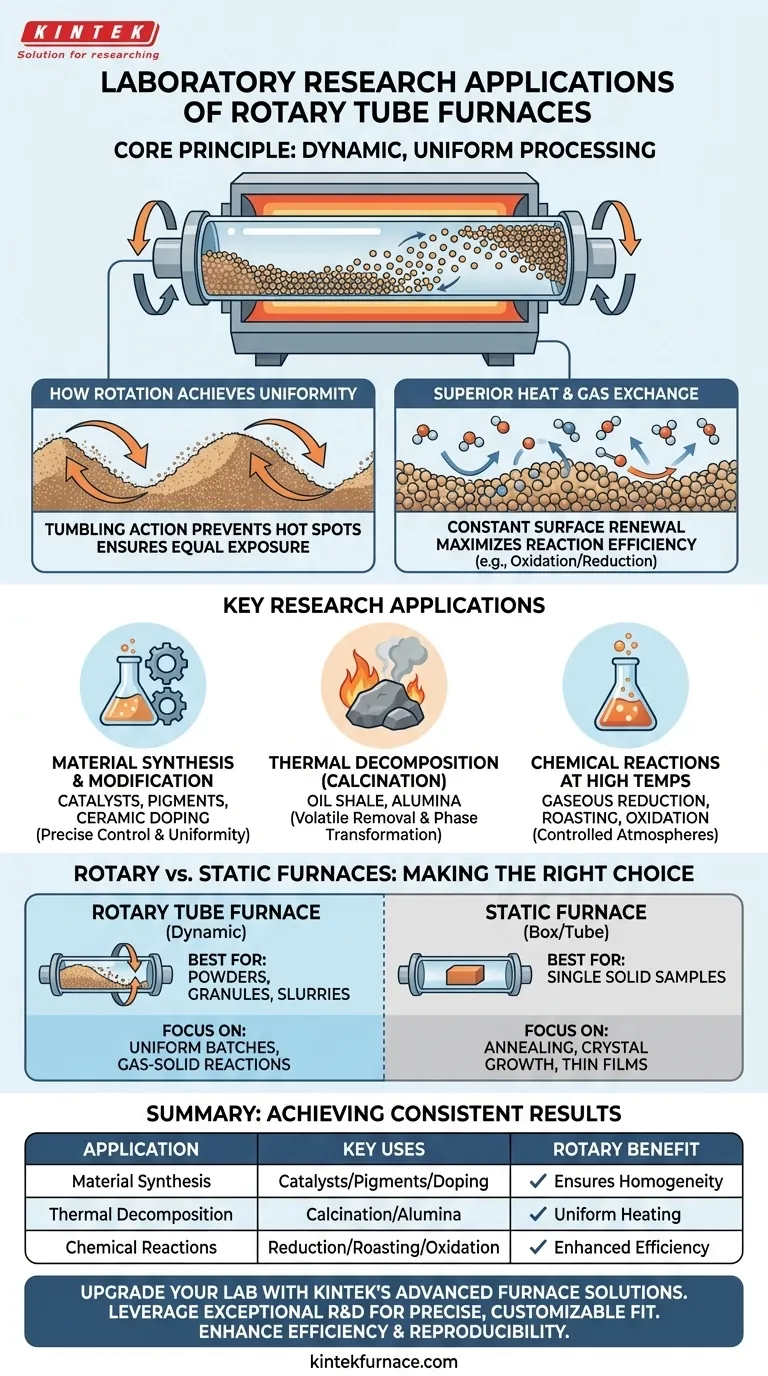
In a laboratory setting, rotary tube furnaces are essential for research applications that require the uniform thermal treatment of powders, granules, or other free-flowing materials. They are commonly used for material synthesis, such as creating catalysts and pigments; chemical reactions like the gaseous reduction of ores; and thermal decomposition processes, including calcination of oil shale or the analysis of metallurgical slags.
The core advantage of a rotary tube furnace is not just its ability to heat a sample, but its capacity to do so with exceptional uniformity. The continuous rotation ensures every particle is equally exposed to the controlled temperature and atmosphere, which is critical for achieving consistent and reproducible research results.

The Core Principle: Dynamic, Uniform Processing
A rotary tube furnace's unique value stems from its dynamic nature. Unlike a static furnace where the sample sits still, the rotation fundamentally changes how the material is processed.
