process variables: temperature, pressure, and vacuum level.
Thermocouples monitor and adjust heat with extreme accuracy, while advanced press systems apply consistent force. This ensures that every production run is identical, a concept known as metallurgical repeatability.
Enabling Advanced Transformations
The controlled environment facilitates material transformations that are difficult or impossible with other methods.
Processes like sintering and diffusion bonding rely on this precise control to create unique microstructures and bond materials without the need for melting or introducing filler adhesives, which could compromise performance.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, a vacuum hot press is a specialized tool with specific considerations. Objectivity requires acknowledging its limitations.
Higher Initial Investment
These are complex systems integrating vacuum, heating, and hydraulic press components. The initial capital cost is significantly higher than that of a standard atmospheric furnace.
Slower Cycle Times
The process of drawing a vacuum, heating, pressing, and cooling in a controlled manner is inherently slower than less-controlled methods. This can make it unsuitable for high-volume, low-margin manufacturing where speed is the primary driver.
Operational Complexity
Operating a vacuum hot press requires skilled technicians who understand the interplay between the vacuum, thermal, and mechanical systems. Maintenance is also more involved compared to simpler equipment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Ultimately, the decision to use a vacuum hot press depends entirely on your project's goals.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum material purity and density: The vacuum hot press is unparalleled because its controlled atmosphere eliminates the oxidation and contamination that degrade material integrity.
- If your primary focus is processing diverse or advanced materials: Its versatility in handling metals, ceramics, and composites makes it an essential tool for research and specialized fabrication.
- If your primary focus is process repeatability for critical components: The high degree of automation and precise control over temperature and pressure ensures consistent, reliable outcomes batch after batch.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production: Carefully weigh the superior quality against the slower cycle times and higher operational costs to determine if the trade-off is justified for your product.
By understanding these core advantages and trade-offs, you can confidently determine if a vacuum hot press is the optimal solution for your material science and manufacturing goals.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Superior Material Quality | High density, purity, and uniform bonding by eliminating oxidation and contamination |
| Versatility | Processes diverse materials like metals, ceramics, and composites |
| Precise Control | Repeatable results with automated temperature, pressure, and vacuum management |
Unlock the full potential of your materials with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with tailored vacuum hot press systems, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, delivering superior performance, reliability, and efficiency. Ready to enhance your processes? Contact us today to discuss how we can support your material science goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What materials can be densified using a vacuum press and what are their applications? Unlock High-Performance Material Densification
- What are the primary components of a vacuum hot press furnace? Master the Core Systems for Precise Material Processing
- How does Vacuum Hot Press equipment contribute to the energy and power generation sector? Boost Efficiency and Durability
- What are the overall benefits of using hot pressing in manufacturing? Achieve Superior Performance and Precision
- How does precise temperature control affect Ti-6Al-4V microstructure? Master Titanium Hot Pressing Accuracy



















