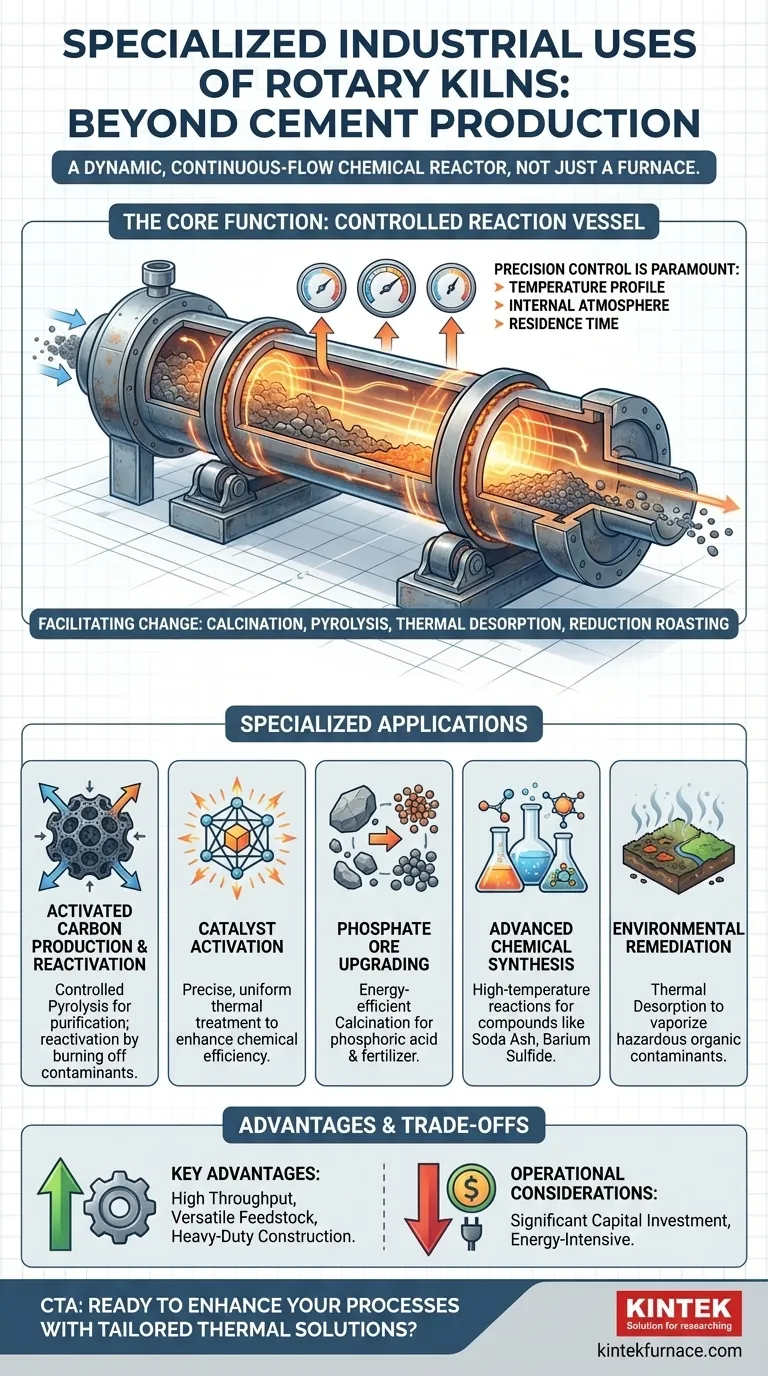
Beyond cement production, rotary kilns are highly specialized thermal processing tools used for a wide range of advanced industrial applications. These include producing and reactivating activated carbon for purification, activating catalysts for the chemical industry, upgrading phosphate ores into fertilizer, and synthesizing various chemical compounds. Their core function is to provide a precisely controlled high-temperature environment to induce specific chemical reactions or physical phase changes in a material.
A rotary kiln is not just a furnace; it is a dynamic, continuous-flow chemical reactor. Its true value lies in its ability to precisely control temperature, atmosphere, and material residence time, making it adaptable for complex processes far beyond simple heating or drying.
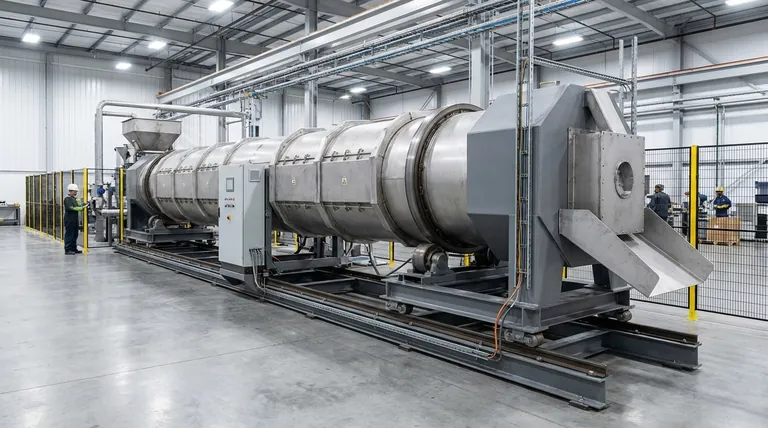

The Core Function: A Controlled Reaction Vessel
The versatility of a rotary kiln stems from its role as a controlled environment where materials are transformed, not just heated. This is what enables its use in highly specialized fields.
