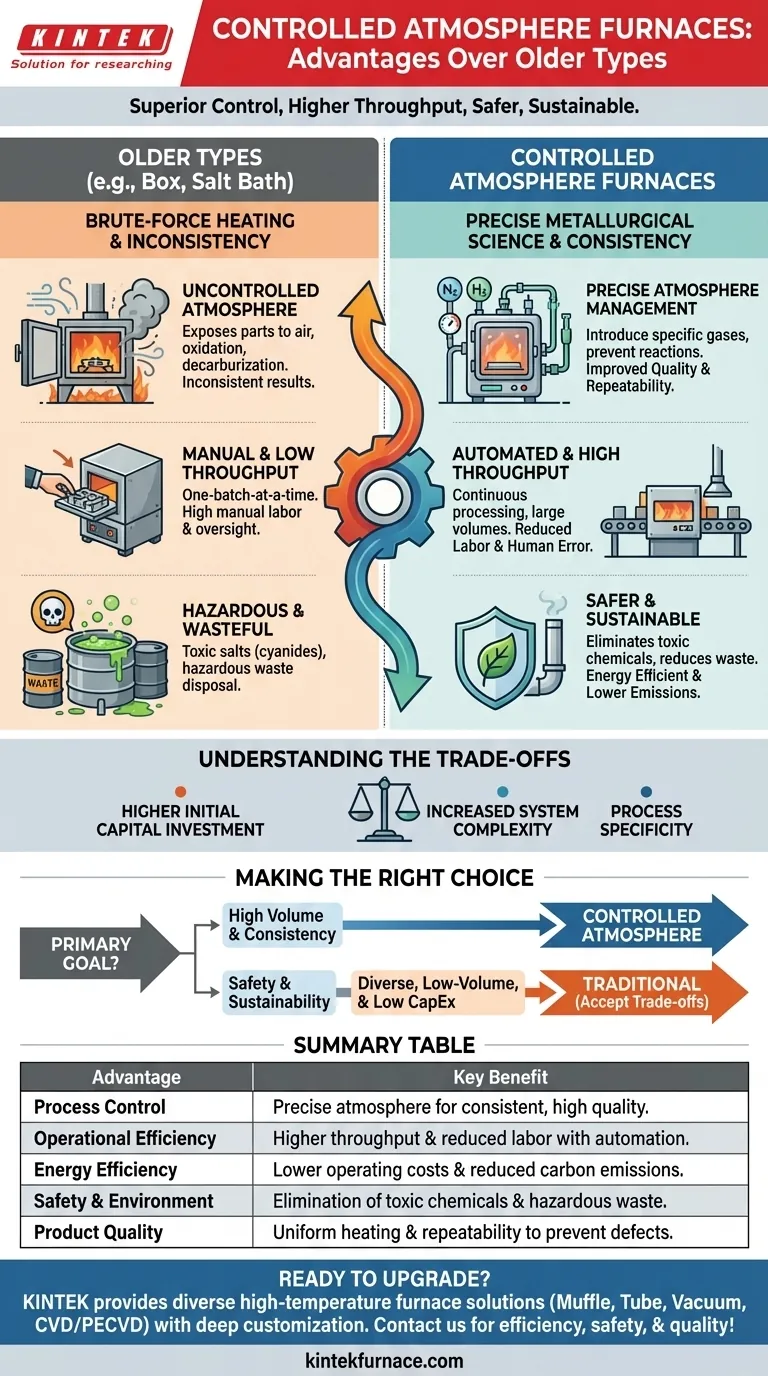
In short, the advantages are significant. Controlled atmosphere furnaces offer superior process control, higher throughput, and reduced labor requirements compared to older methods like box or salt bath furnaces. By precisely managing the internal gaseous environment, they deliver more consistent results, improve energy efficiency, and create a safer, more sustainable manufacturing process.
The fundamental shift is from brute-force heating to precise, repeatable metallurgical science. Moving to a controlled atmosphere furnace isn't just an equipment upgrade; it's an investment in process consistency, operational safety, and environmental responsibility.

Achieving Superior Process Control and Quality
Older furnaces often expose parts to uncontrolled air or combustion byproducts, leading to inconsistent results. Controlled atmosphere furnaces solve this by creating a purpose-built environment around the workpiece.
