In solar cell manufacturing, atmosphere furnaces are essential for fabricating the core components of the cell through high-temperature processes like deposition, annealing, and sintering. By precisely controlling the gaseous environment during heating, these furnaces enable the creation of highly pure, structurally perfect semiconductor layers, which is fundamental to achieving high energy conversion efficiency.
The ultimate goal in solar cell production is to maximize the conversion of sunlight into electricity. Atmosphere furnaces are the critical tool for this, providing the controlled thermal environment needed to manipulate material properties at the atomic level, remove defects, and build the layered structure that makes a photovoltaic cell work.

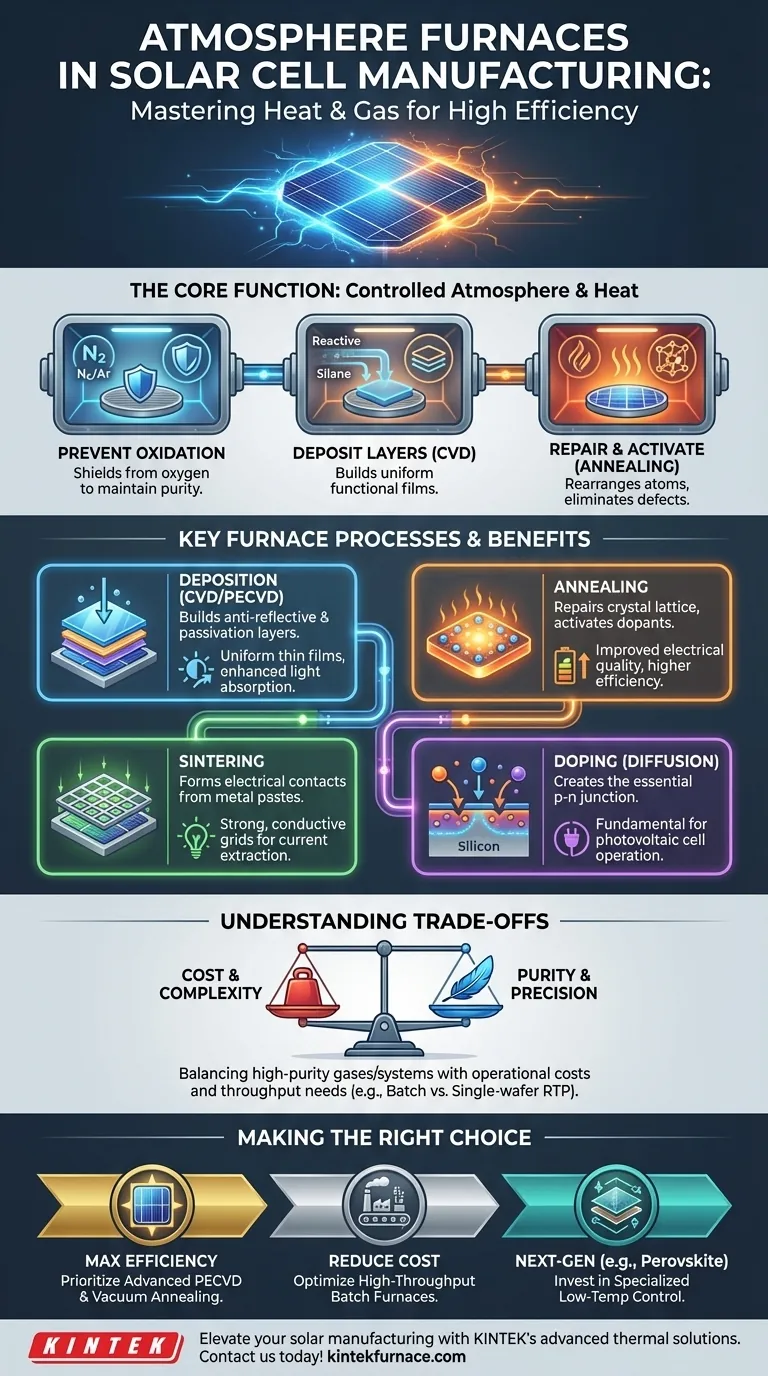
The Core Function: Why Control the Atmosphere?
The performance of a solar cell is dictated by the purity and structure of its semiconductor layers. Atmosphere furnaces provide the meticulously controlled environment required to achieve these properties during high-temperature manufacturing steps.
To Prevent Unwanted Reactions
Most high-temperature processes in solar manufacturing, especially those involving silicon, must be shielded from oxygen. Uncontrolled exposure would cause oxidation, forming an insulating layer of silicon dioxide that severely degrades the cell's electrical performance.
Furnaces filled with an inert gas, such as nitrogen or argon, displace the oxygen and create a neutral environment, protecting the wafer's surface integrity.
To Deposit Functional Layers
Controlled atmospheres are also used to actively build the solar cell. Processes like Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) introduce specific reactive gases into the furnace.
At high temperatures, these gases (e.g., silane for silicon deposition) decompose and deposit a uniform, thin film onto the silicon wafer. This is how critical layers, such as the light-absorbing amorphous silicon or anti-reflective coatings, are created.
