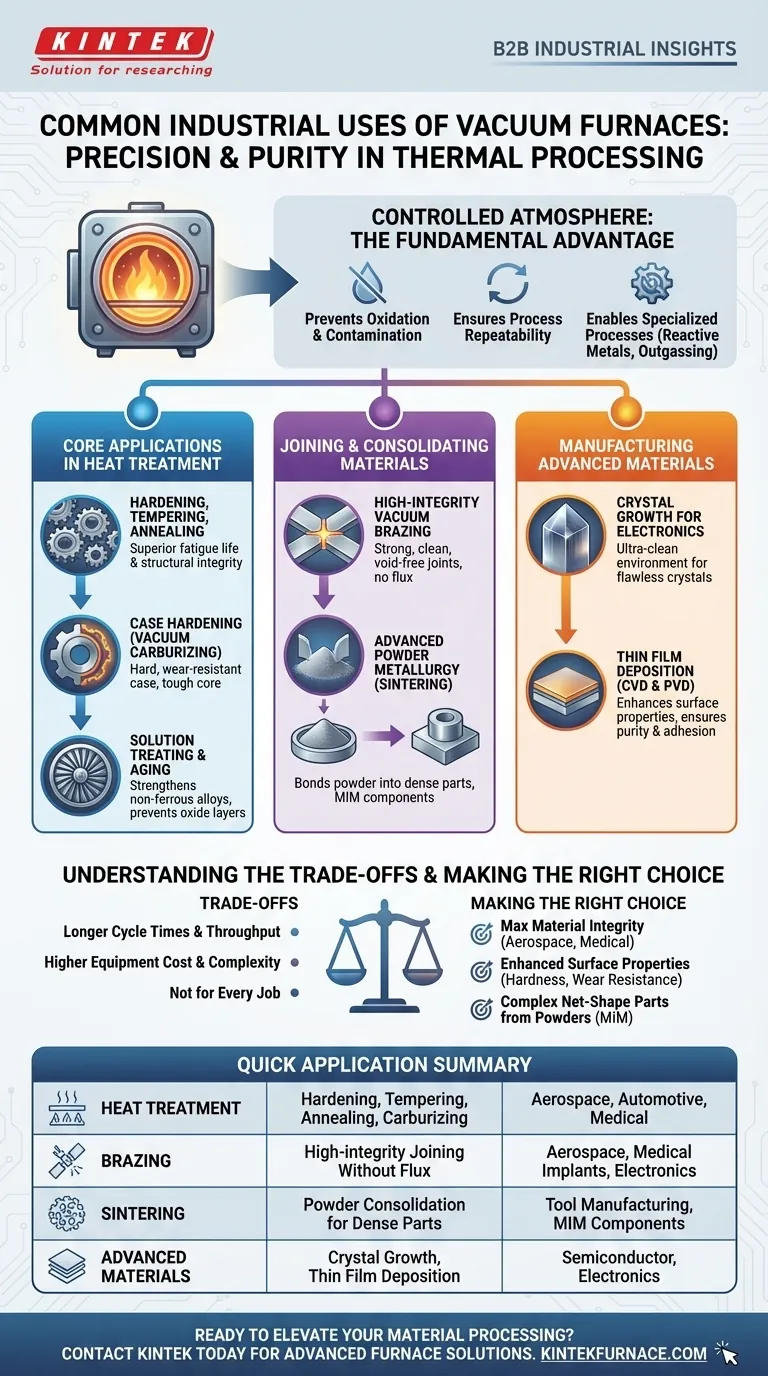
In essence, industrial vacuum furnaces are used for a wide range of thermal processes where preventing contamination is critical. Their most common applications include the heat treatment of metal alloys (such as hardening, tempering, and annealing), high-integrity brazing for joining components, and sintering for consolidating powdered materials into solid parts. They are indispensable in industries like aerospace, medical, and electronics for producing high-quality, reliable components.
The fundamental challenge in high-temperature material processing is that heat accelerates unwanted chemical reactions, primarily oxidation, which degrades a material's quality and performance. Vacuum furnaces solve this by removing the reactive atmosphere, creating a pristine environment for precisely controlled thermal processing.

The Fundamental Advantage: An Uncontaminated Environment
The core value of a vacuum furnace is not the heat itself, but the controlled atmosphere—or lack thereof. By pumping out the air, the furnace removes oxygen, water vapor, and other gases that would react with the material at high temperatures.
Preventing Oxidation and Contamination
Heating metals in the presence of oxygen creates an oxide layer, or scale, on the surface. A vacuum environment eliminates this, resulting in bright, clean parts that require no post-process cleaning. This is critical for parts with complex geometries or for materials where surface integrity is paramount.
Ensuring Process Repeatability
A vacuum provides a highly stable and repeatable environment. Unlike atmosphere furnaces where gas composition can fluctuate, a vacuum is a consistent starting point for every cycle, ensuring that parts produced today are identical to parts produced months from now.
Enabling Specialized Processes
Certain materials, particularly reactive metals and advanced alloys, can only be processed in a vacuum to preserve their unique properties. Furthermore, a vacuum facilitates outgassing, pulling trapped gases out from within the material itself, leading to higher purity and density.
