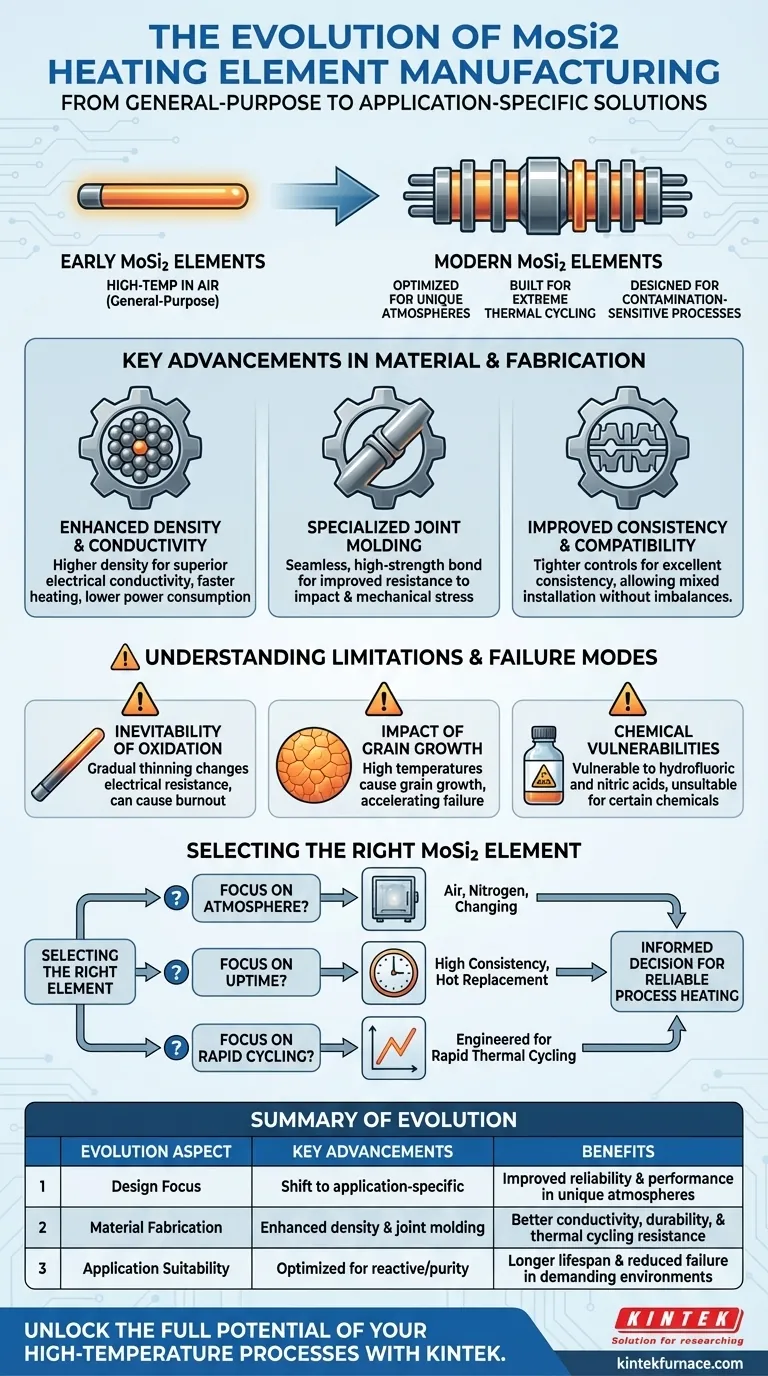
At its core, the manufacturing technology of Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂) heating elements has evolved from producing general-purpose components to engineering highly specialized solutions for specific industrial challenges. This progression has dramatically improved element reliability, performance, and operational lifetime in demanding high-temperature environments.
The most significant advancement in MoSi₂ element technology is not just higher temperature ratings, but the development of application-specific designs. Modern manufacturing focuses on optimizing elements for unique atmospheres, thermal cycling conditions, and process purity requirements, moving far beyond a one-size-fits-all approach.

From General-Purpose to Application-Specific Design
Early MoSi₂ elements were revolutionary for their high-temperature capabilities in air. However, modern industrial processes present far more complex challenges. The evolution of manufacturing has been a direct response to these needs, creating specialized elements that thrive where older designs would fail.
