Grain growth in MoSi2 heating elements is prevented by introducing small amounts of specific additive elements during manufacturing. These additives intentionally disrupt the material's crystal structure, creating different commercial grades of Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2), each optimized to resist grain growth under different operating temperatures and conditions.
While MoSi2 offers exceptional performance at high temperatures, its natural tendency for crystals to grow leads to brittleness and premature failure. The solution is metallurgical control, where specific alloying additives are used to "pin" the crystal grain boundaries, preserving the element's structural integrity.
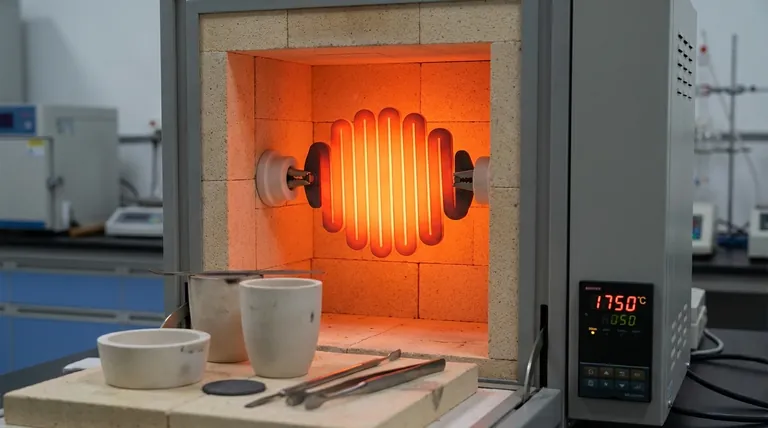

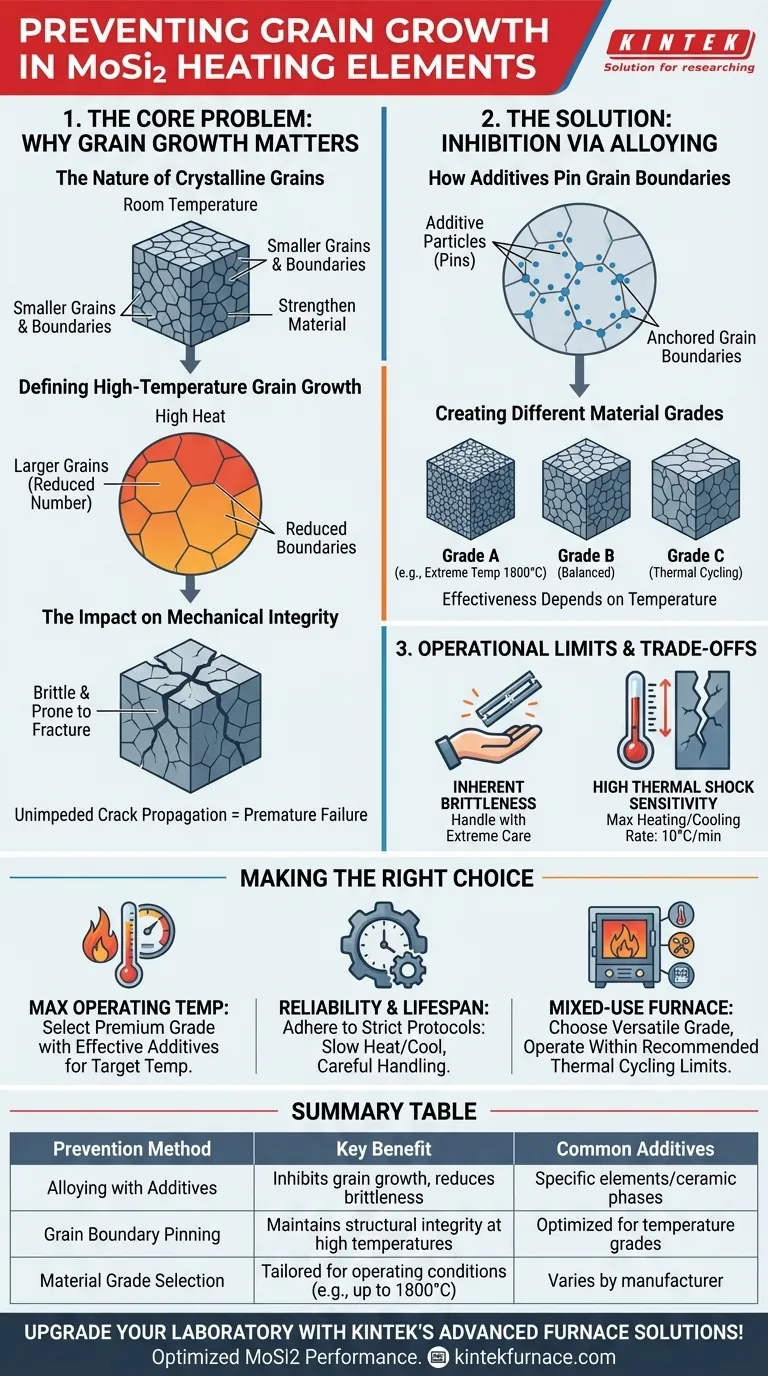
The Core Problem: Why Grain Growth Matters
MoSi2 heating elements are prized for their ability to operate at very high temperatures in oxidizing atmospheres. This is possible because they form a protective, self-healing layer of glassy silica (SiO2) on their surface. However, their underlying crystalline structure presents a significant engineering challenge.