Core Applications in Heat Treatment
Heat treatment modifies a material's microstructure to achieve specific mechanical properties like hardness, toughness, or ductility. Performing these processes in a vacuum elevates the quality of the result.
Hardening, Tempering, and Annealing
These are the most common heat treatment processes. Hardening (via quenching) increases a material's strength, tempering reduces its brittleness, and annealing softens it to improve ductility. In a vacuum, these processes yield parts with superior fatigue life and structural integrity, crucial for high-performance steel alloys.
Case Hardening (Vacuum Carburizing)
This process diffuses carbon into the surface of a steel component at high temperature. The result is a part with an extremely hard, wear-resistant outer case and a softer, tougher core. Vacuum carburizing provides exceptional control over the case depth and uniformity.
Solution Treating and Aging
Used extensively in the aerospace industry, these processes strengthen non-ferrous alloys like aluminum, nickel, and titanium. A vacuum prevents the formation of detrimental oxide layers that can compromise the performance of critical components like turbine blades or structural airframe parts.
Joining and Consolidating Materials
Beyond modifying existing parts, vacuum furnaces are essential for creating and joining them.
High-Integrity Vacuum Brazing
Brazing uses a filler metal to join two components. In a vacuum, this process creates exceptionally strong, clean, and void-free joints without the need for corrosive flux. It is the standard for mission-critical assemblies in aerospace, medical implants, and electrical equipment like vacuum interrupters.
Advanced Powder Metallurgy (Sintering)
Sintering is the process of taking compacted metal or ceramic powders and heating them to just below their melting point, causing the particles to bond into a solid, dense part. Vacuum sintering is used to produce parts from materials like tungsten carbide for cutting tools and to process components made via Metal Injection Molding (MIM). The cycle often includes a debinding phase to remove polymer binders before the final sintering.
Manufacturing Advanced Materials and Components
Vacuum technology is at the forefront of modern materials science and high-tech manufacturing.
Crystal Growth for Electronics
The creation of large, single-crystal silicon ingots for semiconductor wafers requires an environment of extreme purity. Vacuum furnaces provide the ultra-clean, controlled conditions necessary for growing these flawless crystals, which are the foundation of all modern electronics.
Thin Film Deposition (CVD & PVD)
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) and Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) are processes that deposit thin layers of material onto a substrate to enhance its properties (e.g., hardness, low friction). A vacuum is essential for these processes to ensure the purity and adhesion of the deposited film.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, vacuum furnaces are not a universal solution. Understanding their limitations is key to making informed decisions.
Cycle Time and Throughput
Pumping down to a deep vacuum and cooling the workload in a controlled manner takes time. Consequently, vacuum furnace cycle times are often longer than those of conventional atmosphere furnaces, which can impact overall throughput.
Equipment Cost and Complexity
Vacuum furnaces are sophisticated systems involving vacuum pumps, advanced controls, and specialized chamber construction. This results in a higher initial investment and requires more skilled personnel for operation and maintenance.
Not a Fit for Every Job
For low-carbon steels or simple annealing jobs where a small amount of surface oxidation is acceptable and can be easily removed, a less expensive atmosphere furnace is often a more economical choice. The value of a vacuum is directly proportional to the material's cost and the component's performance requirements.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To determine if a vacuum furnace is the right tool, consider your ultimate objective.
- If your primary focus is maximum material integrity: For critical components in aerospace, medical, or defense, vacuum heat treatment and brazing are the correct choice to ensure reliability and performance.
- If your primary focus is enhanced surface properties: For creating parts with extreme hardness and wear resistance, you should investigate vacuum carburizing or PVD coating.
- If your primary focus is creating complex net-shape parts from powders: For applications like carbide tools or intricate MIM components, vacuum debinding and sintering are the industry-standard processes.
Ultimately, choosing a vacuum furnace is a strategic decision to eliminate environmental variables and exert precise control over your material's final properties.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Uses | Industries Benefited |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Treatment | Hardening, tempering, annealing, carburizing | Aerospace, automotive, medical |
| Brazing | High-integrity joining without flux | Aerospace, medical implants, electronics |
| Sintering | Powder consolidation for dense parts | Tool manufacturing, MIM components |
| Advanced Materials | Crystal growth, thin film deposition | Semiconductor, electronics |
Ready to elevate your material processing with precision and purity? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we can precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how our vacuum furnaces can enhance your industrial applications and deliver superior results for your high-performance components!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a vacuum hot pressing furnace play in TiBw/TA15 synthesis? Enhance In-Situ Composite Performance
- Why is a vacuum hot press sintering furnace required for nanocrystalline ceramics? Preserve Structure with Pressure
- How do vacuum sintering and annealing furnaces contribute to the densification of NdFeB magnets?
- What are the advantages of a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace for rare earth copper composites? Density & Purity
- How does pressure application in a vacuum hot press furnace facilitate sintering of copper composites? Optimize Density



