How Rotation Achieves Uniformity
The furnace contains a processing tube that is slowly and continuously rotated while being heated.
This rotation causes the material inside to tumble, much like clothes in a dryer. This tumbling action prevents hot spots and ensures that particles from the center of the batch are constantly moved to the edge, and vice-versa.
Superior Heat and Gas Exchange
This constant mixing action continuously exposes new surfaces of the material to the furnace's heat source and its internal atmosphere.
This is critical for processes that involve reactions with a gas, such as oxidation (reaction with oxygen) or reduction (reaction with a reducing gas like hydrogen). The renewed surface area dramatically increases the efficiency and completeness of the reaction.
Key Research Applications Breakdown
The principle of uniform, dynamic heating makes the rotary tube furnace ideal for several specific areas of laboratory research.
Material Synthesis and Modification
These furnaces are used to create new materials or alter the properties of existing ones.
Applications include the synthesis of catalysts and pigments, where precise temperature control and uniform composition are paramount. They are also used for doping ceramics with rare earth metals, a process that requires homogenous distribution of the dopant throughout the ceramic powder.
Thermal Decomposition (Calcination)
Calcination is a high-temperature process used to remove volatile components or trigger phase transformations in a material.
The uniform heating of a rotary furnace is perfect for the calcination of oil shale to extract kerogen or for producing high-purity materials like alumina from its precursors.
Chemical Reactions at High Temperatures
Many crucial chemical reactions in materials science are performed at elevated temperatures.
A rotary furnace provides the ideal environment for the gaseous reduction of ores into metals, the roasting of sulfide minerals, and the controlled oxidation of various compounds.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Rotary vs. Static Furnaces
Choosing the right furnace is critical. The primary decision is often between a dynamic (rotary) furnace and a static (box or standard tube) furnace.
When to Choose a Rotary Tube Furnace
A rotary tube furnace is the superior choice when your sample is a powder, granulate, or slurry.
If the goal of your research is to ensure every particle in a batch receives the exact same thermal and atmospheric treatment—for processes like coating, calcination, or gas-solid reactions—the rotary design is unmatched.
When a Static Furnace is a Better Fit
A static furnace, such as a box furnace or a standard tube furnace, is more appropriate for treating single, solid samples.
These are used for processes like annealing a metal part, growing a crystal, or processing a thin film on a substrate. In these cases, sample agitation from rotation is unnecessary and often undesirable.
Making the Right Choice for Your Research
Your specific research goal dictates the appropriate tool. Use the following guidelines to make an informed decision.
- If your primary focus is uniform powder processing: A rotary tube furnace is the definitive choice for its ability to eliminate thermal gradients and ensure batch homogeneity.
- If your primary focus is efficient gas-solid reactions: The continuous surface renewal in a rotary tube furnace makes it far more effective than a static alternative.
- If your primary focus is treating a single, solid object: A static box or standard tube furnace provides the stable, non-agitated environment required for this type of work.
Ultimately, selecting the correct furnace is the first step toward achieving reliable, repeatable, and high-quality results in your material processing experiments.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Key Uses |
|---|---|
| Material Synthesis | Catalyst and pigment creation, ceramic doping |
| Thermal Decomposition | Calcination of oil shale, alumina production |
| Chemical Reactions | Gaseous reduction of ores, roasting, oxidation |
| Uniform Processing | Ensures homogeneity in powders and granules |
Upgrade your lab's capabilities with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide rotary tube furnaces and other systems like Muffle, Tube, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization ensures precise fit for your unique experimental needs, enhancing efficiency and reproducibility in material synthesis and thermal processing. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your research goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
People Also Ask
- How do rotary tube furnaces achieve precise temperature control? Master Uniform Heating for Dynamic Processes
- What is the basic construction of a rotary tube furnace? Key Components for Uniform Heating
- What materials can be used to make the rotating tube assembly of these furnaces? Choose the Best for Your High-Temp Needs
- What types of materials are suitable for processing in rotary tube furnaces? Ideal for Free-Flowing Powders and Granules
- What supplementary features can enhance rotary tube furnace performance? Boost Efficiency with Precision Control



















