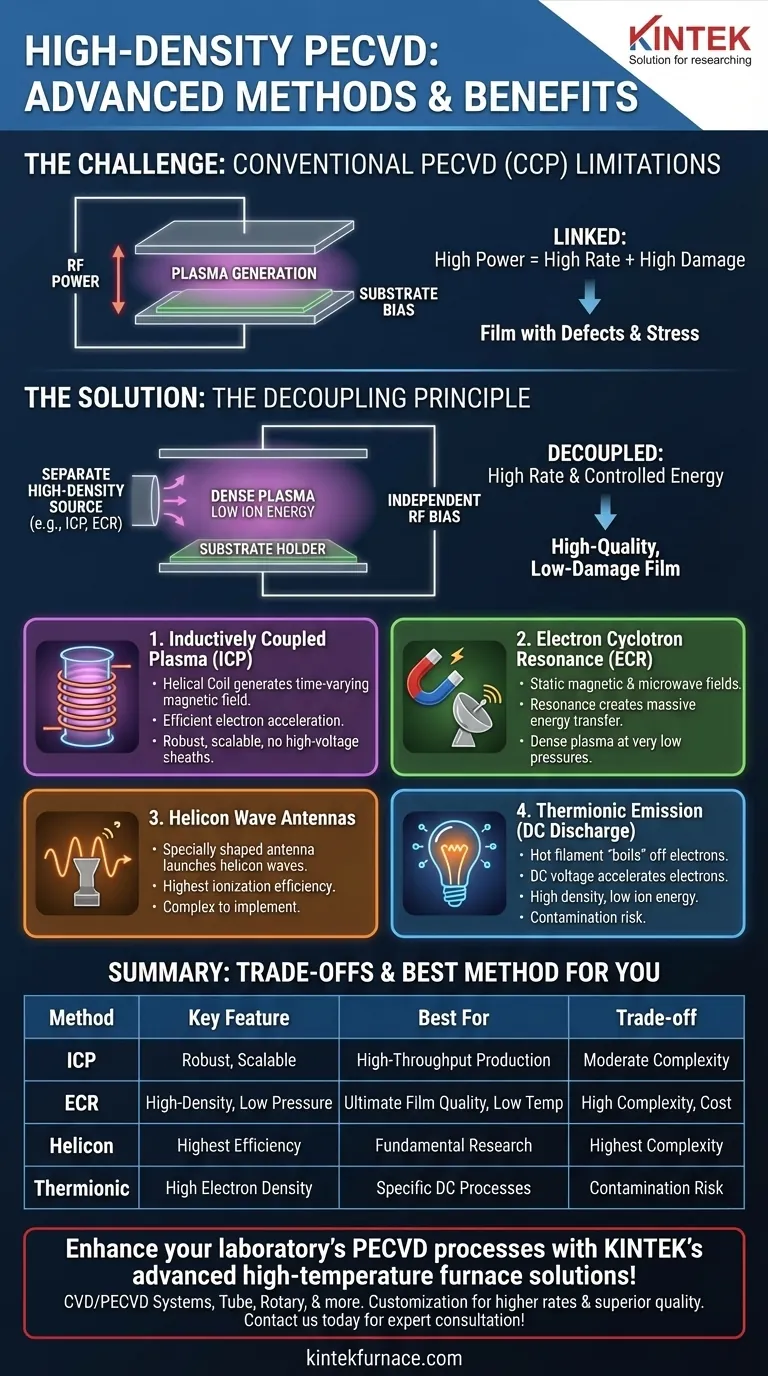
To create a high-density discharge in PECVD, engineers employ advanced energy sources that are more efficient than standard capacitive plates. The primary methods involve using inductive coils, electron cyclotron resonance (ECR), helicon wave antennas, or injecting electrons into a DC discharge using thermionic filaments. These techniques are designed to generate a high concentration of reactive species without simultaneously creating high-energy ions that can damage the substrate.
The core challenge in advanced film deposition is separating plasma density from ion energy. High-density sources solve this by allowing you to generate a dense, reactive plasma independently, which enables high deposition rates with minimal damage to the film's atomic structure.
The Limitation of Conventional PECVD
The "Coupling" Problem
In a standard, parallel-plate PECVD system, the same radio frequency (RF) power source is responsible for two things: generating the plasma and accelerating ions toward the substrate. This is known as a capacitively coupled plasma (CCP).
Increasing the RF power in a CCP system to get a denser plasma (for faster deposition) also inevitably increases the energy of the ions striking the film. This bombardment can cause defects, stress, and damage to sensitive device layers.
Trapped Between Rate and Quality
This coupling forces a difficult trade-off. You can either have a high deposition rate with potential damage or a slow deposition rate to achieve a high-quality, low-damage film. For many advanced applications, neither option is ideal.
