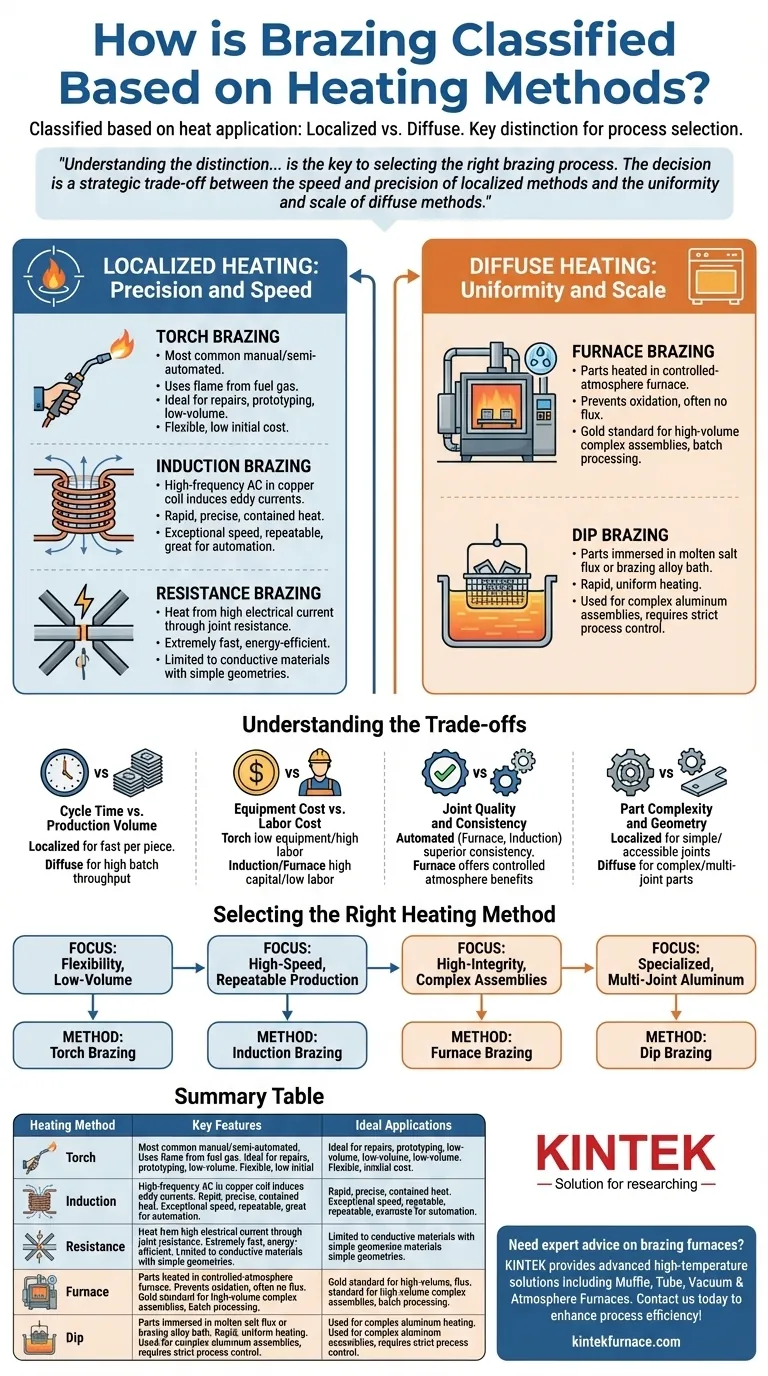
Brazing processes are classified based on how heat is applied to the assembly. The two primary categories are localized heating, which concentrates energy only at the joint area, and diffuse heating, where the entire part or assembly is brought up to brazing temperature. This fundamental choice between a focused or a holistic approach dictates everything from production speed and equipment cost to the final quality and integrity of the joint.
Understanding the distinction between localized and diffuse heating is the key to selecting the right brazing process. The decision is a strategic trade-off between the speed and precision of localized methods and the uniformity and scale of diffuse methods.

Localized Heating: Precision and Speed
Localized heating methods are ideal for applications where heat must be applied quickly and contained to a specific area. This prevents heat damage to the surrounding assembly and allows for faster processing of individual parts.
Torch Brazing
Torch brazing is the most common manual or semi-automated method, using a flame from a fuel gas (like acetylene or propane) mixed with oxygen or air. It is highly versatile and requires relatively low initial investment.
The primary advantage of torch brazing is its flexibility for repairs, prototyping, and low-volume production. However, its quality is highly dependent on operator skill, and there is a risk of inconsistent heating or localized overheating.
Induction Brazing
This method uses a high-frequency alternating current passed through a custom-designed copper coil. The coil induces eddy currents within the part, generating rapid, precise, and contained heat exactly at the joint line.
