In essence, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is a sophisticated process used to apply high-performance thin films onto a surface, known as a substrate. It achieves this by introducing precursor gases into a reaction chamber where they decompose and react on the substrate's surface, forming a solid, highly adherent coating. This technique is widely used to create protective or decorative layers for applications ranging from cutting tools and optics to biomedical implants and glass.
The true value of CVD is not just in applying a layer, but in fundamentally engineering a new surface. It excels at creating exceptionally uniform and durable films that conform perfectly to even the most complex shapes, enhancing a material's inherent properties.

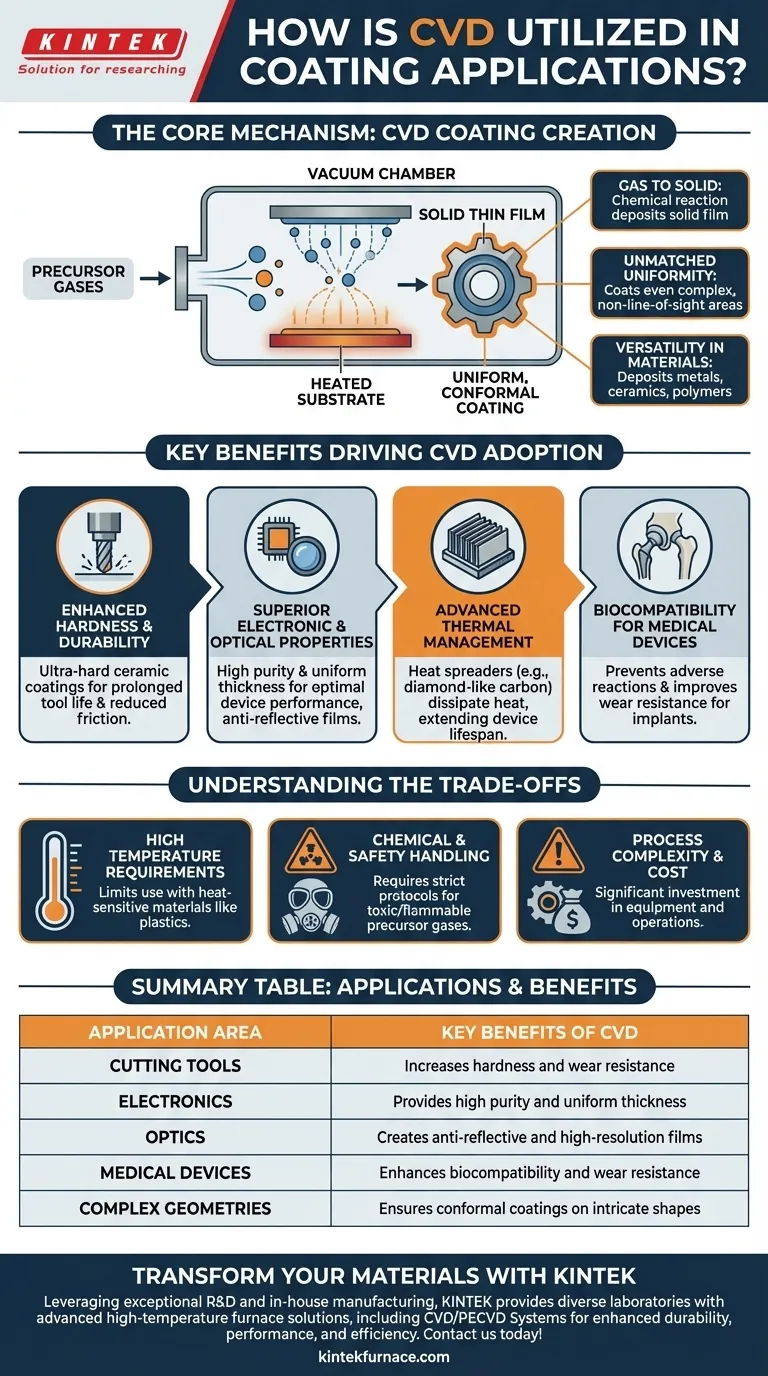
The Core Mechanism: How CVD Creates a Coating
To understand CVD's utility, you must first understand its fundamental process. It is a controlled chemical reaction that builds a coating atom by atom or molecule by molecule.
