In any high-performance laboratory, a muffle furnace is primarily used for sample preparation by subjecting materials to extremely high, controlled temperatures. The most common application is ashing, a process that completely burns off organic substances to isolate the non-combustible, inorganic components left behind for analysis. It is also used for high-temperature drying and removing other volatile impurities.
To prepare a sample for many types of analysis, you must first remove interfering substances like organic matter and water. A muffle furnace accomplishes this with precision by creating an isolated, high-temperature environment that purifies the sample without introducing contamination from the heating elements themselves.
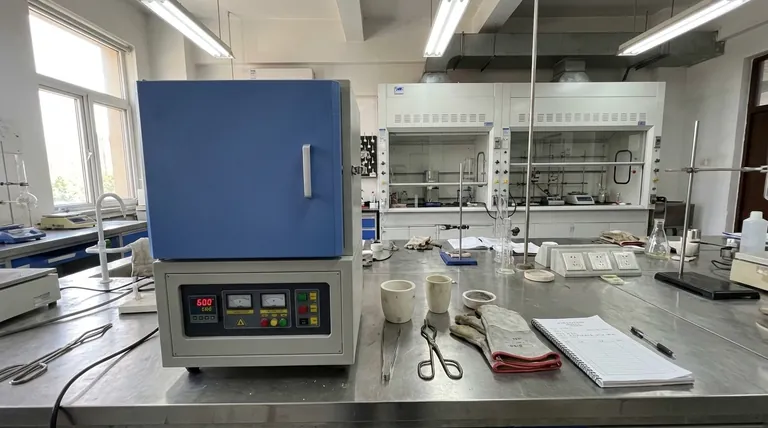

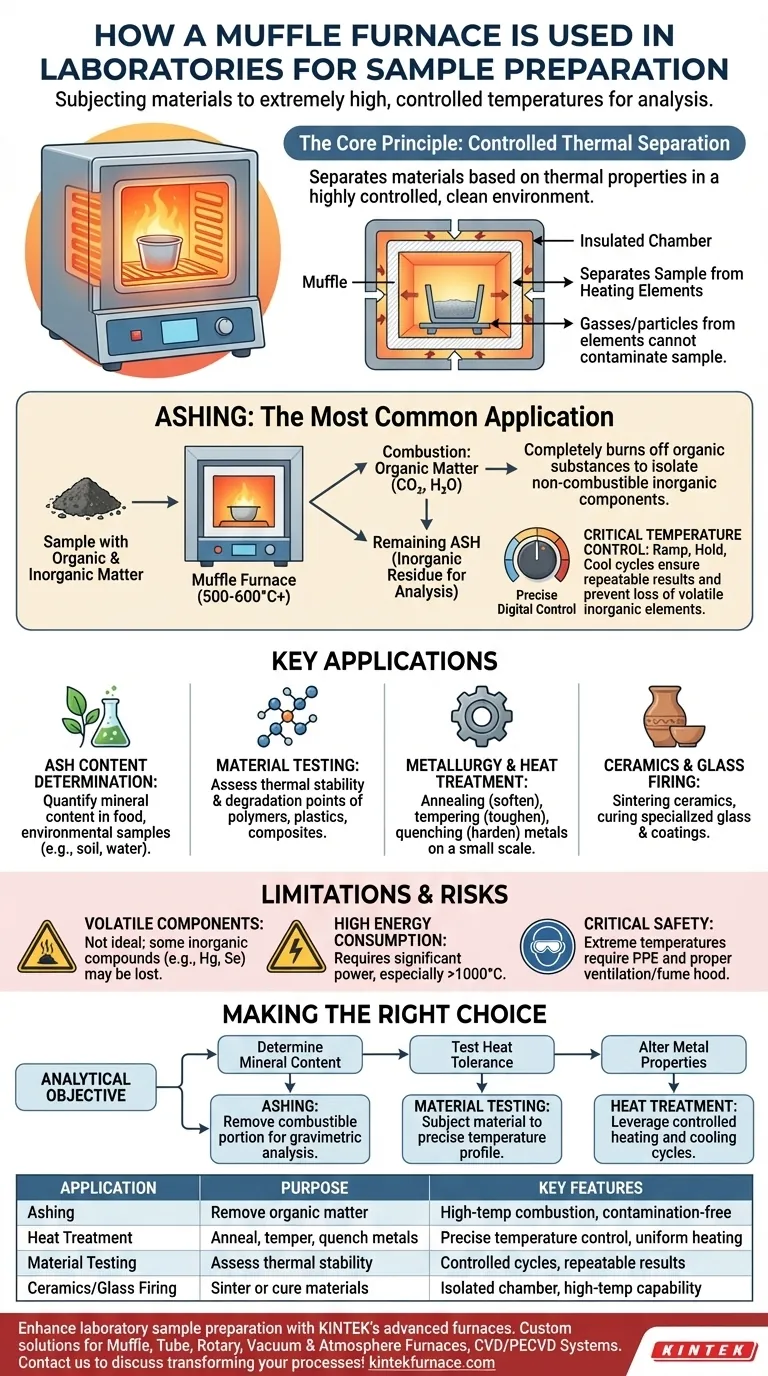
The Core Principle: Controlled Thermal Separation
At its heart, a muffle furnace is an instrument designed to achieve one fundamental goal: separating materials based on their thermal properties. It does this within a highly controlled and clean environment.
