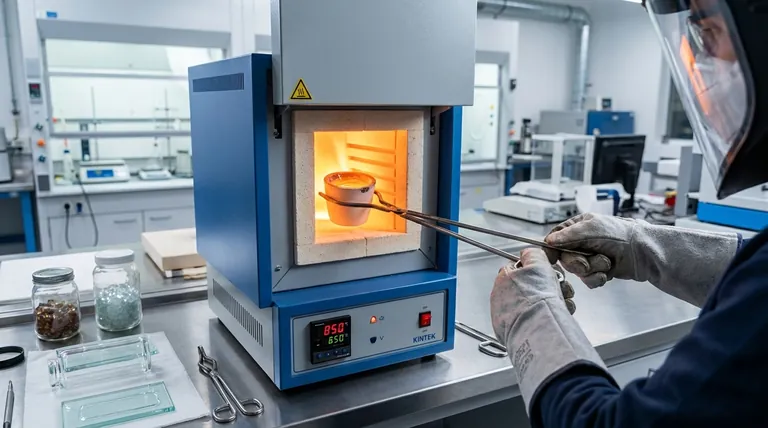
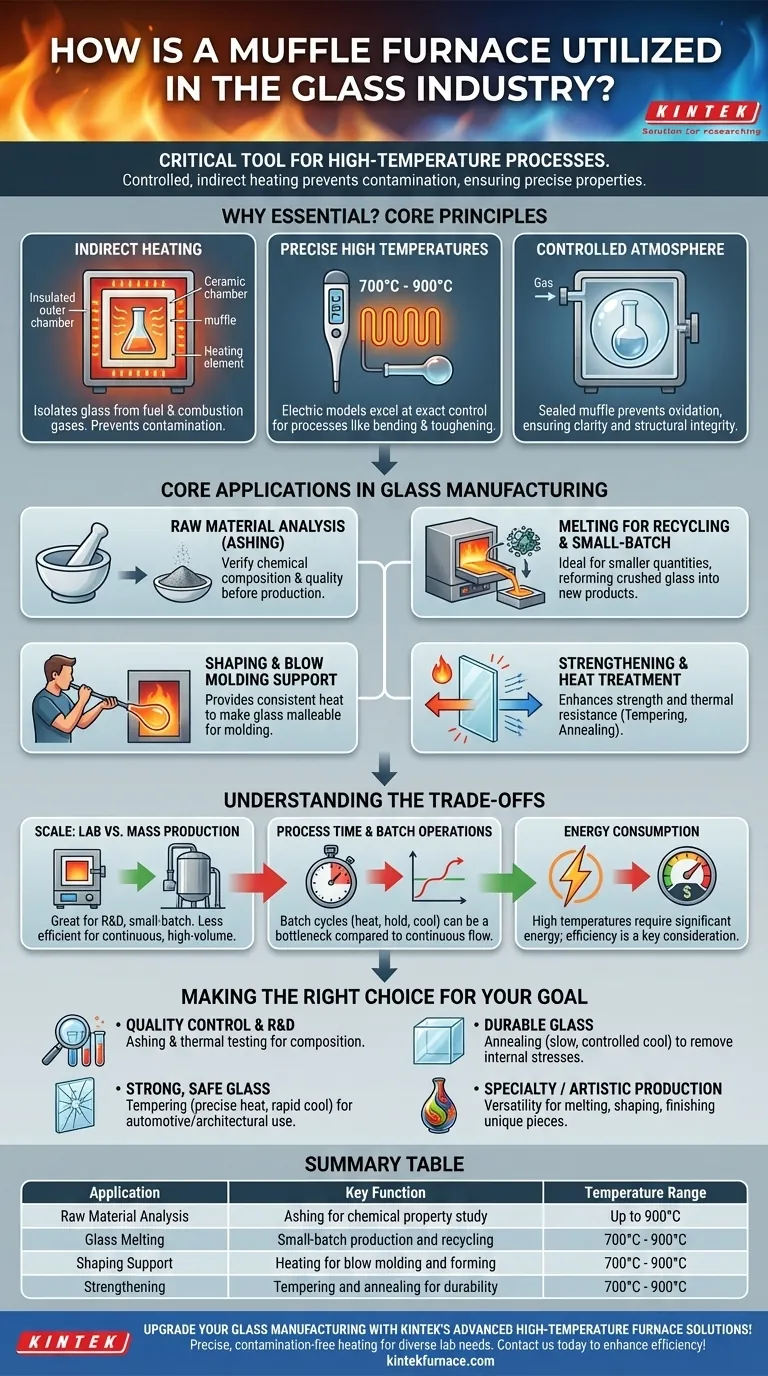
In the glass industry, a muffle furnace is a critical tool for a range of high-temperature processes. Its primary functions include analyzing the chemical properties of raw materials, melting glass for recycling or small-batch production, supporting shaping operations like blow molding, and strengthening the final product through controlled heat treatment.
