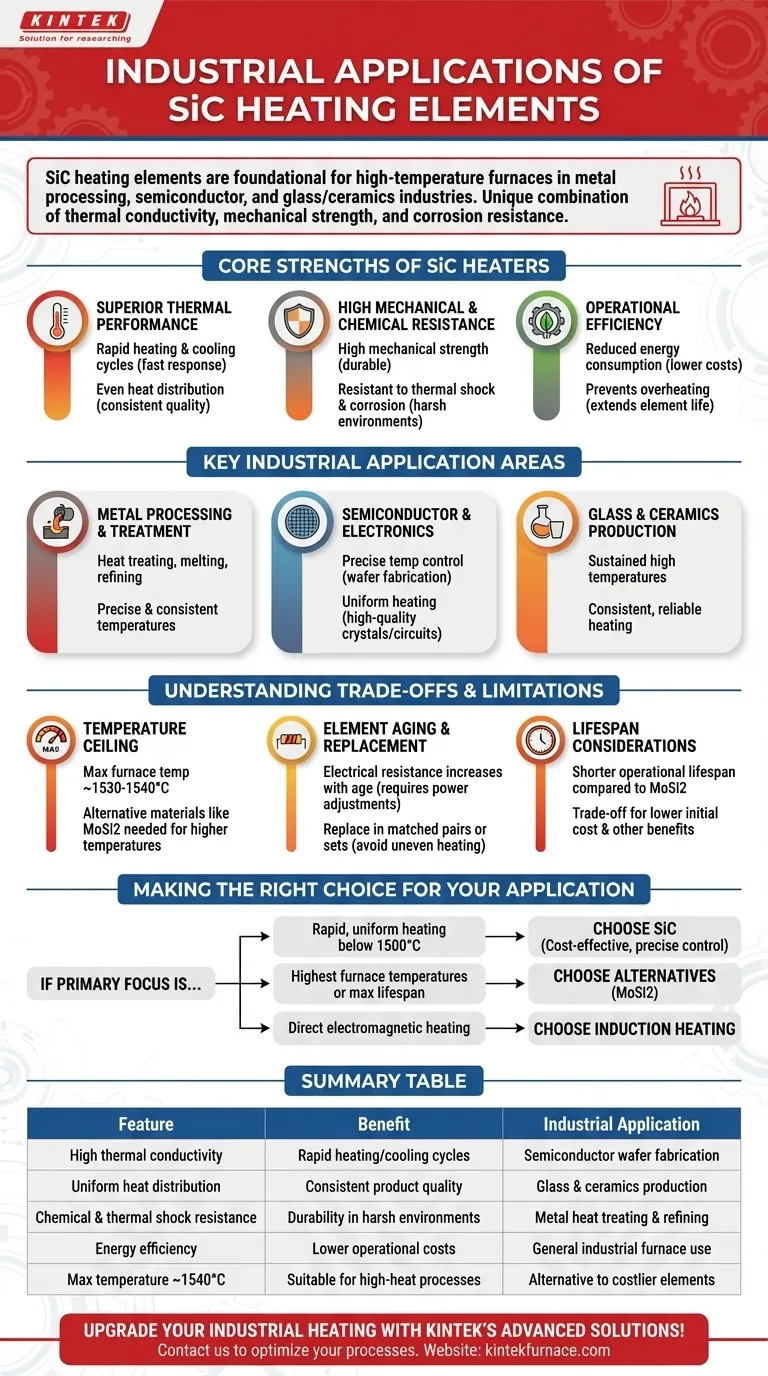
In industrial settings, silicon carbide (SiC) heating elements are foundational components for high-temperature furnaces used in metal processing, semiconductor fabrication, and the production of glass and ceramics. Their value comes from a unique combination of thermal conductivity, mechanical strength, and resistance to chemical corrosion, enabling precise and reliable heating in demanding environments.
Silicon carbide heaters are the technology of choice for applications requiring rapid, uniform heating up to approximately 1540°C. They represent a pragmatic balance between high performance, operational efficiency, and overall cost, distinguishing them from both lower-temperature elements and more expensive, higher-temperature alternatives.