The Nature of Crystalline Grains
Like many metals and ceramics, MoSi2 is a polycrystalline material, meaning it is composed of many small, individual crystals called grains. These grains are randomly oriented and meet at interfaces known as grain boundaries.
At room temperature, these boundaries help strengthen the material. However, at the high operating temperatures MoSi2 is designed for, the atoms have enough energy to move.
Defining High-Temperature Grain Growth
This atomic mobility allows larger grains to grow by consuming their smaller neighbors. This process, known as grain growth or coarsening, reduces the total number of grains in the material, resulting in a structure with fewer, but much larger, individual crystals.
The Impact on Mechanical Integrity
A structure with large grains is significantly more brittle and prone to fracture. The grain boundaries act as obstacles that impede the propagation of microscopic cracks.
When there are fewer boundaries due to grain growth, a crack can travel a longer distance unimpeded, leading to catastrophic failure of the heating element. This phenomenon is a primary cause of reduced element lifespan.
The Solution: Inhibition via Alloying
To counteract this inherent weakness, manufacturers modify the composition of the MoSi2 material itself. This is a far more effective strategy than simply controlling the operating environment.
How Additives Pin Grain Boundaries
The primary method for preventing grain growth is the introduction of small amounts of other elements or ceramic phases. These additives are carefully selected to migrate to the grain boundaries.
Once at the boundaries, these additive particles act as physical "pins." They anchor the grain boundaries in place, dramatically increasing the energy required for them to move and thereby stopping larger grains from consuming smaller ones.
Creating Different Material Grades
There is no single additive that works for all situations. The effectiveness of a grain growth inhibitor depends heavily on temperature.
This has led to the development of different grades of MoSi2. Some grades are designed with additives that are most effective at extreme temperatures (e.g., 1800°C), while others are optimized for longevity in slightly less demanding thermal cycling applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Operational Limits
Even with advanced material engineering, MoSi2 elements possess fundamental characteristics that require careful management. Understanding these limitations is critical for successful operation.
Inherent Brittleness
Even with grain growth properly controlled, MoSi2 is an exceptionally brittle ceramic material, particularly at room temperature. The elements must be handled with extreme care during shipping, installation, and furnace maintenance to prevent fracture.
High Sensitivity to Thermal Shock
The material has very low resistance to thermal shock. Rapid heating or cooling induces internal stresses that can easily cause the element to crack.
Most manufacturers recommend a maximum heating and cooling rate of no more than 10°C per minute, especially when passing through lower temperature ranges where the material is less ductile.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting and operating MoSi2 elements requires balancing material science with operational discipline.
- If your primary focus is maximum operating temperature: You must select a premium MoSi2 grade specifically engineered with additives that effectively inhibit grain growth at your target temperature.
- If your primary focus is reliability and lifespan: You must adhere to strict operational protocols, including slow, controlled heating/cooling rates and exceptionally careful handling, to mitigate the material's inherent brittleness.
- If your primary focus is managing a mixed-use furnace: Choose a versatile, high-quality grade and always operate within the recommended thermal cycling limits to prevent premature failure.
By understanding the interplay between material composition and operational care, you can maximize the performance and lifespan of your MoSi2 heating elements.
Summary Table:
| Prevention Method | Key Benefit | Common Additives |
|---|---|---|
| Alloying with additives | Inhibits grain growth, reduces brittleness | Specific elements/ceramic phases |
| Grain boundary pinning | Maintains structural integrity at high temperatures | Optimized for temperature grades |
| Material grade selection | Tailored for operating conditions (e.g., up to 1800°C) | Varies by manufacturer |
Upgrade your laboratory's high-temperature capabilities with KINTEK's advanced furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with tailored high-temperature furnace systems, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, such as optimizing MoSi2 heating element performance for enhanced durability and efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can drive your research forward!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is silicon carbide resistant to chemical reactions in industrial furnaces? Unlock Durable High-Temp Solutions
- Why are SiC heating elements considered environmentally friendly? Discover Their Eco-Efficiency & Lifespan Insights
- What are the advantages of using high purity green silicon carbide powder in heating elements? Boost Efficiency and Lifespan
- Why are silicon carbide heating elements essential in high-temperature industries? Unlock Reliable, Extreme Heat Solutions
- What makes silicon carbide heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Protective Oxide Layer



















