For high-temperature laboratory vacuum furnaces, the primary heating elements are Graphite, Molybdenum (Mo), and Tungsten (W). Graphite and Molybdenum elements are commonly used for temperatures up to 2200°C, while Tungsten is employed for extreme applications, capable of reaching temperatures as high as 3000°C. These materials are chosen specifically for their ability to withstand intense heat in a non-oxidizing vacuum environment.
The most critical factor in selecting a heating element is not just its maximum temperature but the furnace's operating atmosphere. Elements like Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂) and Silicon Carbide (SiC) excel in air but fail in a vacuum, whereas Graphite, Molybdenum, and Tungsten are the workhorses specifically for vacuum applications.
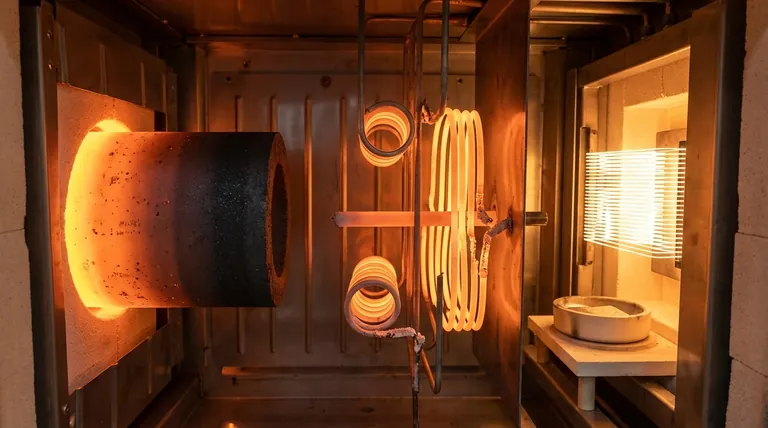
The Workhorses of High-Temperature Vacuum Furnaces
The choice of a heating element is a foundational design decision that dictates the furnace's capabilities, cost, and the types of materials you can process. In a vacuum, the absence of oxygen prevents the rapid oxidation that would destroy these elements at high temperatures.
Graphite: The Versatile Standard (Up to 2200°C+)
Graphite is the most common heating element in high-temperature vacuum furnaces due to its excellent balance of performance and cost.
It is easily machined into complex shapes, has low density, and exhibits high thermal stability. Most general-purpose vacuum furnaces operating in the 1200°C to 2200°C range rely on graphite elements.
Molybdenum (Mo): The Refractory Metal (Up to 1800°C)
Molybdenum is a refractory metal used when carbon contamination from a graphite element is a concern for the sample being processed.
While it can technically reach higher temperatures, it is most reliably used for applications up to about 1800°C. It is more expensive than graphite and becomes very brittle after thermal cycling, requiring careful handling.
Tungsten (W): The Ultimate Temperature Leader (Up to 3000°C)
For processes requiring the highest possible temperatures, tungsten is the undisputed choice. It has the highest melting point of any metal, allowing furnaces to reach 3000°C.
This performance comes at a high cost. Tungsten is expensive, dense (requiring more structural support), and demands significantly more electrical power to reach its peak temperature.
Why Some Common Elements Are Unsuitable for High-Vacuum
You will often see other high-temperature elements mentioned for furnaces, but they are typically designed for operation in air, not vacuum. Understanding this distinction is crucial to avoid costly mistakes.
The Muffle Furnace Distinction: MoSi₂ and SiC
Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂, up to 1800°C) and Silicon Carbide (SiC, up to 1600°C) are exceptional heating elements for furnaces that operate in an oxidizing atmosphere (like air).
At high temperatures, they form a protective surface layer of glassy silicon dioxide (SiO₂). This layer prevents the underlying element from burning away.
The Problem in a Vacuum
In a high-vacuum environment, there is insufficient oxygen to form or maintain this protective oxide layer.
Without it, the raw element material is exposed directly to the high heat, causing it to rapidly degrade or "sublime," contaminating the furnace and the product while destroying the element itself.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting an element involves balancing three key factors: temperature, chemical compatibility, and cost.
Temperature vs. Cost
There is a direct correlation between maximum temperature and cost. Graphite offers the best performance-per-dollar up to 2200°C. Molybdenum represents a moderate increase in cost for a carbon-free environment, while Tungsten represents the premium, high-cost option for ultimate temperature capability.
Chemical Compatibility
The element must not react with the material being processed. Graphite can introduce carbon into a sample (a process called carburization), which can be undesirable for certain metal alloys or ceramics. In these cases, a metallic Molybdenum or Tungsten element is necessary.
Longevity and Maintenance
All high-temperature elements are consumables that degrade over time. Graphite elements become thinner and more fragile. Refractory metals like Molybdenum and Tungsten become extremely brittle after their first heat cycle and must be handled with care during maintenance.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your specific application and experimental goals will determine the ideal heating element.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective general-purpose heating up to 2200°C: Graphite is the standard and most economical choice.
- If your primary focus is avoiding carbon contamination in the 1300°C to 1800°C range: Molybdenum is the superior metallic option for processing sensitive materials.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest possible temperatures (above 2000°C and up to 3000°C): Tungsten is the definitive, albeit most expensive, solution.
- If your process operates in an air or oxidizing atmosphere: You must use elements designed for it, such as MoSi₂ or SiC, not vacuum furnace elements.
Matching the heating element material to the furnace atmosphere and process requirements is the key to successful high-temperature work.
Summary Table:
| Heating Element | Max Temperature | Key Features | Best Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|
| Graphite | Up to 2200°C | Cost-effective, versatile, easy to machine | General-purpose heating in vacuum |
| Molybdenum (Mo) | Up to 1800°C | Carbon-free, avoids contamination | Sensitive materials processing |
| Tungsten (W) | Up to 3000°C | Highest temperature capability, expensive | Extreme high-temperature applications |
Need a Custom High-Temperature Furnace Solution?
At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your unique experimental requirements. Leveraging our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer a diverse product line including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Whether you're working with graphite, molybdenum, or tungsten elements, our strong deep customization capability ensures precise performance for your lab's needs—enhancing efficiency, reliability, and results.
Contact us today to discuss how we can support your high-temperature processes and deliver the perfect furnace for your application!
Visual Guide

Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the benefits of vacuum heat treatment? Achieve Superior Metallurgical Control
- What are the components of a vacuum furnace? Unlock the Secrets of High-Temperature Processing
- What are the functions of a high-vacuum furnace for CoReCr alloys? Achieve Microstructural Precision and Phase Stability
- What are the general operational features of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Superior Material Purity & Precision
- How does a vacuum heat treatment furnace influence Ti-6Al-4V microstructure? Optimize Ductility and Fatigue Resistance



