What Makes it a "Muffle" Furnace?
The defining feature is the muffle, an insulated inner chamber that holds the sample. This chamber separates the material from the actual heating elements.
This design is critical because it prevents contamination. Gasses or particles from the heating elements cannot come into contact with the sample, ensuring the integrity of the analysis.
The Goal of Ashing
Ashing is the most frequent use of a muffle furnace in sample preparation. The objective is to heat a sample to a temperature (typically 500-600°C or higher) where all organic matter combusts and turns into carbon dioxide and water.
What remains is the ash—the inorganic residue, such as minerals, salts, and metallic compounds. This allows for the precise measurement of a sample's inorganic content.
Why Temperature Control is Critical
Different materials combust or transform at different temperatures. A muffle furnace provides precise digital control over the heating process, including the rate of temperature increase, the hold time at a peak temperature, and the cooling profile.
This precision is essential for repeatable results and prevents the loss of volatile inorganic elements that could be driven off if the temperature were too high or uncontrolled.
Key Applications in Laboratory Work
While ashing is central, the controlled environment of a muffle furnace makes it a versatile tool for several high-temperature tasks.
Ash Content Determination
This is a standard quantitative test in many industries. For example, food scientists ash samples to determine mineral content, and environmental labs ash soil or water residue to analyze for heavy metals.
Material Testing and Analysis
Researchers use muffle furnaces to test how materials like polymers, plastics, and composites behave under extreme heat. This helps determine their thermal stability, degradation points, and fire resistance.
Metallurgy and Heat Treatment
On a smaller, laboratory scale, muffle furnaces are used to heat-treat metals. Processes like annealing (softening metal), tempering (increasing toughness), and quenching (hardening) can be performed with high precision.
Ceramics and Glass Firing
The furnace is used for sintering ceramics, a process where powdered material is heated to create a solid object. It is also used for firing and curing specialized glass and coatings.
Understanding the Limitations and Risks
While powerful, a muffle furnace is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to using it correctly.
Not Ideal for Volatile Components
The high heat that makes ashing effective can be a drawback if you need to analyze for volatile inorganic compounds (like mercury or selenium), which can be lost during the process.
High Energy Consumption
Reaching temperatures of 1000°C or more requires a significant amount of electrical energy. This makes them one of the more power-intensive pieces of equipment in a lab.
Critical Safety Protocols
Operating a muffle furnace involves extreme temperatures. Proper personal protective equipment (PPE), such as heat-resistant gloves and safety glasses, is mandatory. Furthermore, because the process can release fumes, the furnace must be operated in a well-ventilated area or under a fume hood.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The specific use of a muffle furnace depends entirely on your analytical objective.
- If your primary focus is determining mineral content in organic matter: You will use the furnace for ashing to completely remove the combustible portion of your sample for gravimetric analysis.
- If your primary focus is testing the heat tolerance of a new polymer: You will use the furnace to subject the material to a precise temperature profile and observe its structural changes or degradation.
- If your primary focus is altering the properties of a small metal component: You will use heat treatment processes like annealing or tempering, leveraging the furnace's controlled heating and cooling cycles.
Ultimately, a muffle furnace is a tool for purification and transformation, enabling precise analysis by controllably removing everything you don't want to measure.
Summary Table:
| Application | Purpose | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Ashing | Remove organic matter to isolate inorganic ash | High-temperature combustion, contamination-free |
| Heat Treatment | Anneal, temper, or quench metals | Precise temperature control, uniform heating |
| Material Testing | Assess thermal stability and degradation | Controlled heating cycles, repeatable results |
| Ceramics/Glass Firing | Sinter or cure materials | Isolated chamber, high-temperature capability |
Enhance your laboratory's sample preparation with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnaces! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse labs with tailored solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, boosting efficiency and accuracy. Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can transform your processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the biomass carbonization process? Achieve Precise Biochar Production
- What is the primary function of a muffle furnace for BaTiO3? Master High-Temp Calcination for Ceramic Synthesis



