Precise Atmosphere Management
A controlled atmosphere furnace allows you to introduce specific gases to achieve a desired metallurgical outcome. This prevents unwanted chemical reactions like oxidation (scaling) and decarburization that can ruin a part's surface properties.
Improved Product Quality
By eliminating the variables of an uncontrolled atmosphere, you achieve far greater repeatability. This leads to improved product quality, as every part in every batch receives the exact same, optimized thermal treatment.
Uniform Heating
Modern furnace designs, whether batch or continuous, are engineered for uniform heating. This ensures that large or complex parts are heated evenly, preventing distortion and ensuring consistent properties throughout the material.
Boosting Operational and Financial Efficiency
Beyond quality, the move to a controlled atmosphere furnace has a direct impact on your bottom line and your facility's productivity.
Increased Throughput
Many modern furnaces are designed for continuous or semi-continuous processing. This ability to handle large volumes of material in an automated flow is a dramatic improvement over the one-batch-at-a-time nature of older box furnaces.
Reduced Labor Requirements
Processes that once demanded constant manual oversight, loading, and unloading can now be largely automated. This frees up skilled labor for more valuable tasks and reduces the chance of human error, making operations less labor-demanding.
Higher Energy Efficiency
These systems are built with superior insulation, advanced heating elements, and optimized cycle times. This focus on energy efficiency not only lowers operating costs but also reduces the facility's carbon emissions.
Enhancing Safety and Environmental Responsibility
Perhaps the most critical advantage is the move away from the hazardous practices associated with legacy heat treatment methods.
Eliminating Toxic Chemicals
Controlled atmosphere furnaces eliminate the need for toxic salts, such as the cyanides used in older salt bath furnaces. This immediately removes a significant health and safety hazard from your shop floor.
Reducing Hazardous Waste
The switch means you no longer have to deal with the disposal of waste salts, contaminated jigs, or other hazardous waste byproducts. This reduces both environmental liability and disposal costs.
Creating a Sustainable Process
By using less energy, eliminating toxic inputs, and reducing waste, controlled atmosphere furnaces make heat treatment a far more sustainable part of the manufacturing lifecycle.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While the benefits are clear, a balanced assessment requires acknowledging the considerations of adopting this technology.
Higher Initial Capital Investment
An advanced controlled atmosphere system represents a significantly higher upfront cost compared to a simple box or salt bath furnace. This investment must be weighed against the long-term gains in efficiency, quality, and safety.
Increased System Complexity
These furnaces are more sophisticated machines. They rely on precise gas flow controls, safety interlocks, and advanced monitoring, which may require more specialized knowledge for operation and maintenance.
Process Specificity
While highly customizable, a furnace optimized for a specific process (like carburizing) may not be as flexible as a general-purpose box furnace for one-off jobs. The equipment is often tailored to a specific production need.
Making the Right Choice for Your Operation
Your decision should be guided by your primary operational goals and long-term strategy.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production and consistency: A controlled atmosphere furnace is the clear choice for its superior throughput and process repeatability.
- If your primary focus is safety and environmental compliance: The elimination of toxic materials and the reduction in emissions make modern furnaces essential for sustainable manufacturing.
- If your primary focus is processing diverse, low-volume jobs with minimal capital outlay: A traditional box furnace may still have a place, but you must accept the trade-offs in quality control and manual labor.
Adopting a controlled atmosphere furnace empowers your operation to move from approximation to precision in thermal processing.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Process Control | Precise atmosphere management for consistent, high-quality results |
| Operational Efficiency | Higher throughput and reduced labor with automation |
| Energy Efficiency | Lower operating costs and reduced carbon emissions |
| Safety & Environment | Elimination of toxic chemicals and hazardous waste |
| Product Quality | Uniform heating and repeatability to prevent defects |
Ready to upgrade your thermal processing with advanced controlled atmosphere furnaces? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements for improved efficiency, safety, and quality. Contact us today to discuss how we can tailor a solution for your needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the benefits of inert atmosphere heat treating? Prevent Oxidation and Preserve Material Integrity
- What is the main purpose of heat treatment? Transform Metal Properties for Superior Performance
- Why is moisture control critical in inert atmosphere heat treating? Prevent Oxidation and Ensure Material Integrity
- How does the inert atmosphere heat treating process work? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Material Quality
- What is the use of nitrogen in furnace? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Heat Treatment



















