In short, a muffle furnace is a foundational tool used across nearly every industry that involves creating or testing physical materials. Its applications range from high-tech aerospace and biomedical sectors to fundamental industries like ceramics, metallurgy, and materials science. The furnace is indispensable for any process requiring high-temperature heating in a controlled, contaminant-free environment.
The unifying principle behind the muffle furnace's broad use is its ability to thermally isolate a sample. By separating the material from the direct heat source and its combustion byproducts, it ensures process purity, making it essential for both precise material transformation and accurate chemical analysis.
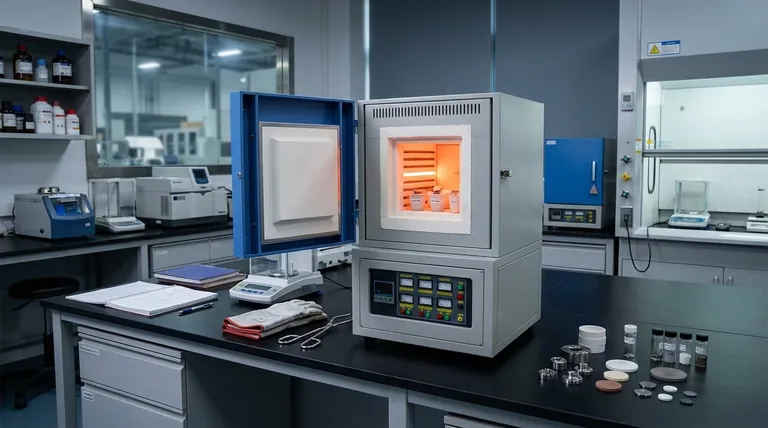

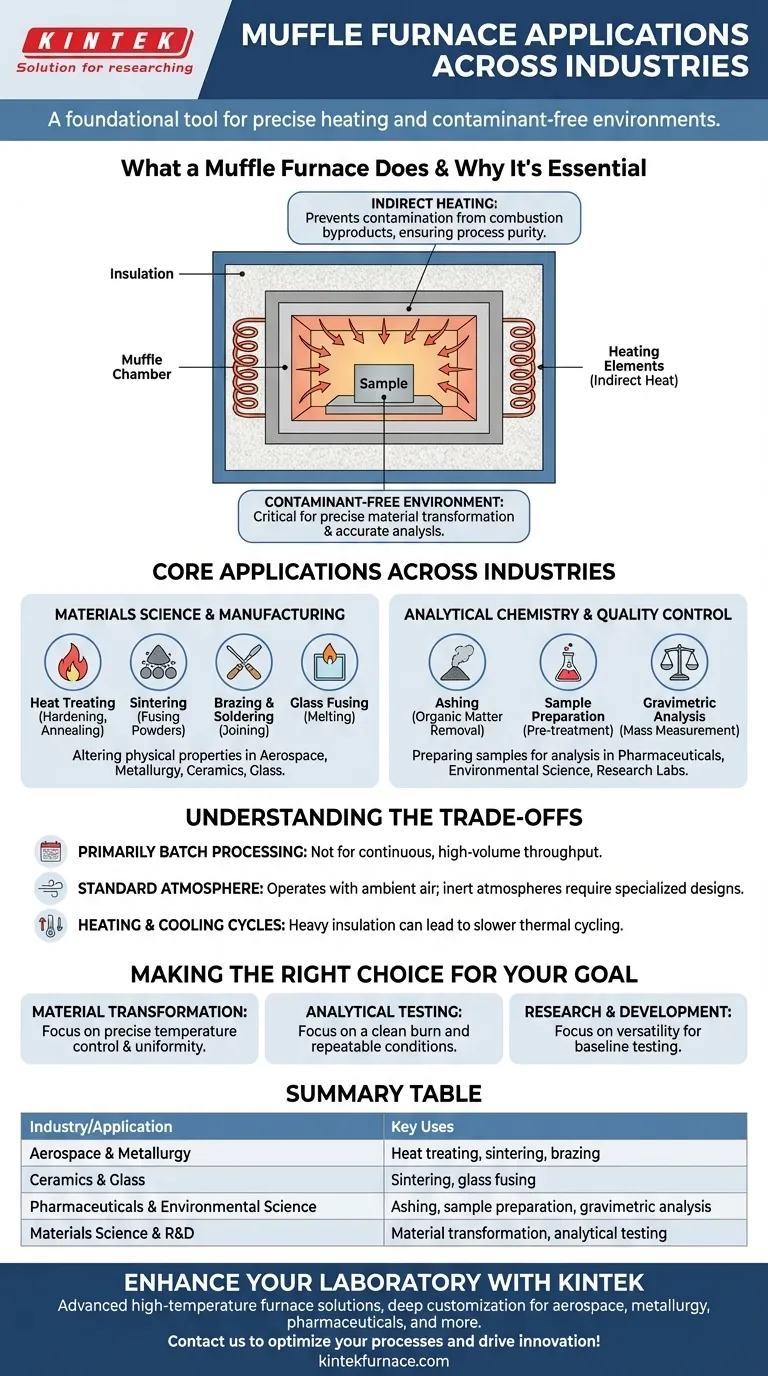
What a Muffle Furnace Does and Why It's Essential
At its core, a muffle furnace is a high-temperature oven. Its defining feature is the "muffle," an insulated inner chamber that contains the sample and separates it from the external heating elements.