Induction brazing is prized in high-volume manufacturing for its exceptional speed and repeatability. Once set up, it produces extremely consistent results with minimal operator input, making it perfect for automation.
Resistance Brazing
Resistance brazing generates heat by passing a high electrical current through the joint area, using the components' natural resistance to create thermal energy. The parts are typically held between two electrodes.
This process is extremely fast and energy-efficient but is generally limited to joining electrically conductive materials with relatively simple, overlapping joint geometries.
Diffuse Heating: Uniformity and Scale
Diffuse heating methods are used when the entire assembly must be heated uniformly to avoid thermal stress or when the part has multiple or complex joints that are inaccessible to localized methods.
Furnace Brazing
In furnace brazing, parts are pre-assembled with the filler metal placed at the joints and then heated in a controlled-atmosphere furnace. The protective atmosphere (e.g., nitrogen, hydrogen, or a vacuum) prevents oxidation, often eliminating the need for flux.
This method is the gold standard for high-volume production of complex assemblies, as it can braze hundreds or thousands of joints simultaneously. It produces clean, strong, and stress-relieved parts of the highest quality.
Dip Brazing
Dip brazing involves immersing the pre-assembled parts into a bath of molten salt flux or, less commonly, a bath of the molten brazing alloy itself. The bath provides rapid, uniform heating and fluxes the entire assembly.
This technique is predominantly used for complex aluminum assemblies like heat exchangers, where it can join many intricate, hard-to-reach joints at once. It requires strict process control to manage the corrosive flux and ensure part cleanliness.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Localized vs. Diffuse
Choosing between these two families of processes involves balancing competing priorities of speed, cost, quality, and part complexity.
Cycle Time vs. Production Volume
Localized methods like induction offer the fastest cycle time per piece. However, diffuse methods like furnace brazing deliver a higher overall throughput for large batches, as thousands of parts can be processed in a single furnace cycle.
Equipment Cost vs. Labor Cost
Torch brazing has a low initial equipment cost but a high recurring labor cost and dependency on skilled operators. In contrast, induction and furnace brazing require significant capital investment but offer low labor costs and high automation potential.
Joint Quality and Consistency
Automated diffuse and localized methods (furnace, induction) provide superior consistency and repeatability compared to manual torch brazing. Furnace brazing adds the significant benefit of a controlled atmosphere, which prevents oxidation and results in cleaner, stronger joints without flux.
Part Complexity and Geometry
Localized methods are best for simple, accessible joints on a larger assembly. Diffuse methods are the only viable option for parts with many joints, complex internal geometries, or a need to minimize thermal distortion across the entire component.
Selecting the Right Heating Method for Your Application
Your choice should be guided by your specific project goals and manufacturing environment.
- If your primary focus is flexibility and low-volume work: Torch brazing offers unmatched versatility and low setup costs for repairs and prototypes.
- If your primary focus is high-speed, repeatable production: Induction brazing delivers exceptional speed and consistency for automated manufacturing lines.
- If your primary focus is high-integrity, complex assemblies: Furnace brazing provides the highest quality, stress-free results for batch production.
- If your primary focus is specialized, multi-joint aluminum components: Dip brazing is the industry-standard method for ensuring complete and uniform joint formation.
By matching the heating method to the demands of the part and production scale, you can ensure a reliable, efficient, and cost-effective joining process.
Summary Table:
| Heating Method | Key Features | Ideal Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Torch Brazing | Manual, flexible, low equipment cost | Repairs, prototyping, low-volume production |
| Induction Brazing | Automated, fast, precise, repeatable | High-volume manufacturing, automation |
| Resistance Brazing | Fast, energy-efficient, limited to conductive materials | Simple, overlapping joint geometries |
| Furnace Brazing | Uniform heating, controlled atmosphere, high-quality joints | Complex assemblies, high-volume batch production |
| Dip Brazing | Immersive heating, uniform, flux-based | Aluminum assemblies, multiple intricate joints |
Need expert advice on selecting the right brazing furnace for your lab? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. With strong deep customization capabilities, we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements for brazing and beyond. Contact us today to enhance your process efficiency and joint quality!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering and Brazing Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1200℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What are the key features of an atmosphere box furnace? Unlock Precise Heat Processing in Controlled Environments
- What is an atmosphere protection muffle furnace? Unlock Precise Heat Treatment in Controlled Environments
- What are the primary inert gases used in vacuum furnaces? Optimize Your Heat Treatment Process
- How does the pressure range change under vacuum conditions in an atmosphere box furnace? Explore Key Shifts for Material Processing
- What are some specific applications of atmosphere furnaces in the ceramics industry? Enhance Purity and Performance



