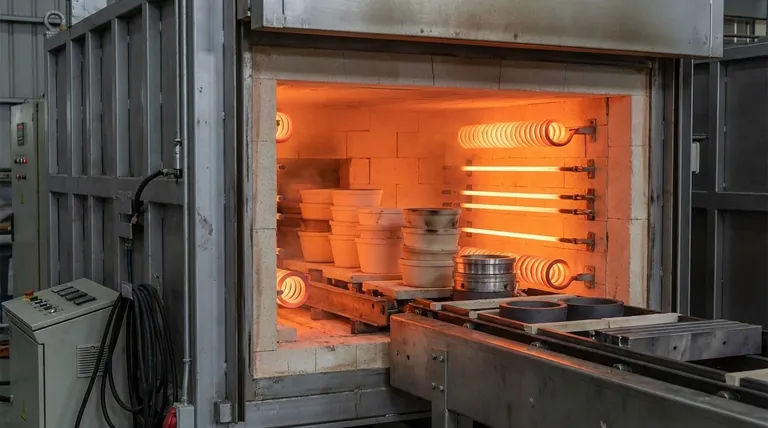

The Core Strengths of SiC Heaters
Superior Thermal Performance
SiC elements possess excellent thermal conductivity. This allows for very fast heating and cooling cycles, which is critical for batch processing in industries like electronics.
This property also ensures even heat distribution within a furnace, reducing the risk of hot spots and ensuring consistent product quality.
High Mechanical and Chemical Resistance
These elements exhibit significant mechanical strength even at high temperatures, making them durable and less prone to breakage.
Furthermore, SiC is highly resistant to thermal shock and chemical corrosion. This makes it ideal for harsh furnace atmospheres found in metal treatment and ceramics firing.
Operational Efficiency
SiC heaters provide notable efficiency benefits, including reduced energy consumption compared to less advanced resistive elements. This leads directly to lower operational costs and a smaller carbon footprint.
Their ability to manage heat effectively prevents overheating, which helps extend the element's lifespan and protects the furnace and its contents.
Key Industrial Application Areas
Metal Processing and Treatment
In metallurgy, SiC elements are used for processes like heat treating, melting, and refining metals. The ability to maintain precise and consistent temperatures is essential for achieving desired material properties.
Semiconductor and Electronics Manufacturing
The semiconductor industry relies on SiC heaters for precise temperature control during wafer fabrication and the manufacturing of other electronic components. Uniform heating is non-negotiable for producing high-quality crystals and integrated circuits.
Glass and Ceramics Production
Producing glass and firing ceramics involves extreme conditions and sustained high temperatures. SiC elements are used extensively in these applications because they can provide consistent, reliable heating day after day.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
Temperature Ceiling
SiC elements have a maximum surface temperature of around 1600°C, which translates to a maximum furnace operating temperature of 1530-1540°C. For processes requiring temperatures above this, alternative materials like Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) are necessary.
Element Aging and Replacement
The electrical resistance of SiC elements changes and increases as they age. This requires periodic adjustments to the power supply to maintain consistent output.
When one element in a series fails, it is critical to replace them in matched pairs or as a complete set. Mismatched resistances can lead to uneven heating and premature failure of the new and old elements.
Lifespan Considerations
Compared to MoSi2 elements, SiC heaters generally have a shorter operational lifespan. This trade-off is often accepted in exchange for SiC's other benefits, especially in applications where cost is a significant factor.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Choosing the correct heating technology requires a clear-eyed assessment of your process needs.
- If your primary focus is rapid, uniform heating for processes below 1500°C: SiC is an excellent, cost-effective choice that delivers precise thermal control.
- If your primary focus is reaching the highest possible furnace temperatures or maximizing element lifespan: You should evaluate alternatives like Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2), which operate at higher temperatures and typically last longer.
- If your primary focus is direct, electromagnetic heating of a conductive material: You should investigate induction heating, which is a fundamentally different technology used for tasks like metal melting and surface hardening.
Ultimately, selecting the right heating element requires a clear understanding of your specific temperature, cycle time, and budgetary requirements.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit | Industrial Application |
|---|---|---|
| High thermal conductivity | Rapid heating/cooling cycles | Semiconductor wafer fabrication |
| Uniform heat distribution | Consistent product quality | Glass and ceramics production |
| Chemical and thermal shock resistance | Durability in harsh environments | Metal heat treating and refining |
| Energy efficiency | Lower operational costs | General industrial furnace use |
| Max temperature ~1540°C | Suitable for high-heat processes | Alternative to costlier elements |
Upgrade your industrial heating with KINTEK's advanced solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnace systems like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, enhancing efficiency and reliability. Contact us today to discuss how our SiC heating elements and other products can optimize your processes and deliver superior performance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of using high purity green silicon carbide powder in heating elements? Boost Efficiency and Lifespan
- What is the maximum temperature silicon carbide heating elements can withstand? Key Factors for Longevity and Performance
- Why is silicon carbide resistant to chemical reactions in industrial furnaces? Unlock Durable High-Temp Solutions
- Why are SIC heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Self-Protecting Mechanism
- What makes SIC heating elements superior for high-temperature applications? Unlock Efficiency and Durability



















