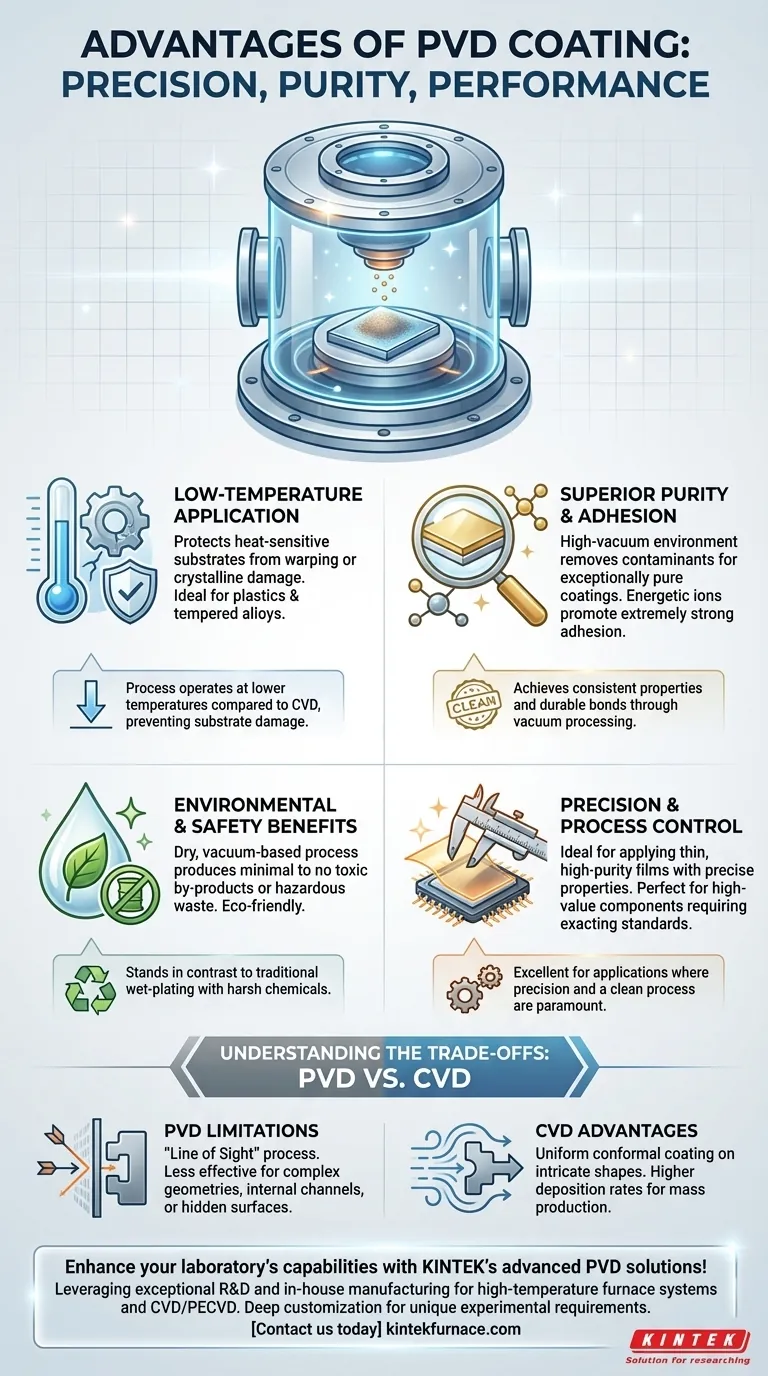
The primary advantages of Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) are its ability to apply high-performance coatings at low temperatures, its environmental friendliness, and the exceptional purity and adhesion of the final layer. This makes PVD a superior choice for coating heat-sensitive materials or applications where precision and a clean process are paramount.
While often evaluated for its durability, the true value of PVD lies in its precision and process control. It excels at applying thin, high-purity films onto components that cannot withstand the high temperatures of alternative methods like Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD).