The Principle of Indirect Heating
The heating elements (coils) heat the chamber from the outside. The heat then radiates inward to bake the sample.
This indirect heating prevents contamination from the byproducts of combustion, which would occur if a fuel-fired heat source were used directly. This separation is critical for achieving pure, repeatable results.
The Benefit of a Contaminant-Free Environment
By preventing exposure to flame or electrical elements, the muffle ensures that any changes to the sample are purely the result of heat.
This level of control is non-negotiable in scientific and quality control applications where even trace contaminants could invalidate results.
Core Applications Across Industries
The muffle furnace's simple yet critical function serves two primary purposes: transforming materials through heat treatment and analyzing materials through decomposition.
Materials Science & Manufacturing
Industries like metallurgy, aerospace, ceramics, and glass manufacturing rely on muffle furnaces to alter the physical properties of materials.
Key processes include:
- Heat Treating: Hardening, annealing, or tempering metals to achieve desired strength and ductility.
- Sintering: Fusing ceramic or metal powders into a solid mass below their melting point.
- Brazing & Soldering: Joining components in a controlled, high-temperature environment.
- Glass Fusing: Creating art or functional glass pieces by melting them together.
Analytical Chemistry & Quality Control
In pharmaceuticals, environmental science, and research laboratories, the furnace is used to prepare samples for analysis. The goal here is to break a material down to its essential components.
Common applications include:
- Ashing: Burning off all organic matter to determine the non-combustible ash content of a sample. This is critical in food, coal, plastics, and paint quality control.
- Sample Preparation: Pre-treating samples for further analysis, such as in drug testing or water quality analysis.
- Gravimetric Analysis: Measuring a sample's change in mass after heating.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While versatile, the muffle furnace is not the solution for every heating application. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Primarily for Batch Processing
Muffle furnaces are designed for small-batch or individual sample processing. They are not suited for the continuous, high-volume throughput required in large-scale industrial manufacturing, where tunnel kilns or conveyor ovens are used instead.
Standard Atmosphere Control
A standard muffle furnace operates with ambient air inside the chamber. While it prevents contamination from the heat source, it does not control the atmospheric gases themselves.
Processes that require an inert (e.g., argon, nitrogen) or reactive atmosphere demand specialized, more complex furnace designs.
Heating and Cooling Cycles
Due to their heavy insulation, muffle furnaces can have relatively slow heat-up and cool-down times. This can be a bottleneck in workflows that require rapid thermal cycling.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your specific application will determine which function of the muffle furnace is most important.
- If your primary focus is material transformation: You need a furnace with highly precise temperature control and uniformity to ensure consistent changes to your material's physical properties.
- If your primary focus is analytical testing: Your priority is a clean burn and repeatable conditions to accurately determine ash content or prepare samples for further chemical analysis.
- If your primary focus is research and development: You need a versatile furnace that provides a reliable baseline for testing new materials and processes on a small, controlled scale.
Ultimately, the muffle furnace serves as a cornerstone of material integrity, providing the pure thermal environment needed for discovery, creation, and quality assurance.
Summary Table:
| Industry/Application | Key Uses |
|---|---|
| Aerospace & Metallurgy | Heat treating, sintering, brazing |
| Ceramics & Glass | Sintering, glass fusing |
| Pharmaceuticals & Environmental Science | Ashing, sample preparation, gravimetric analysis |
| Materials Science & R&D | Material transformation, analytical testing |
Enhance your laboratory's capabilities with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide muffle, tube, rotary, vacuum, atmosphere furnaces, and CVD/PECVD systems tailored to your unique needs. Our deep customization ensures precise performance for industries like aerospace, metallurgy, and pharmaceuticals. Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can optimize your processes and drive innovation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the study of biochar regeneration and reuse? Unlock Sustainable Water Treatment
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating



















