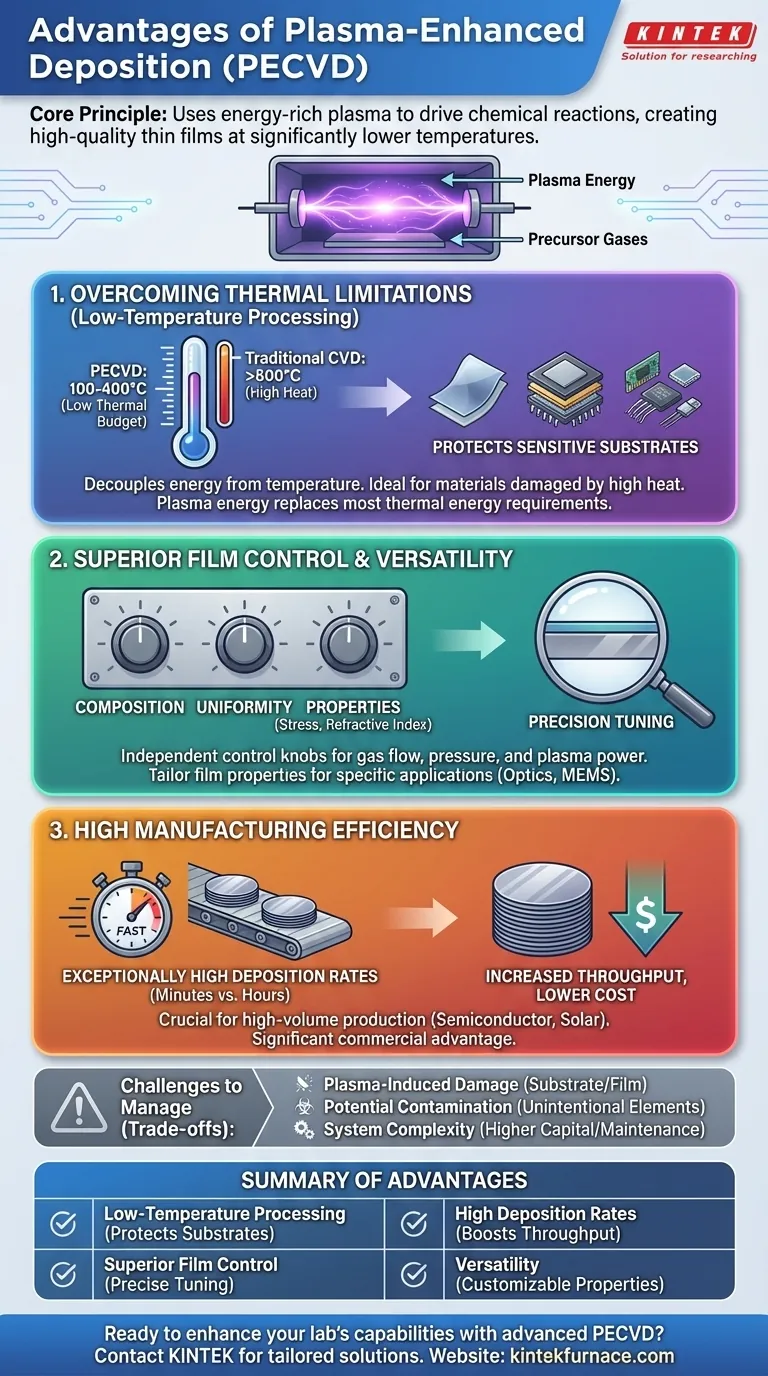
At its core, plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition (PECVD) allows for the creation of high-quality thin films at significantly lower temperatures than traditional methods. It achieves this by using an energy-rich plasma to drive the chemical reactions, providing superior control over the film's properties and achieving much faster deposition rates.
The fundamental advantage of PECVD is its ability to decouple the energy required for deposition from the substrate's temperature. This single principle makes it possible to deposit advanced materials onto sensitive substrates that would be damaged or destroyed by conventional high-temperature processes.

The Core Advantage: Overcoming Thermal Limitations
The defining feature of PECVD is its ability to operate at low temperatures, typically in the range of 100-400°C. This unlocks capabilities that are impossible with traditional Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), which often requires temperatures exceeding 600°C.
