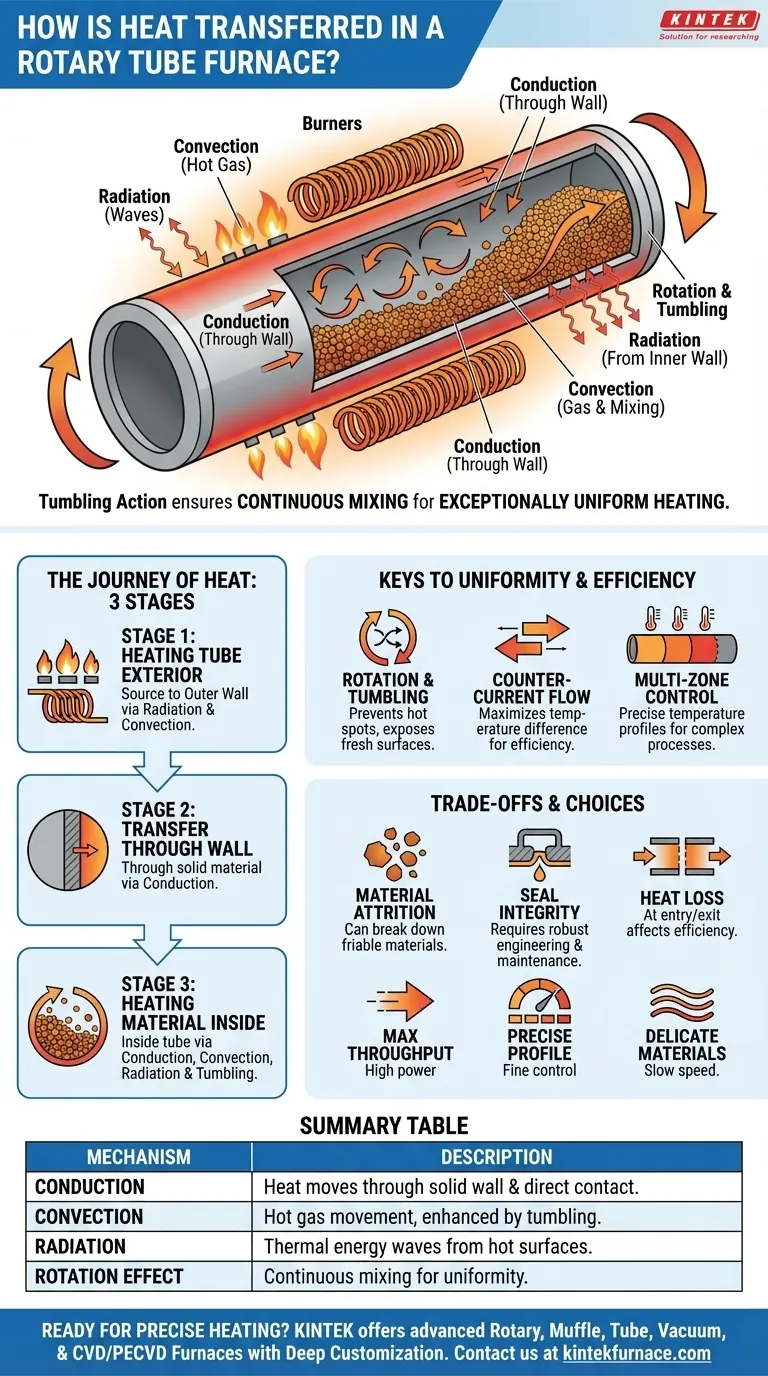
In a rotary tube furnace, heat is transferred from external heating elements or burners to the rotating tube wall, and then from the hot tube wall to the material inside. This process relies on a combination of conduction, convection, and radiation, with the tube's rotation ensuring the material is continuously mixed for exceptionally uniform heating.
The core challenge in heating bulk solids or powders is ensuring every particle reaches the target temperature without overheating. A rotary tube furnace solves this by combining multi-modal heat transfer with continuous mechanical agitation, creating an efficient and highly uniform thermal processing environment.
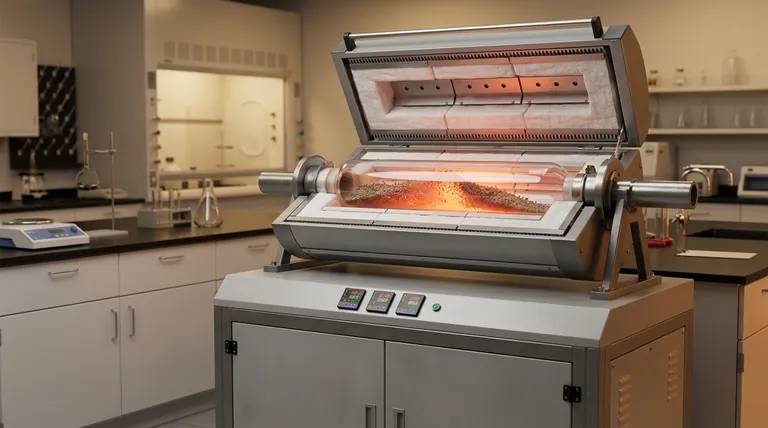

The Journey of Heat: From Source to Sample
To understand the furnace's effectiveness, we must trace the path of thermal energy from its origin to the material being processed. This occurs in three distinct stages.
