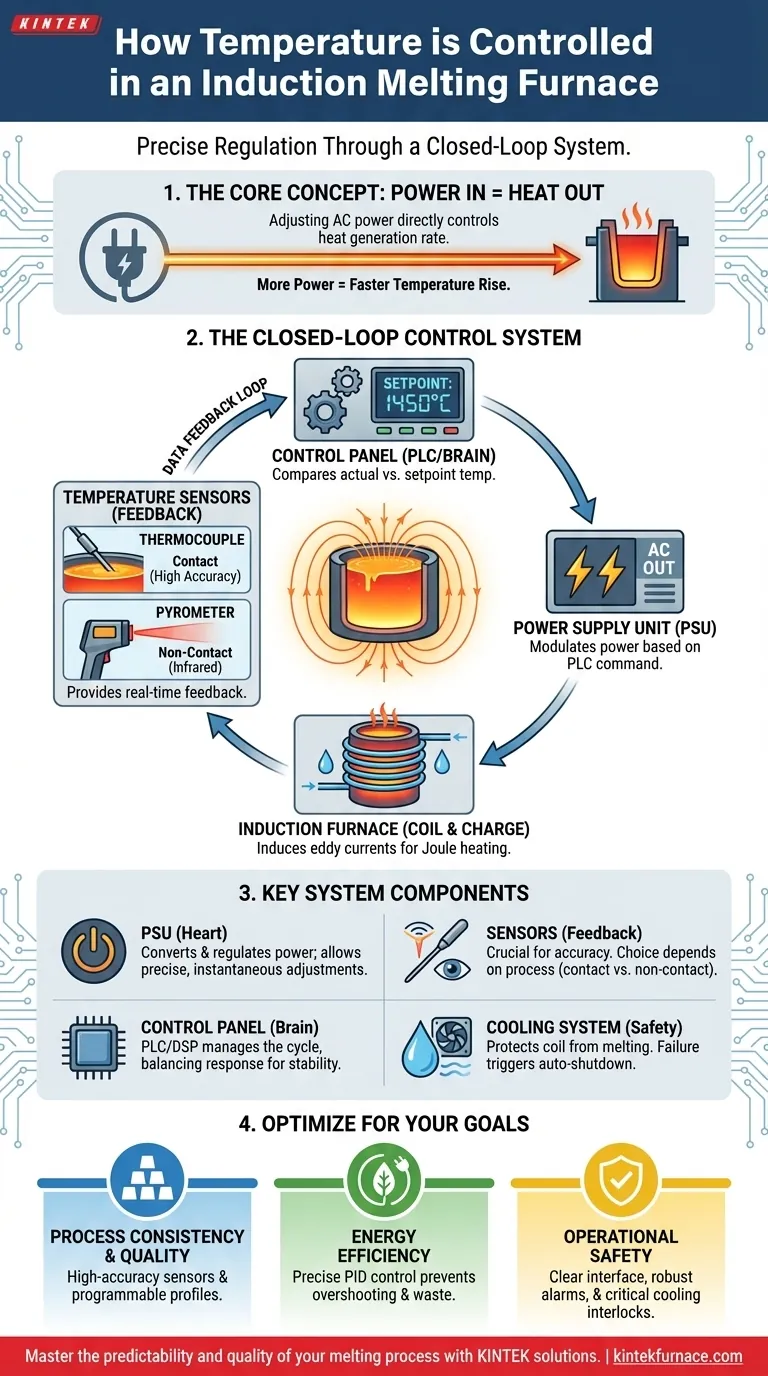
At its core, temperature control in an induction melting furnace is achieved by precisely regulating the amount of alternating current (AC) power sent to the induction coil. By increasing or decreasing the power input, an operator or an automated system directly controls the rate of heat generation within the metal charge. This allows for accurate melting and the ability to hold a specific temperature required for casting or alloying.
The direct mechanism for temperature control is adjusting electrical power. However, effective and precise control relies on a sophisticated closed-loop system where real-time temperature sensors provide constant feedback to a controller, which then automatically modulates the power supply to maintain the exact target temperature.

The Fundamental Principle: Power In Equals Heat Out
To understand temperature control, you must first understand how an induction furnace generates heat. The process is elegant and highly efficient, based on fundamental principles of physics.
How Induction Generates Heat
An induction furnace does not use any external heating elements. Instead, it passes a high-frequency alternating current through a water-cooled copper coil.
This current generates a powerful and rapidly changing magnetic field around the coil. When a conductive material like metal is placed inside this field, the magnetic field induces powerful electrical currents, known as eddy currents, within the metal itself.
The metal's natural electrical resistance fights against these eddy currents, generating immense heat through a process called Joule heating. This heat is produced directly inside the material, leading to rapid and uniform melting.