To Repair and Activate Materials
Heat treatment, known as annealing, is used to repair damage in the silicon crystal lattice caused by previous manufacturing steps like ion implantation.
Heating the wafer in a vacuum or inert gas allows the atoms to rearrange into a more perfect crystalline structure. This process eliminates defects that trap charge carriers and is also used to electrically "activate" dopants that form the essential p-n junction.
Key Furnace Processes in Solar Cell Manufacturing
Different types of atmosphere furnaces are deployed for specific tasks, each contributing to the final efficiency and stability of the solar cell.
Deposition (CVD and PECVD)
This is the process of building the solar cell layer by layer. Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition (PECVD) is a crucial low-temperature variant used for thin-film cells.
These furnaces are used to deposit layers like amorphous silicon (the primary light-absorbing layer) and silicon nitride, which serves as both a protective passivation layer and an anti-reflective coating to maximize light absorption.
Annealing
After layers are deposited or doped, the wafer undergoes annealing to improve its electrical and optical quality. Vacuum annealing furnaces are particularly effective at this.
By heating the wafers in a high vacuum, impurities are removed, and crystal defects are healed, directly enhancing the cell's conversion efficiency and long-term stability.
Sintering
Once the semiconductor structure is complete, metal pastes (often silver) are screen-printed onto the cell to form the electrical contacts that extract current.
The cell is then passed through a sintering furnace. The controlled, high-temperature cycle burns off organic binders in the paste and fuses the metal particles into a solid, highly conductive grid.
Doping (Diffusion)
To create the p-n junction—the engine of the solar cell—impurities (dopants) must be introduced into the silicon. This is often done in a diffusion furnace.
Wafers are heated in the presence of a dopant gas, which allows dopant atoms to diffuse a short distance into the silicon surface, creating the necessary positive and negative regions.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While essential, the choice and operation of atmosphere furnaces involve balancing competing priorities of performance, cost, and complexity.
Cost vs. Purity
Achieving a high-purity environment is expensive. High-purity process gases and the robust vacuum systems needed for annealing and deposition represent a significant capital and operational cost. Manufacturers must balance the efficiency gains from a purer process against the added expense.
Throughput vs. Precision
Furnace design impacts production speed. Batch furnaces can process hundreds of wafers at once, offering high throughput ideal for processes like diffusion and sintering. However, they can suffer from minor temperature variations across the batch.
In contrast, single-wafer rapid thermal processing (RTP) systems offer superior temperature uniformity and control but have much lower throughput, making them suitable for the most critical annealing steps.
Process Complexity and Safety
Processes like CVD involve highly toxic, flammable, or corrosive gases. Managing these materials requires complex gas delivery systems, exhaust abatement, and rigorous safety protocols, adding another layer of complexity to the manufacturing facility.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The specific furnace process you prioritize depends entirely on your primary objective, whether it's pushing the boundaries of efficiency or optimizing for mass production.
- If your primary focus is maximizing cell efficiency: Prioritize advanced PECVD for superior anti-reflection and passivation layers, combined with high-vacuum annealing to perfect the crystal quality.
- If your primary focus is reducing manufacturing cost: Optimize high-throughput batch furnaces for diffusion and sintering, and explore atmospheric pressure CVD (APCVD) as a lower-cost alternative for certain layers.
- If your primary focus is developing next-generation cells (e.g., Perovskite, CIGS): Invest in highly specialized, lower-temperature furnaces with precise atmospheric control to process these thermally sensitive materials without degrading them.
Ultimately, mastering thermal processing in controlled atmospheres is not just a manufacturing step; it is fundamental to advancing the power and affordability of solar technology.
Summary Table:
| Process | Purpose | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Deposition (CVD/PECVD) | Build functional layers like anti-reflective coatings | Uniform thin films, enhanced light absorption |
| Annealing | Repair crystal defects and activate dopants | Improved electrical quality, higher efficiency |
| Sintering | Form electrical contacts from metal pastes | Strong, conductive grids for current extraction |
| Doping (Diffusion) | Create p-n junctions by introducing impurities | Essential for photovoltaic cell operation |
Ready to elevate your solar cell manufacturing with precision-controlled thermal solutions? Contact KINTEK today to discuss how our advanced high-temperature furnaces—including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems—can be customized to meet your unique needs. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we help labs achieve superior efficiency, purity, and cost-effectiveness in processes like deposition, annealing, and sintering. Let's innovate together for a brighter solar future!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the main purpose of heat treatment? Transform Metal Properties for Superior Performance
- How does a chemically inert atmosphere function in a furnace? Prevent Oxidation and Ensure Material Purity
- What is nitrogen used for in a furnace? Prevent Oxidation and Control Heat Treatment Quality
- How does nitrogen atmosphere heat treatment improve surface strengthening? Enhance Durability and Performance
- What does inert mean in furnace atmospheres? Protect materials from oxidation with inert gases.



