Stage 1: Heating the Tube Exterior
The process begins with the heat source, which is typically electric heating elements or gas burners surrounding the furnace tube.
Heat is transferred from this source to the outer wall of the tube primarily through thermal radiation (energy traveling as electromagnetic waves) and convection (heat carried by the movement of hot air or combustion gases in the chamber).
Stage 2: Transfer Through the Tube Wall
Once the exterior of the tube is hot, that thermal energy must travel to the inner surface.
This transfer occurs almost entirely through conduction, as heat moves directly through the solid material of the tube wall, whether it is metal, quartz, or ceramic.
Stage 3: Heating the Material Inside the Tube
This is the most critical stage, where the furnace's design truly excels. The rotation of the tube facilitates three transfer mechanisms simultaneously.
- Conduction: Material in direct physical contact with the hot inner wall of the tube is heated by conduction.
- Convection: As the tube rotates, the material bed is lifted and tumbles. This constant mixing exposes new particles to the hot wall and allows them to move through any hot gas or controlled atmosphere inside the tube, facilitating convective heat transfer.
- Radiation: The hot inner surface of the tube radiates thermal energy directly to the surface of the material bed below it.
The continuous tumbling action is the key, ensuring that particles do not remain static, which would lead to poor heat distribution.
The Keys to Uniformity and Efficiency
The effectiveness of a rotary tube furnace is not just about the modes of heat transfer, but how the design manipulates them to achieve specific goals.
The Role of Rotation and Tumbling
The primary purpose of rotation is to ensure uniform heating. By constantly lifting and mixing the material, the furnace prevents hot spots and ensures that every particle is exposed to the heat sources over time.
This agitation continuously presents a fresh surface layer of material for heating, dramatically increasing the overall rate and evenness of the process compared to a static bed.
The Advantage of Counter-Current Flow
In many industrial designs, the heating gases are made to flow in the opposite direction of the material's travel (counter-current).
This configuration is highly efficient because it maintains the largest possible temperature difference between the hot gas and the cooler material along the entire length of the furnace, maximizing the rate of heat exchange.
Multi-Zone Control for Precision
Advanced furnaces are often divided into multiple, independently controlled heating zones along the tube's length.
This allows operators to create a precise temperature profile, enabling complex processes that require specific heating, soaking, and cooling rates as the material travels through the furnace.
Understanding the Inherent Trade-offs
While highly effective, the design of a rotary tube furnace presents practical challenges that must be managed.
Material Attrition
The tumbling action that ensures uniform heating can also cause friable or delicate materials to break down, creating dust or altering particle size. The rotation speed and fill level must be carefully optimized to minimize this effect.
Atmosphere and Seal Integrity
Maintaining a perfectly sealed, controlled atmosphere (like inert gas or vacuum) is more complex than in a static furnace. The rotating seals at the inlet and outlet are points of potential mechanical failure and leakage that require robust engineering and regular maintenance.
Heat Loss at Entry and Exit
The openings at the feed and discharge ends, along with the seals, can be significant sources of heat loss. This can impact overall energy efficiency and make it more difficult to control the temperature profile at the very ends of the tube.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
The optimal use of a rotary tube furnace depends entirely on your primary processing goal.
- If your primary focus is maximum throughput: Prioritize a design with efficient counter-current gas flow and high-power heating zones to drive heat transfer as quickly as possible.
- If your primary focus is a precise temperature profile: Select a furnace with multiple, independently controlled heating zones and fine control over the tube's rotation speed.
- If your primary focus is processing delicate materials: Carefully control the rotation speed and tilt angle to achieve a gentle cascading motion rather than a hard tumble, minimizing attrition.
Ultimately, the rotary tube furnace excels by transforming a static heating problem into a dynamic one, using mechanical motion to achieve unparalleled thermal uniformity.
Summary Table:
| Heat Transfer Mechanism | Description |
|---|---|
| Conduction | Heat moves through solid tube wall and direct contact with material. |
| Convection | Hot gases or air transfer heat via movement, enhanced by material tumbling. |
| Radiation | Thermal energy radiates from hot surfaces to material as electromagnetic waves. |
| Rotation Effect | Ensures continuous mixing for uniform heating and efficiency. |
Ready to achieve precise and uniform heating in your lab? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Rotary Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Tube Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. With strong deep customization capabilities, we tailor our products to meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can enhance your material processing efficiency and results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What materials can be used to make the rotating tube assembly of these furnaces? Choose the Best for Your High-Temp Needs
- What factors should be considered when selecting a tube for a rotary tube furnace? Ensure Optimal Performance and Longevity
- What is the purpose of the rotation mechanism in a rotary tube furnace? Achieve Uniform Heating and Enhanced Process Control
- What is the basic construction of a rotary tube furnace? Key Components for Uniform Heating
- What are the common approaches to mixing in rotary furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Efficiency in Thermal Processing



