High-Density Sources: The Decoupling Principle
High-density plasma sources were developed to break this compromise. Their fundamental advantage is the decoupling of plasma generation from substrate biasing.
A separate, highly efficient source generates a very dense plasma with low intrinsic ion energy. A second, independent RF bias can then be applied to the substrate holder to carefully control the energy of ions arriving at the surface.
This allows you to independently control plasma density (which dictates the deposition rate) and ion energy (which influences film properties like density and stress).
Method 1: Inductively Coupled Plasma (ICP)
An Inductively Coupled Plasma (ICP) source uses a helical coil, typically outside the chamber, to which RF power is applied. This creates a time-varying magnetic field that, in turn, induces a circular electric field within the chamber.
This induced electric field efficiently accelerates electrons, creating a very dense plasma without the need for high-voltage sheaths at the boundaries. ICP is a robust and widely used high-density technique.
Method 2: Electron Cyclotron Resonance (ECR)
An ECR source uses a combination of a static magnetic field and a microwave-frequency electric field. The magnetic field forces electrons into a circular path.
When the microwave frequency matches the natural "cyclotron" frequency of the electrons, a resonance occurs, efficiently transferring massive amounts of energy to the electrons. This process creates an extremely dense plasma at very low pressures.
Method 3: Helicon Wave Antennas
Helicon sources are among the most efficient at generating plasma. They use a specially shaped antenna to launch a type of low-frequency electromagnetic wave, called a helicon wave, into the plasma.
This wave is exceptionally effective at being absorbed by electrons, leading to the highest levels of ionization and plasma density, but these systems are often more complex to implement.
Method 4: DC Discharge with Thermionic Emission
This method takes a different approach. Instead of using RF or microwave fields to generate plasma, it uses a hot filament (like in a lightbulb) to "boil" electrons off into the chamber through thermionic emission.
These free electrons are then accelerated by a DC voltage to create the discharge. This produces a very high density of electrons and, consequently, a dense plasma with low ion energies.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Contamination Risk
Methods involving internal components, particularly the heated filaments in thermionic emission sources, pose a risk of sputtering and contaminating the film. This makes them less suitable for ultra-pure electronic applications.
System Complexity and Cost
High-density sources are significantly more complex and expensive than simple CCP systems. ECR sources, requiring strong magnetic fields and microwave hardware, and Helicon sources are typically the most complex, while ICP offers a more moderate balance.
Process Control
While offering more control, these systems also require more sophisticated process tuning. Optimizing power, pressure, gas flow, and substrate bias in a decoupled system requires a deeper understanding of the plasma physics at play.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The best method depends entirely on the technical requirements and budget for your specific deposition process.
- If your primary focus is high-throughput production with good quality: ICP offers a robust, scalable, and well-understood balance of performance and cost.
- If your primary focus is ultimate film quality at low temperatures: ECR provides a very high-density, low-ion-energy plasma that is ideal for depositing delicate films on sensitive substrates.
- If your primary focus is fundamental research or maximum ionization efficiency: Helicon sources are unparalleled in their ability to generate dense plasma, though they carry the highest complexity.
- If your primary focus is a specific DC-based process: Thermionic emission is an effective way to enhance DC discharges, provided potential filament contamination is not a concern.
Ultimately, selecting a high-density source is about matching the required deposition energy and rate to the specific demands of your material and substrate.
Summary Table:
| Method | Key Feature | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Inductively Coupled Plasma (ICP) | Robust, scalable, decouples plasma density and ion energy | High-throughput production with good quality |
| Electron Cyclotron Resonance (ECR) | High-density, low-ion-energy plasma at low pressures | Ultimate film quality at low temperatures |
| Helicon Wave Antennas | Highest ionization efficiency and plasma density | Fundamental research or maximum efficiency |
| DC Discharge with Thermionic Emission | High electron density from hot filaments | Specific DC-based processes, if contamination is not a concern |
Enhance your laboratory's PECVD processes with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse labs with tailored systems like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, helping you achieve higher deposition rates and superior film quality. Ready to optimize your plasma processes? Contact us today for expert consultation and solutions!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between PVD and PECVD? Choose the Right Thin-Film Coating Technology
- What is the role of temperature in PECVD? Optimize Film Quality and Substrate Protection
- What are the future trends in CVD technology? AI, Sustainability, and Advanced Materials
- How does a CVD system ensure the quality of carbon layers? Achieving Nanometer Precision with KINTEK
- What are gas barrier films, and how is PECVD involved in their creation? Discover Advanced Packaging Solutions



