The Core Advantages of PVD Explained
Understanding why PVD is chosen requires looking beyond the surface-level benefits. The advantages stem directly from the physics of its vacuum-based process.
Low-Temperature Application for Sensitive Materials
PVD is fundamentally a low-temperature process compared to CVD. This is its most significant advantage for a wide range of modern materials.
By operating at lower temperatures, PVD prevents the substrate material from warping, changing its crystalline structure, or losing its temper. This allows for the coating of plastics, tempered alloys, and other heat-sensitive components without damaging them.
However, it's important to note that careful process control is still necessary, as certain high-energy PVD processes can generate localized heat that may affect extremely sensitive substrates.
Superior Purity and Adhesion
The PVD process takes place in a high-vacuum chamber, which is critical for achieving high-purity coatings.
This vacuum environment removes atmospheric and other contaminants, ensuring that the deposited material is exceptionally pure. The result is a coating with predictable and consistent properties.
Furthermore, the energetic ions in many PVD processes (like sputtering) bombard the substrate, creating a microscopically clean and activated surface that promotes extremely strong adhesion between the coating and the part.
Environmental and Safety Benefits
PVD is widely regarded as an environmentally friendly coating technology.
The process is dry and occurs in a vacuum, producing minimal to no toxic by-products or hazardous waste. This stands in stark contrast to traditional wet-plating processes that rely on harsh chemicals and produce significant chemical waste.
Understanding the Trade-offs: PVD vs. Alternatives
No technology is perfect for every scenario. The advantages of PVD are best understood by acknowledging its limitations, particularly when compared to Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD).
The "Line of Sight" Limitation
PVD is a "line-of-sight" process, meaning the coating material travels in a straight line from the source to the substrate.
This restricts its effectiveness on parts with complex geometries, internal channels, or hidden surfaces. If a surface cannot be "seen" by the coating source, it will not be coated uniformly, if at all.
CVD, by contrast, uses a chemical gas that can flow around and into intricate shapes, providing a highly uniform and conformal coating even on the most complex parts.
Deposition Rate and Production Scale
In general, PVD has a slower deposition rate than CVD. This makes it less efficient for coating very thick layers or for extremely high-volume mass production.
PVD is therefore often better suited for high-value components where precision, purity, and low-temperature application are more critical than raw throughput. CVD's higher deposition rates make it more economical for many large-scale industrial applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct coating technology requires matching the process capabilities to your project's specific requirements.
- If your primary focus is performance on heat-sensitive components: PVD is the superior choice due to its low-temperature application, which protects the substrate's integrity.
- If your primary focus is coating complex, internal geometries: You should strongly consider CVD for its ability to provide a uniform coating on non-line-of-sight surfaces.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, cost-effective production: The typically faster deposition rates of CVD often make it the more efficient option for mass manufacturing.
- If your primary focus is environmental impact and coating purity: PVD's clean, vacuum-based process offers a distinct advantage over chemical-heavy alternatives.
Ultimately, choosing the right coating is an engineering decision based on a clear understanding of these fundamental trade-offs.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Low-Temperature Application | Protects heat-sensitive substrates from damage |
| Superior Purity and Adhesion | Ensures high-quality, durable coatings in vacuum environments |
| Environmental and Safety Benefits | Minimizes toxic by-products and hazardous waste |
| Precision and Process Control | Ideal for thin, high-purity films on sensitive components |
Enhance your laboratory's capabilities with KINTEK's advanced PVD solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnace systems like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements for PVD coatings, delivering superior performance, purity, and efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your projects and drive innovation in your lab!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano Diamond Coating
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
People Also Ask
- What is PECVD equipment? A Guide to Low-Temperature Thin-Film Deposition
- What role does PECVD play in optical coatings? Essential for Low-Temp, High-Precision Film Deposition
- What is PECVD and how does it differ from traditional CVD? Unlock Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What gases are used in the PECVD system? Optimize Thin Film Deposition with Precise Gas Selection
- How does plasma vapor deposition work? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings



















