In research and development, furnace brazing is a fundamental tool for material innovation and advanced prototyping. It is used to study material behavior under precisely controlled thermal conditions, develop novel joining techniques for dissimilar materials, and create functional prototypes of complex components for testing and validation.
The true value of furnace brazing in R&D lies in its precision. The ability to control the heating, cooling, and atmospheric environment allows researchers to isolate variables and reliably test the limits of new materials and designs.

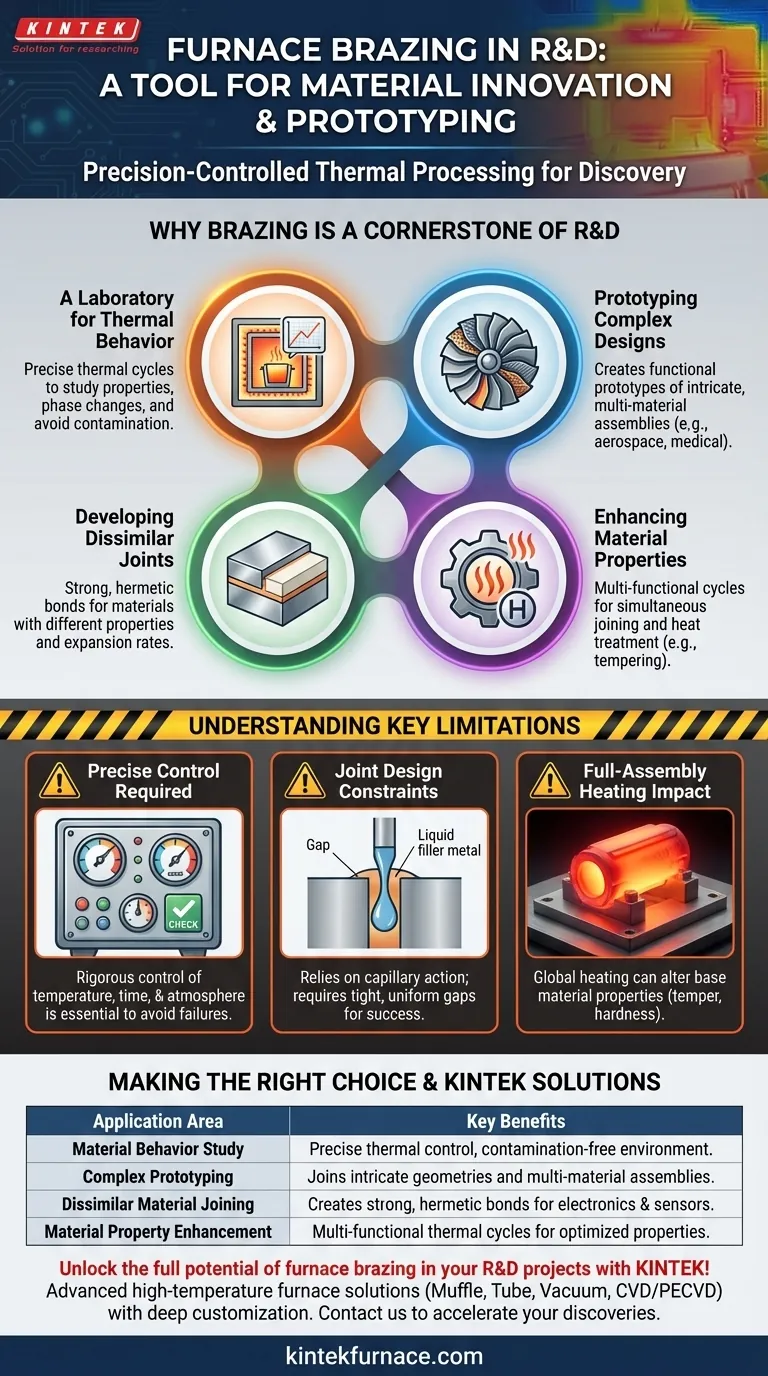
Why Brazing is a Cornerstone of R&D
Furnace brazing provides a controlled environment that is essential for experimentation and discovery. This makes it an indispensable process for pushing the boundaries of material science and engineering design.