The Power of Low-Temperature Processing
This low thermal budget is critical when working with substrates that cannot withstand high heat. This includes integrated circuits with previously fabricated metal layers, flexible polymer substrates, or other temperature-sensitive electronic components.
Energy from Plasma, Not Just Heat
In traditional CVD, high temperatures are required to provide the thermal energy needed to break down precursor gases and initiate film growth.
PECVD replaces most of this thermal energy requirement with energy from a plasma. By applying a strong electromagnetic field (typically radio frequency), precursor gases are ionized into a highly reactive state, allowing deposition to occur efficiently without extreme heat.
Unlocking Superior Film Control
The use of plasma provides several independent control "knobs" that are not available in purely thermal processes. This allows for precise tuning of the final film to meet specific performance requirements.
Precision Control Over Composition and Uniformity
By carefully managing gas flow rates, pressure, and plasma power, engineers can achieve tight control over the film's stoichiometry and chemical composition. The plasma also helps ensure the reactive species are distributed evenly, leading to excellent film uniformity across large wafers.
Adjustable Film Properties
This control extends directly to the film's physical properties. Parameters like intrinsic stress, refractive index, and hardness can be deliberately adjusted by fine-tuning the deposition conditions. This is crucial for applications in optics and microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) where these properties are paramount.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, PECVD is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Risk of Plasma-Induced Damage
The same energetic ions that enable low-temperature deposition can, if not properly controlled, cause damage to the substrate surface or the growing film. This can be a concern for fabricating highly sensitive electronic devices.
Potential for Contamination
Because the plasma is so effective at dissociating gases, elements from the precursor molecules (like hydrogen or carbon) can be unintentionally incorporated into the film. This can impact electrical or optical properties and must be carefully managed.
System Complexity
PECVD systems are inherently more complex than simple thermal CVD reactors. They require sophisticated vacuum systems, high-frequency power supplies, and matching networks, which can lead to higher capital and maintenance costs.
The Impact on Manufacturing Efficiency
For many industrial applications, speed is directly tied to cost. This is an area where PECVD provides a significant commercial advantage.
Exceptionally High Deposition Rates
Compared to many other deposition techniques, PECVD is remarkably fast. It can deposit films in a matter of minutes that might take hours with traditional thermal CVD or physical vapor deposition (PVD) methods.
Increased Throughput and Lower Cost
This high deposition rate translates directly to increased manufacturing throughput. For high-volume production, such as in the semiconductor and solar industries, this efficiency dramatically reduces the cost per wafer, making it a highly cost-effective solution.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a deposition method depends entirely on the constraints and objectives of your project.
- If your primary focus is compatibility with temperature-sensitive substrates: PECVD is often the only viable choice, as it protects delicate components from thermal damage.
- If your primary focus is tuning specific film properties: PECVD offers unparalleled control over stress, refractive index, and density by allowing you to adjust plasma energy independently of temperature.
- If your primary focus is high-volume manufacturing: The high deposition rates of PECVD make it a more cost-effective and efficient solution for mass production compared to many slower methods.
By understanding its unique ability to substitute plasma energy for thermal energy, you can leverage PECVD to create advanced materials and solve deposition challenges that are otherwise out of reach.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Low-Temperature Processing | Operates at 100-400°C, protecting sensitive substrates like polymers and ICs. |
| Superior Film Control | Allows precise tuning of stress, refractive index, and uniformity via plasma parameters. |
| High Deposition Rates | Faster than traditional methods, boosting throughput and reducing costs in manufacturing. |
| Versatility | Suitable for optics, MEMS, and semiconductor applications with customizable film properties. |
Ready to enhance your lab's capabilities with advanced plasma-enhanced deposition? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide high-temperature furnace solutions like CVD/PECVD Systems, tailored to your unique needs. Our deep customization ensures precise performance for temperature-sensitive substrates and high-volume production. Contact us today to discuss how our PECVD technologies can drive your innovations forward!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does chemical vapour deposition (CVD) differ from PVD? Key Differences in Thin-Film Coating Methods
- How does a CVD system ensure the quality of carbon layers? Achieving Nanometer Precision with KINTEK
- What is resistance heating and how is it classified? Discover the Best Method for Your Thermal Needs
- What are gas barrier films, and how is PECVD involved in their creation? Discover Advanced Packaging Solutions
- What are the future trends in CVD technology? AI, Sustainability, and Advanced Materials



















