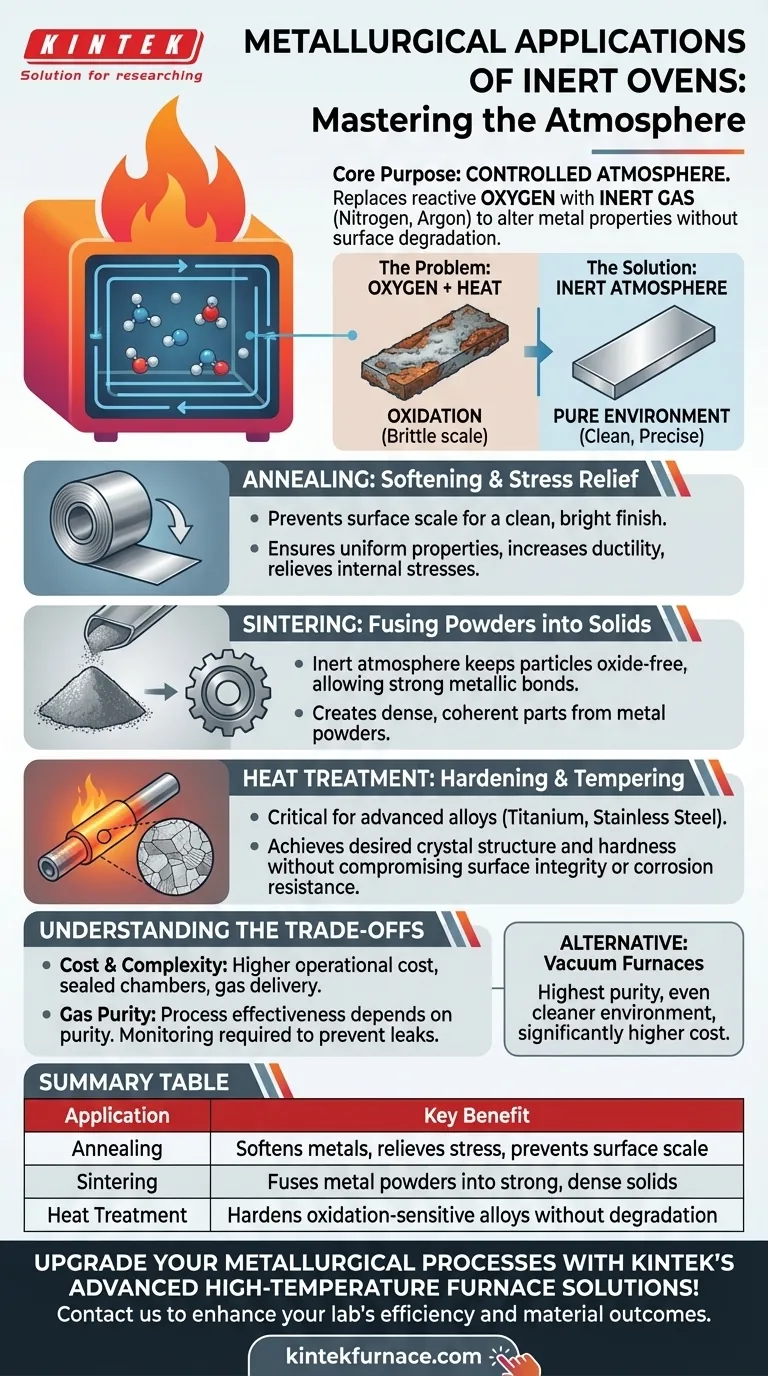
In metallurgy, inert ovens are primarily used for three critical thermal processes: annealing, sintering, and the heat treatment of oxidation-sensitive alloys. These controlled-atmosphere furnaces are essential for heating metals to enhance their properties without the degradation caused by oxidation or other unwanted chemical reactions.
The core purpose of using an inert oven in metallurgy is not the heat itself, but the control of the atmosphere. By replacing reactive oxygen with an inert gas like nitrogen or argon, you can fundamentally alter a metal's properties without compromising its surface integrity or chemical composition.