The Direct Link Between Power and Temperature
The amount of heat generated is directly proportional to the power supplied to the coil. More power creates a stronger magnetic field, which in turn induces stronger eddy currents, resulting in a faster temperature rise.
By carefully modulating the power output from the furnace's power supply unit, the system can ramp up to the melting point, hold a precise temperature for extended periods, or cool down in a controlled manner.
The Anatomy of a Modern Control System
While adjusting power is the method, it is the control system that provides the intelligence and precision needed for modern industrial processes. This is not a simple manual dial; it is a network of interconnected components.
The Power Supply Unit (PSU)
The PSU is the heart of the furnace. It takes standard utility power and converts it into the high-frequency AC current required for induction. Modern PSUs, often using IGBT technology, allow for instantaneous and highly precise adjustments to the power level, forming the basis of all temperature control.
The Temperature Sensor (The Feedback Loop)
To have a closed-loop system, the controller must know the actual temperature of the molten bath. This is typically accomplished using one of two methods:
- Thermocouple: A probe, often a Type K or S, is dipped directly into the molten metal for a highly accurate reading.
- Infrared Pyrometer: A non-contact sensor that measures the temperature by reading the infrared energy radiating from the surface of the melt.
This real-time temperature data is fed back to the control system, closing the feedback loop.
The Control Panel and PLC
The brain of the operation is the control panel, typically run by a Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) or a dedicated digital controller (DSP/ARM). This unit compares the actual temperature from the sensor to the desired setpoint temperature programmed by the operator.
If the temperature is too low, the PLC instructs the PSU to increase power. If it's too high, it reduces power. This constant cycle of measuring and adjusting happens many times per second, allowing for incredible stability.
The Cooling System's Indirect Role
While not a direct control mechanism, the closed-loop water cooling system is critical. It protects the induction coil from melting. A failure in the cooling system will trigger an automatic shutdown from the control panel, preventing catastrophic damage and ensuring safety.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Key Considerations
Achieving perfect temperature control involves balancing several competing factors. Understanding these trade-offs is crucial for optimizing any melting operation.
The Challenge of Temperature Uniformity
While induction heating is inherently uniform, large baths can still have minor temperature variations. The stirring action created by the magnetic field helps mix the metal and even out the temperature, but sensor placement is critical to ensure the reading represents the true average temperature.
Sensor Accuracy and Placement
Thermocouples provide a very accurate reading but are consumable and must be physically introduced into the melt, which can interrupt a process. Pyrometers are non-contact and convenient but can be affected by smoke, slag, or alloy composition on the surface, potentially leading to inaccurate readings.
Response Time vs. Stability
A system that reacts too quickly to temperature fluctuations can cause the power supply to constantly hunt or "overshoot" the setpoint, wasting energy and potentially stressing components. A well-tuned system balances a rapid response with smooth, stable power delivery to hold the temperature steady without constant, drastic adjustments.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The sophistication of your temperature control system should align with your operational priorities.
- If your primary focus is process consistency and quality: Invest in a closed-loop system with high-accuracy sensors and a PLC that allows for programmable melt profiles and data logging.
- If your primary focus is energy efficiency: A modern IGBT power supply paired with a precise PID control loop is essential to prevent temperature overshooting and minimize energy waste during holding periods.
- If your primary focus is operational safety and ease of use: Ensure the control panel has a clear interface, robust alarms, and interlocks tied to both temperature limits and the critical cooling system.
Ultimately, mastering temperature control is not just about managing heat; it is about mastering the predictability, efficiency, and quality of your entire melting process.
Summary Table:
| Control Component | Primary Function | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Power Supply Unit (PSU) | Converts and regulates power to the coil | Modern IGBT technology allows for precise, instantaneous adjustments |
| Temperature Sensor (Thermocouple/Pyrometer) | Provides real-time temperature feedback | Accuracy and placement are critical for reliable control |
| Control Panel (PLC) | Compares actual temperature to setpoint and adjusts power | Balances rapid response with stability to prevent overshooting |
| Cooling System | Protects the coil from overheating | An essential safety interlock; failure triggers shutdown |
Master the predictability and quality of your melting process with KINTEK solutions.
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse foundries and metallurgical labs with advanced induction melting solutions. Our product line, including Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, is complemented by strong deep customization capability to precisely meet your unique temperature control requirements—ensuring process consistency, energy efficiency, and operational safety.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can optimize your melting operations.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- How does vacuum melting technology contribute to sustainability? Boost Durability and Recycling Efficiency
- What is vacuum induction melting technology and why is it important? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications
- How does the Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) process work? Achieve Superior Metal Purity and Control
- Why is a Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace essential? Unlock Purity for Aerospace and Semiconductors
- What are the common applications of Vacuum Induction Melting? Essential for High-Performance Metals and Alloys



