A Laboratory for Thermal Behavior
In R&D, understanding how a material behaves when heated is critical. A brazing furnace acts as a high-temperature laboratory, enabling researchers to execute precise thermal cycles.
This controlled heating and cooling allows for the study of material properties, phase changes, and the effects of heat treatment without atmospheric contamination, which is crucial for developing and validating new alloys.
Prototyping Complex and Multi-Material Designs
Many advanced components, from aerospace turbine blades to medical implants, feature intricate geometries and are made from multiple materials.
Furnace brazing excels at joining these complex assemblies. It enables the creation of fully functional prototypes that would be impossible to machine from a single piece, allowing for realistic performance testing early in the development cycle.
Developing Joints for Dissimilar Materials
A significant challenge in engineering is joining materials with different properties, such as metals to ceramics or alloys with different thermal expansion rates.
Furnace brazing is a primary method for tackling this problem. R&D in electronics, for example, relies on brazing to develop new sensors and semiconductor packages by creating strong, hermetic bonds between these dissimilar materials.
Enhancing Material Properties
The furnace brazing process isn't just for joining; it's also used for material optimization. The controlled thermal cycle can be engineered to serve multiple purposes.
For instance, a single furnace run can be designed to braze a tool-steel assembly while also tempering it to achieve a specific hardness and wear resistance. This multi-function capability is explored extensively in R&D to improve manufacturing efficiency.
Understanding the Key Limitations
While powerful, furnace brazing is a highly technical process with specific constraints that must be understood and managed, especially in an experimental R&D context.
The Requirement for Precise Control
Success in furnace brazing depends on rigorous control over temperature, time, and atmosphere (e.g., vacuum or a specific gas).
Minor deviations can lead to failed joints, undesirable metallurgical changes in the base materials, or damaged components. This demands significant process expertise, especially when working with new or unproven materials.
Joint Design Constraints
The process relies on capillary action to draw the molten filler metal into the joint. This requires a specific, uniform, and very narrow gap between the parts being joined.
Designs must be created with these tight clearances in mind from the start. This can limit geometric freedom compared to other joining methods like welding.
The Impact of Full-Assembly Heating
Unlike welding, which applies localized heat, furnace brazing heats the entire assembly to the filler metal's melting temperature.
This global heating can alter the properties of the base materials, such as their temper or hardness. Researchers must carefully plan the thermal cycle to ensure the final component meets all material specifications, not just the joint strength.
Making the Right Choice for Your R&D Goal
How you leverage furnace brazing depends entirely on your research objective.
- If your primary focus is new material discovery: Use the controlled furnace environment to test the bondability, thermal stability, and heat treatment response of novel alloys and composites.
- If your primary focus is functional prototyping: Leverage brazing to create complex, multi-material assemblies for performance testing, particularly for components like heat exchangers, sensors, or medical devices.
- If your primary focus is process innovation: Employ furnace brazing to develop and refine joining techniques for high-performance applications, optimizing for strength, leak-tightness, and efficiency.
Ultimately, mastering furnace brazing provides a powerful capability to transform theoretical material science into tangible, high-performance innovations.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Key Benefits |
|---|---|
| Material Behavior Study | Precise thermal control, contamination-free environment for alloy development |
| Complex Prototyping | Joins intricate geometries and multi-material assemblies for realistic testing |
| Dissimilar Material Joining | Creates strong, hermetic bonds for electronics and sensors |
| Material Property Enhancement | Multi-functional thermal cycles for optimized hardness and efficiency |
Unlock the full potential of furnace brazing in your R&D projects with KINTEK! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored for material innovation and prototyping. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental needs. From studying material behavior to developing complex prototypes, KINTEK furnaces ensure precise control and reliability. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can accelerate your discoveries and bring your innovations to life!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is inert gas technology used for in high-temperature atmosphere vacuum furnaces? Protect Materials and Speed Up Cooling
- How does the pressure range change under vacuum conditions in an atmosphere box furnace? Explore Key Shifts for Material Processing
- What are the key features of an atmosphere box furnace? Unlock Precise Heat Processing in Controlled Environments
- What are some specific applications of atmosphere furnaces in the ceramics industry? Enhance Purity and Performance
- Can box type high-temperature resistance furnaces control the atmosphere? Unlock Precision in Material Processing



