Facilitating Chemical and Physical Change
A kiln facilitates several core thermal processes. The specific process chosen depends entirely on the desired outcome for the material being treated.
Key processes include calcination (heating to drive off volatile components like water or CO₂), pyrolysis (thermal decomposition in the absence of oxygen), thermal desorption (using heat to vaporize contaminants from a solid), and reduction roasting (using a reducing gas to change a metal's oxidation state).
Precision Control is Paramount
The ability to manipulate three key variables is what makes a kiln so adaptable for specialized tasks. These are temperature profile, internal atmosphere (oxidizing, inert, or reducing), and residence time (how long the material spends in the kiln). This precision ensures the desired reaction occurs without damaging the product.
Specialized Applications in Detail
While commonly associated with cement and lime, the most innovative uses of rotary kilns are found in niche chemical and environmental sectors.
Activated Carbon Production & Reactivation
Rotary kilns are used to create the porous structure of activated carbon through controlled pyrolysis. They are also essential for reactivation, where they use high heat to burn off contaminants that have been absorbed by used carbon, restoring its adsorptive properties for reuse in water and air purification.
Catalyst Activation
Many industrial chemical processes rely on catalysts. A rotary kiln provides the precise, uniform thermal treatment needed to activate these catalysts, bringing them to their most effective chemical state without overheating or destroying their delicate structure.
Upgrading Phosphate Ores
A specialized process developed in the 1960s uses rotary kilns to produce phosphoric acid and calcined phosphate fertilizer. This method is valued because it uses less energy and electricity, does not require sulfuric acid, and can effectively process low-grade phosphate rock that is unsuitable for other methods.
Advanced Chemical Synthesis
In the chemical industry, kilns function as high-temperature reactors to produce compounds like soda ash, barium sulfide, and other inorganic chemicals. The kiln provides the sustained energy and controlled environment needed to drive these endothermic reactions to completion.
Environmental Remediation
Rotary kilns are used for thermal desorption to clean contaminated soils. By heating the soil, hazardous organic contaminants are vaporized and collected for safe disposal, leaving the clean soil behind.
Understanding the Advantages and Trade-offs
The decision to use a rotary kiln is based on its unique strengths, but it also involves practical considerations.
Key Advantages
The primary advantages of a rotary kiln are its high throughput from continuous operation and its ability to handle a wide variety of feedstock, from fine powders to granular solids. Their heavy-duty construction ensures a long service life even under demanding high-temperature conditions.
Operational Considerations
The main trade-off is resource intensity. Rotary kilns represent a significant capital investment and are energy-intensive to operate due to the high temperatures required. While highly customizable, this also means that an off-the-shelf solution is rare; each kiln often requires specific engineering for the intended process.
Matching the Kiln to the Industrial Goal
Choosing to use a rotary kiln depends on your primary objective. Its adaptability allows it to solve different problems with equal effectiveness.
- If your primary focus is material purification (e.g., activated carbon, soil remediation): The key is the kiln's ability to use controlled heat and atmosphere to drive off volatile compounds via pyrolysis or thermal desorption.
- If your primary focus is chemical synthesis (e.g., catalysts, fertilizers): The key is the kiln's function as a high-temperature reactor that enables specific chemical transformations like calcination or reduction.
- If your primary focus is high-volume resource processing (e.g., mineral upgrading): The key is the kiln's robust, continuous-flow design built for processing large quantities of raw material efficiently.
Ultimately, the rotary kiln is a foundational tool of modern industry, enabling the creation and refinement of materials essential for manufacturing, agriculture, and environmental protection.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Process | Primary Use |
|---|---|---|
| Activated Carbon Production & Reactivation | Pyrolysis | Purification in water and air systems |
| Catalyst Activation | Controlled thermal treatment | Enhancing chemical reactions in industry |
| Phosphate Ore Upgrading | Calcination | Fertilizer production with energy efficiency |
| Advanced Chemical Synthesis | High-temperature reactions | Producing compounds like soda ash and barium sulfide |
| Environmental Remediation | Thermal desorption | Cleaning contaminated soils by vaporizing contaminants |
Ready to enhance your industrial processes with tailored thermal solutions? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including rotary kilns. Our product line—featuring Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems—is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental and production needs. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your operations with reliable, efficient technology!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does automated control in electric rotary kilns benefit industrial processes? Achieve Unmatched Precision & Efficiency
- What advantages do electrically heated rotary kilns offer in temperature control? Achieve Precision and Uniformity for Superior Results
- What is the basic working principle of a rotary kiln? Master Industrial Thermal Processing Efficiency
- How is bed depth controlled in a rotary kiln and why is it important? Optimize Heat Transfer and Efficiency
- What is an electric heating rotary kiln and what industries use it? Discover Precision Heating for High-Purity Materials



















