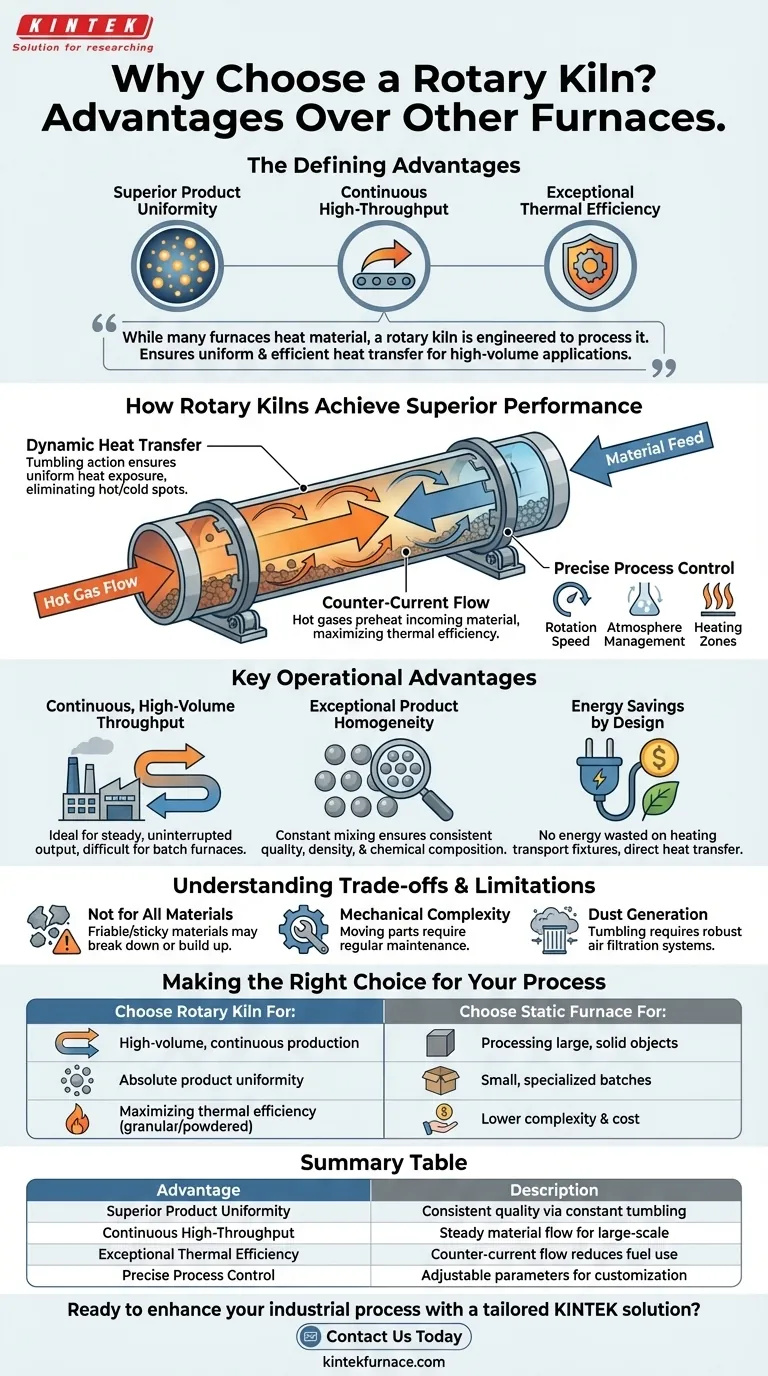
The defining advantages of a rotary kiln are its ability to achieve superior product uniformity, operate continuously for high-throughput production, and maintain exceptional thermal efficiency. By constantly tumbling the material, a rotary kiln ensures every particle is evenly exposed to heat, eliminating the inconsistencies and energy losses common in static furnace designs.
While many furnaces heat material, a rotary kiln is engineered to process it. Its core advantage isn't just reaching a target temperature, but ensuring every part of the material reaches that temperature uniformly and efficiently, making it the superior choice for high-volume, quality-critical applications.
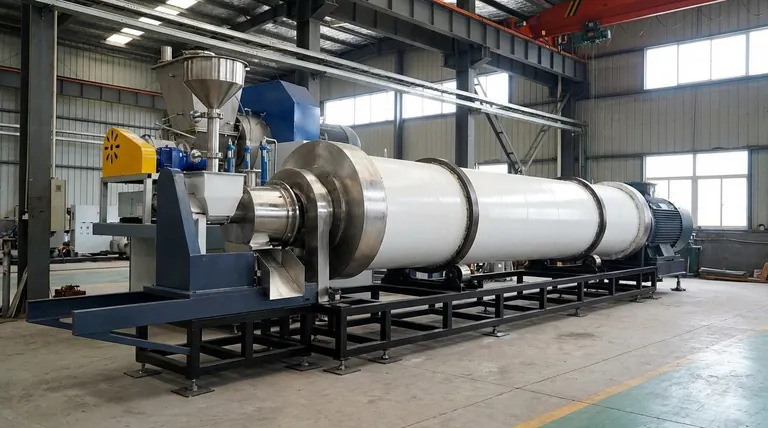

How Rotary Kilns Achieve Superior Performance
A rotary kiln's advantages stem directly from its unique mechanical design: a rotating, inclined cylinder. This dynamic approach to heating fundamentally changes how energy is transferred to the material being processed.