Why an Inert Atmosphere is Critical
The Problem with Oxygen and Heat
When most metals are heated in the presence of air, they react with oxygen. This process, known as oxidation, forms a brittle layer of scale on the surface.
This oxide layer can ruin a part's dimensional accuracy, prevent proper bonding in subsequent processes, and degrade the material's mechanical properties. An inert oven prevents this by purging the oxygen and replacing it with a non-reactive gas.
Creating a Controlled Environment
An inert oven is sealed and filled with a gas like nitrogen or argon. These gases do not react with the metal, even at extreme temperatures.
This creates a pure environment where thermal processes can be performed precisely, ensuring the final product meets exact specifications without contamination or surface damage.
Key Metallurgical Applications Explained
Annealing: Softening and Stress Relief
Annealing is a heat treatment process used to soften metals, increase their ductility, and relieve internal stresses created during manufacturing.
Using an inert oven for annealing is crucial because it prevents the formation of surface scale. This results in a clean, bright finish and ensures the material's properties are uniform throughout, without a brittle oxide layer on the exterior.
Sintering: Fusing Powders into Solids
Sintering is the process of compacting and heating powdered material—typically metal or ceramic—to form a solid, coherent mass. The heat causes the individual particles to fuse together.
In an inert atmosphere, the metal powder particles remain pure and oxide-free. This allows them to form strong, direct metallic bonds upon heating. If oxygen were present, it would coat each particle with an oxide layer, preventing proper fusion and resulting in a weak, porous final part.
Heat Treatment: Hardening and Tempering
Many advanced alloys, such as titanium alloys and certain grades of stainless steel, are highly susceptible to oxidation at the temperatures required for hardening or tempering.
For these materials, an inert atmosphere is non-negotiable. It allows the metallurgist to achieve the desired crystal structure and mechanical properties (like hardness and strength) without simultaneously creating a detrimental oxide layer that would compromise the component's performance and corrosion resistance.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Cost and Complexity
The primary trade-off is cost. Inert gas furnaces are more complex and expensive to operate than standard air furnaces due to the need for sealed chambers, gas delivery systems, and the ongoing cost of high-purity nitrogen or argon.
Ensuring Gas Purity
The effectiveness of the process is entirely dependent on the purity of the inert atmosphere. Any leaks in the oven chamber that allow air to enter can compromise the entire batch. Continuous monitoring of the atmosphere is often required for critical applications.
Vacuum Furnaces as an Alternative
For the most sensitive materials or applications requiring the absolute highest level of purity, a vacuum furnace may be necessary. A vacuum furnace removes nearly all atmospheric molecules, providing an even cleaner environment than a standard inert gas oven, albeit at a significantly higher cost and complexity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Choosing the correct thermal process depends entirely on your material and desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is softening a metal for further forming: Inert annealing will deliver a ductile, stress-relieved part with a clean, scale-free surface.
- If your primary focus is creating a dense, solid part from metal powder: Inert sintering is essential to ensure strong metallic bonding between particles.
- If your primary focus is hardening an oxidation-prone alloy like titanium: A high-purity inert atmosphere is the only way to achieve target mechanical properties without damaging material integrity.
Ultimately, mastering thermal processing in metallurgy is about mastering the atmosphere in which it occurs.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Annealing | Softens metals, relieves stress, prevents surface scale |
| Sintering | Fuses metal powders into strong, dense solids |
| Heat Treatment | Hardens oxidation-sensitive alloys without degradation |
Upgrade your metallurgical processes with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capability ensures precise solutions for your unique experimental needs, such as oxidation-free annealing, sintering, and heat treatment. Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can enhance your lab's efficiency and material outcomes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a mixed gas flow control system maintain stability during high-temperature nitriding? Precision Gas Ratios
- Can box type high-temperature resistance furnaces control the atmosphere? Unlock Precision in Material Processing
- How do argon and nitrogen protect samples in vacuum furnaces? Optimize Your Thermal Process with the Right Gas
- What are the key features of an atmosphere box furnace? Unlock Precise Heat Processing in Controlled Environments
- What are the development prospects of atmosphere box furnaces in the aerospace industry? Unlock Advanced Material Processing for Aerospace Innovation



