The core value of a muffle furnace lies in its ability to create a highly controlled, high-temperature environment. By heating the glass indirectly, it prevents contamination from combustion byproducts, which is essential for achieving the specific chemical and structural properties required in modern glass manufacturing.

What Makes a Muffle Furnace Essential?
A muffle furnace operates on a simple but powerful principle that makes it indispensable for precision work with sensitive materials like glass.
The Principle of Indirect Heating
A muffle furnace contains an insulated outer chamber that heats an inner chamber, or "muffle." The material inside the muffle is heated by thermal radiation and convection, never by direct flame.
This separation is crucial. It isolates the glass from fuel, combustion gases, and other contaminants that could cause defects or alter the glass's chemical composition.
Achieving Precise High Temperatures
Glass production demands exact temperature control. Muffle furnaces, especially electric models, excel at reaching and maintaining the high temperatures needed, typically between 700°C and 900°C, for processes like bending and toughening.
Controlling the Atmosphere
Because the muffle is a sealed chamber, the atmosphere inside can be tightly controlled. This is a key feature of atmosphere furnaces, a category to which muffle furnaces belong. Controlling the atmosphere prevents unwanted oxidation on the glass surface, ensuring clarity and structural integrity.
Core Applications in Glass Manufacturing
The muffle furnace is not a single-purpose tool. It plays a role at multiple stages of the glass lifecycle, from initial design to final strengthening.
Raw Material Analysis and Quality Control
Before production begins, muffle furnaces are used to analyze raw materials. By converting a sample into ash (ashing), technicians can study its chemical properties and composition, ensuring the material meets quality standards for the intended product.
Melting for Recycling and Small-Batch Production
While large-scale production uses massive industrial furnaces, muffle furnaces are ideal for melting smaller quantities of glass. This is particularly common in glass recycling, where batches of cullet (crushed glass) are melted down to be reformed into new products.
Shaping and Blow Molding Support
The furnace provides the consistent heat needed for shaping processes like blow molding. Glass is heated until it becomes malleable, allowing it to be molded or blown into a desired shape, from simple bottles to complex artistic forms.
Strengthening and Heat Treatment
Perhaps the most critical application is heat treatment to enhance glass strength and thermal resistance. This involves heating the glass to a precise temperature before cooling it under controlled conditions.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the muffle furnace is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Scale: Lab vs. Mass Production
Muffle furnaces are ideal for laboratory R&D, quality control, and small-batch or artistic production. However, their batch-based nature and size make them less efficient for the continuous, high-volume melting required in mass production, where larger tank furnaces are used.
Process Time and Batch Operations
Each cycle in a muffle furnace involves heating, holding at temperature, and cooling. This batch processing can be time-consuming compared to the continuous flow of a large industrial furnace, creating a bottleneck in high-throughput environments.
Energy Consumption
Reaching and maintaining temperatures of 900°C requires significant electrical energy. While modern furnaces are increasingly efficient, energy cost remains a primary operational consideration, especially for larger units or continuous use.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The specific use of a muffle furnace depends entirely on the desired outcome for the glass.
- If your primary focus is quality control and R&D: Use the furnace for ashing and thermal testing to verify raw material composition and predict performance.
- If your primary focus is creating strong, safe glass: Master the process of tempering, using the furnace's precise heat and a rapid cooling phase to create high-strength products for automotive or architectural use.
- If your primary focus is removing internal stresses for durability: Implement a slow, controlled cooling cycle known as annealing to produce stable and workable glass.
- If your primary focus is specialty or artistic production: Leverage the furnace's versatility for melting, shaping, and finishing unique, small-batch glass pieces.
Ultimately, the muffle furnace empowers glassmakers with the precise thermal control needed to transform a raw material into a finished product with purpose and durability.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Function | Temperature Range |
|---|---|---|
| Raw Material Analysis | Ashing for chemical property study | Up to 900°C |
| Glass Melting | Small-batch production and recycling | 700°C - 900°C |
| Shaping Support | Heating for blow molding and forming | 700°C - 900°C |
| Strengthening | Tempering and annealing for durability | 700°C - 900°C |
Upgrade your glass manufacturing with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with precise, contamination-free heating for processes like recycling, shaping, and strengthening. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to enhance your lab's efficiency and achieve superior glass quality!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How is a laboratory muffle furnace utilized during the debinding stage of HAp green bodies? Precision Thermal Control
- What are the advantages of muffle furnaces in terms of energy efficiency and heating speed? Achieve Fast, Efficient Heat Processing
- What is a box furnace and what are its other names? Discover Its Key Uses and Benefits
- What role does a muffle furnace play in 600°C carbonization of palm shells? Unlock High-Performance Activated Carbon
- What role does heating equipment play in the synthesis of PdPc? Mastering Precision Thermal Fusion
- What is the function of a high-temperature muffle furnace in g-C3N4 synthesis? Optimize Your Photocatalyst Production
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the post-treatment of cobalt-based catalysts? Optimize Phase Purity via Annealing
- How is a muffle furnace utilized in ash testing? Achieve Accurate Mineral Analysis for Your Lab



