The Principle of Dynamic Heat Transfer
The kiln's rotation is the key to its effectiveness. Unlike a static furnace where material sits motionless, a rotary kiln constantly lifts and tumbles the processing charge.
This action ensures uniform heat exposure, eliminating the hot and cold spots that can plague batch furnaces. Every particle is continuously brought to the surface, where it can directly absorb radiant heat from the kiln walls and hot gases.
Counter-Current Flow and Thermal Efficiency
Most rotary kilns operate on a counter-current flow principle. Material is fed into the high end of the inclined cylinder and travels downward, while hot gas from a burner at the low end flows upward.
This design is incredibly efficient. The hot gases preheat the incoming material as they travel toward the exhaust, transferring energy that would otherwise be wasted. This significantly reduces the fuel required to bring the material to its final processing temperature.
Precise Control Over the Process
Modern rotary kilns offer a high degree of control over the treatment environment. Key parameters can be precisely managed to suit a specific process.
This includes adjusting the rotation speed to control how long the material stays in the kiln (residence time), managing the atmosphere inside the kiln (e.g., oxidizing or inert), and implementing multiple heating zones to create a specific temperature profile along the length of the kiln.
Key Operational Advantages
The physical principles translate into clear operational benefits, particularly for industrial-scale applications.
Continuous, High-Volume Throughput
A rotary kiln is designed for continuous material flow. Raw material can be constantly fed into one end while the finished product is discharged from the other.
This makes it ideal for large-scale industrial processes that require a steady, uninterrupted output, a capability that batch-style furnaces cannot match without significant complexity and material handling.
Exceptional Product Homogeneity
The constant mixing action ensures the final product is extremely homogeneous. All particles undergo the same thermal treatment, resulting in consistent quality, density, and chemical composition.
This is especially critical when processing powders, granules, or slurries, where achieving a uniform result in a static furnace is nearly impossible.
Energy Savings by Design
Beyond the efficiency of counter-current flow, the rotary kiln design reduces energy loss in other ways. For example, unlike a shuttle or car-bottom furnace, there is no need to waste energy heating up heavy carts or other transport fixtures along with the product. The heat is focused directly on the material itself.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
No technology is perfect for every scenario. The strengths of a rotary kiln also define its limitations.
Not Ideal for All Materials
The tumbling action can be detrimental to certain materials. Friable or delicate products may break down, while sticky or low-melting-point materials can agglomerate and build up on the kiln walls, disrupting flow.
Mechanical Complexity and Maintenance
The rotation system—including the drive motor, gears, support wheels, and seals—introduces mechanical complexity. These moving parts require regular maintenance and are potential points of failure not present in simpler static furnaces.
Dust Generation and Control
The same tumbling that ensures uniformity can also generate significant dust. This necessitates robust air filtration and dust collection systems to control emissions and, in some cases, to prevent loss of valuable product.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Selecting the correct furnace technology depends entirely on your primary goal. A rotary kiln is a specialized tool that excels in specific applications.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, continuous production: A rotary kiln is the definitive choice for its ability to handle a constant flow of material.
- If your primary focus is absolute product uniformity: The unique mixing action of a rotary kiln ensures a level of homogeneity that static furnaces cannot achieve.
- If your primary focus is maximizing thermal efficiency: The counter-current heat exchange inherent in the rotary kiln design makes it one of the most energy-efficient options available.
- If your primary focus is processing large, solid objects or small, specialized batches: A simpler, less expensive static box or shuttle furnace is likely a more practical solution.
Ultimately, choosing a rotary kiln is a decision to prioritize processing consistency, thermal efficiency, and high throughput for granular or powdered materials.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Superior Product Uniformity | Constant tumbling ensures even heat exposure for consistent quality. |
| Continuous High-Throughput | Allows steady material flow, ideal for large-scale production. |
| Exceptional Thermal Efficiency | Counter-current flow design reduces energy waste and fuel use. |
| Precise Process Control | Adjustable rotation speed, atmosphere, and heating zones for customization. |
Ready to enhance your industrial process with a tailored rotary kiln solution?
At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Rotary Furnaces, Muffle, Tube, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental and production requirements.
Whether you're focused on high-volume output, product homogeneity, or energy savings, our experts can help you achieve superior results. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your process with our reliable and efficient furnace technologies!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
People Also Ask
- What technical requirements are placed on heating equipment for fast pyrolysis? Master High-Yield Bio-Oil Production
- What is the role of indirect-fired rotary kilns in energy production? Unlock Sustainable Waste-to-Energy Solutions
- What is the significance of rotation in a pyrolysis rotary kiln reactor? Unlock Efficient Waste-to-Energy Conversion
- How do pyrolysis rotary kiln reactors function? Unlock Efficient Waste-to-Value Conversion
- Why must precise temperature measurement and upper-limit control be implemented during the rotary furnace melting of ductile iron?



















