In heat treatment, a muffle furnace is used to execute critical processes like annealing, hardening, tempering, and normalizing. It does this by heating materials, typically metals and alloys, to precise temperatures in a highly controlled environment. This targeted heating fundamentally alters the material's internal structure to achieve desired properties such as increased hardness, improved ductility, or greater strength.
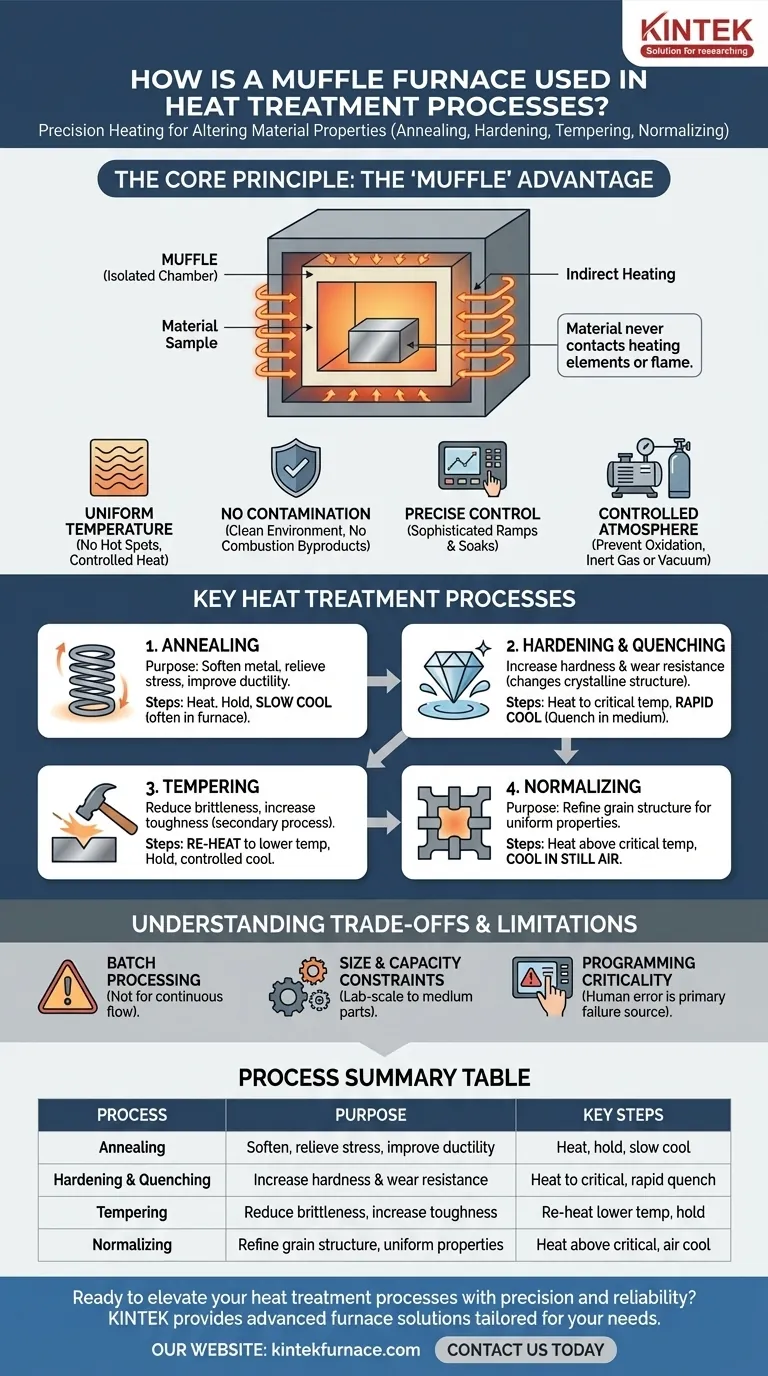
The defining feature of a muffle furnace isn't just its ability to reach high temperatures, but its use of an isolated chamber—the "muffle"—to provide extremely uniform, controlled heat. This separation between the heating elements and the material is what makes predictable and repeatable changes to a material's properties possible.
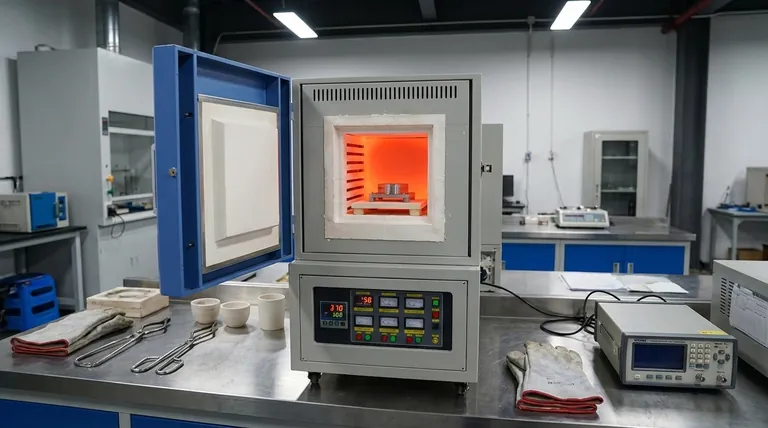

The Core Principle: Why a 'Muffle' is Critical
The term "muffle" refers to the furnace's design, which is central to its function in high-precision applications. Understanding this principle explains why it is a superior choice for heat treatment over simpler ovens.