From Gas to Solid
The process begins by introducing one or more volatile precursor gases into a vacuum chamber containing the substrate. When these gases reach the heated substrate, they undergo a chemical reaction or decomposition, leaving behind a solid material that deposits onto the surface. This creates a thin, dense, and solid film.
Unmatched Uniformity
A key advantage of CVD is its ability to produce highly conformal coatings. Because the deposition occurs from a gas phase, the precursor molecules can reach every part of the substrate's surface, including complex, non-line-of-sight areas. This results in a coating of uniform thickness, even on intricate shapes.
Versatility in Materials
CVD is not limited to a single type of material. The process is incredibly versatile and can be used to deposit a wide range of substances, including metals, hard ceramics (like titanium nitride), and even specific polymers, simply by changing the precursor gases.
Key Benefits Driving CVD Adoption
The choice to use CVD is driven by the significant performance enhancements it delivers. The resulting coatings provide functional benefits that are critical in high-technology fields.
Enhanced Hardness and Durability
For applications like cutting tools and industrial components, CVD is used to deposit ultra-hard ceramic coatings. These layers dramatically increase surface hardness and reduce friction, leading to significantly prolonged tool life and superior performance under extreme conditions.
Superior Electronic and Optical Properties
In the semiconductor industry, CVD is essential for building the microscopic layers that form integrated circuits. The process provides the high purity and uniform thickness needed for optimal device performance. Similarly, for optical applications, CVD creates anti-reflective coatings or films that provide superior brightness and resolution.
Advanced Thermal Management
Certain CVD-deposited materials, such as diamond-like carbon, possess extremely high thermal conductivity. These coatings are used as heat spreaders in high-power electronics, effectively dissipating heat and extending the lifespan and reliability of the device.
Biocompatibility for Medical Devices
In biomedical applications, specific CVD coatings are used on implants and surgical tools. These films can enhance biocompatibility, preventing adverse reactions with the body, while also improving wear resistance for joint replacements and other medical hardware.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, CVD is not a universal solution. Its process parameters introduce specific constraints that must be considered.
High Temperature Requirements
Traditional CVD processes often require very high substrate temperatures (hundreds or even over a thousand degrees Celsius) to drive the necessary chemical reactions. This can limit the types of materials that can be coated, as many plastics or lower-melting-point metals cannot withstand the heat.
Chemical and Safety Handling
The precursor gases used in CVD can be highly toxic, flammable, or corrosive. Implementing a CVD process requires significant investment in safety protocols, gas handling infrastructure, and exhaust treatment systems to ensure safe operation.
Process Complexity and Cost
CVD systems are complex machines involving vacuum chambers, precise gas flow controllers, and heating systems. The initial capital investment and operational costs can be substantial, making the process best suited for high-value applications where the performance benefits justify the expense.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a coating technology depends entirely on your end goal. CVD offers distinct advantages for specific, high-performance needs.
- If your primary focus is mechanical durability: CVD excels at creating ultra-hard, wear-resistant coatings that dramatically extend the life of tools and components.
- If your primary focus is advanced electronics or optics: The process provides the unparalleled purity and uniformity required for high-performance semiconductor and optical films.
- If your primary focus is coating complex geometries: CVD's conformal nature ensures a consistent film thickness even on the most intricate surfaces, where other methods would fail.
By understanding its principles and benefits, you can leverage CVD not just as a coating method, but as a transformative surface engineering process.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Key Benefits of CVD |
|---|---|
| Cutting Tools | Increases hardness and wear resistance for longer tool life |
| Electronics | Provides high purity and uniform thickness for optimal performance |
| Optics | Creates anti-reflective and high-resolution films |
| Medical Devices | Enhances biocompatibility and wear resistance for implants |
| Complex Geometries | Ensures conformal coatings on intricate shapes |
Transform your materials with precision coatings! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements for enhanced durability, performance, and efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how our CVD systems can elevate your applications!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition
- Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
People Also Ask
- How does plasma enhanced CVD work? Achieve Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What are the main components of a PECVD system? Unlock Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What gases are used in the PECVD system? Optimize Thin Film Deposition with Precise Gas Selection
- What is PECVD equipment? A Guide to Low-Temperature Thin-Film Deposition
- What role does PECVD play in optical coatings? Essential for Low-Temp, High-Precision Film Deposition



