What is a Muffle?
A muffle is an enclosed chamber, often made of ceramic, that contains the material being heated. This chamber is then heated from the outside by heating elements.
The material inside the muffle never comes into direct contact with the flame or heating elements.
The Benefit of Indirect Heating
This indirect heating method ensures exceptionally uniform temperature across the entire sample. There are no "hot spots" that could cause inconsistent results.
It also prevents contamination of the material from combustion byproducts (in fuel-fired models) or direct radiation damage from electric elements.
Achieving Precise Temperature Control
Modern muffle furnaces are equipped with sophisticated digital controllers. Combined with the uniform heating environment, this allows for very precise and stable temperature ramps and soaks.
This level of control is non-negotiable for heat treatment, where a deviation of even a few degrees can ruin the outcome.
Controlling the Atmosphere
Because the muffle is a sealed chamber, the atmosphere inside can be controlled. Air can be evacuated to create a vacuum or replaced with an inert gas like argon or nitrogen.
This prevents oxidation and scaling on the material's surface, which is crucial for maintaining surface finish and dimensional accuracy.
Key Heat Treatment Processes in a Muffle Furnace
A muffle furnace's precision makes it ideal for the most common metallurgical processes. Each process follows a specific heating and cooling profile to produce a different result.
Annealing
The goal of annealing is to soften metal, relieve internal stresses, and improve its ductility (ability to be deformed without fracturing).
This involves heating the material to a specific temperature, holding it there, and then cooling it very slowly, often by leaving it inside the furnace as it cools.
Hardening & Quenching
Hardening increases a metal's resistance to deformation and wear. The material is heated to a critical temperature to change its crystalline structure.
It is then rapidly cooled, or quenched, in a medium like water, oil, or air. This speed is what locks in the hard, brittle structure.
Tempering
A hardened part is often too brittle for practical use. Tempering is a secondary process used to reduce that brittleness and increase toughness.
The hardened part is re-heated to a much lower temperature and held for a specific time. This carefully relieves some of the internal stress from the hardening process.
Normalizing
Normalizing is used to refine the grain structure of a metal, making its mechanical properties more uniform and predictable. It creates a consistent baseline state before further hardening or machining.
The process involves heating the material above its critical temperature and then cooling it in still air, which is faster than annealing but slower than quenching.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, a muffle furnace is not the solution for every scenario. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Batch Processing vs. Continuous Flow
Muffle furnaces are batch processors. You load a part or a set of parts, run the cycle, and then unload them.
They are not suited for continuous, assembly-line-style manufacturing where parts are constantly moving through a heating zone. Other furnace designs, like tunnel or belt furnaces, serve that purpose.
Size and Capacity Constraints
Most muffle furnaces are designed for laboratory-scale work or the treatment of small- to medium-sized components.
Treating very large or heavy industrial parts requires massive, purpose-built industrial furnaces that may or may not use a muffle design.
The Critical Role of Programming
The primary source of failure in heat treatment is often human error, not equipment failure. An incorrect temperature, hold time, or cooling rate will produce the wrong material properties.
Successful heat treatment depends entirely on programming the correct thermal profile for the specific alloy and the desired outcome.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your choice of heat treatment process is dictated entirely by the final properties your material needs to have.
- If your primary focus is to soften metal and improve ductility: Annealing is your required process, demanding a slow, controlled cool-down.
- If your primary focus is to maximize hardness and wear resistance: You will use a hardening and quenching cycle, which requires rapid cooling.
- If your primary focus is to reduce brittleness in a hardened part: Tempering is the necessary follow-up step, using lower, precise temperatures.
- If your primary focus is to refine the grain structure for uniform properties: Normalizing provides a consistent baseline for further treatment or use.
Ultimately, the muffle furnace serves as the precise instrument needed to reliably perform these metallurgical transformations.
Summary Table:
| Process | Purpose | Key Steps |
|---|---|---|
| Annealing | Soften metal, relieve stress, improve ductility | Heat to specific temperature, hold, slow cool in furnace |
| Hardening & Quenching | Increase hardness and wear resistance | Heat to critical temperature, rapid cool (quench) in medium |
| Tempering | Reduce brittleness, increase toughness in hardened parts | Re-heat to lower temperature, hold for specific time |
| Normalizing | Refine grain structure for uniform properties | Heat above critical temperature, cool in still air |
Ready to elevate your heat treatment processes with precision and reliability? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored for laboratories and industrial applications. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can enhance your material properties and efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the study of biochar regeneration and reuse? Unlock Sustainable Water Treatment
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure
- What is the primary function of a muffle furnace for BaTiO3? Master High-Temp Calcination for Ceramic Synthesis



