Optimized for Reactive Atmospheres
Modern elements are now engineered to perform reliably at high temperatures in reactive atmospheres, such as nitrogen. This required advancements in material composition and surface technology to prevent degradation that would occur with standard elements.
Built for Extreme Thermal Cycling
Processes involving rapid heating and cooling place immense stress on heating elements. New manufacturing techniques create elements specifically for laboratory and high-temperature sintering furnaces, ensuring they withstand rapid thermal cycling without premature failure.
Designed for Contamination-Sensitive Processes
In industries like semiconductor or medical device manufacturing, even trace contamination from a heating element can be catastrophic. Specialized, high-purity MoSi₂ elements are now produced to ensure process integrity in these sensitive applications.
Key Advancements in Material and Fabrication
This evolution in application is underpinned by tangible improvements in how MoSi₂ elements are made. These changes enhance both their physical durability and electrical performance.
Enhanced Density and Conductivity
Modern fabrication processes achieve a higher material density in the finished element. This results in superior electrical conductivity, leading to a faster heating rate and lower overall power consumption for the furnace.
Specialized Joint Molding
The connection point between the hot zone and the cooler terminals is a common point of failure. Manufacturers have developed special joint molding processes that create a seamless, high-strength bond, dramatically improving the element's resistance to impact and mechanical stress during installation and operation.
Improved Consistency and Compatibility
Tighter manufacturing controls ensure excellent consistency from one element to the next. This allows new elements to be installed alongside older ones without causing electrical imbalances, a critical factor for ongoing furnace maintenance.
Understanding the Inherent Limitations and Failure Modes
Even with modern advancements, it is crucial to understand the fundamental physics that govern the life of a MoSi₂ element. Acknowledging these trade-offs is key to proper application and maintenance.
The Inevitability of Oxidation
The primary failure mode for MoSi₂ elements is gradual thinning due to oxidation over their service life. As the element thins, its electrical resistance changes, and it can eventually reach a point where the power density is too high, causing localized overheating and burnout.
The Impact of Grain Growth
At very high operating temperatures, the crystalline grains within the material can grow larger. This phenomenon, which can give the surface an "orange-peel" texture, contributes to the thinning process and can accelerate element failure.
Chemical Vulnerabilities
While highly resistant to most acids and alkalis, MoSi₂ elements have specific chemical weaknesses. They will be attacked and dissolved by hydrofluoric acid and nitric acid, making them unsuitable for processes where these chemicals are present.
Selecting the Right MoSi₂ Element for Your Process
Understanding this technological evolution allows you to make a more informed decision for your specific high-temperature application.
- If your primary focus is process atmosphere: Choose a modern element specifically designed and rated for your working environment, whether it's air, nitrogen, or a changing atmosphere.
- If your primary focus is maximum uptime: Select elements known for high consistency and a design that allows for replacement while the furnace is hot, minimizing production downtime.
- If your primary focus is rapid cycling: Prioritize elements explicitly engineered for rapid thermal cycling to ensure a long and predictable service life.
By matching the right element technology to your specific goal, you can fully leverage the advancements in MoSi₂ manufacturing for more reliable and efficient process heating.
Summary Table:
| Evolution Aspect | Key Advancements | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Design Focus | Shifted from general-purpose to application-specific | Improved reliability and performance in unique atmospheres |
| Material Fabrication | Enhanced density and specialized joint molding | Better conductivity, durability, and thermal cycling resistance |
| Application Suitability | Optimized for reactive atmospheres and contamination-sensitive processes | Longer lifespan and reduced failure in demanding environments |
Unlock the Full Potential of Your High-Temperature Processes with KINTEK
At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities. Whether you're in semiconductor, medical device manufacturing, or other demanding fields, we can design MoSi2 heating elements that precisely meet your unique experimental requirements for reliability, efficiency, and purity.
Contact us today to discuss how our specialized solutions can enhance your lab's performance and reduce downtime!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- How does the ultra-low oxygen environment of vacuum sintering affect titanium composites? Unlock Advanced Phase Control
- What tasks does a high-temperature vacuum sintering furnace perform for PEM magnets? Achieve Peak Density
- Why is a vacuum environment essential for sintering Titanium? Ensure High Purity and Eliminate Brittleness
- Why is a high-vacuum environment necessary for sintering Cu/Ti3SiC2/C/MWCNTs composites? Achieve Material Purity
- Why is a high vacuum essential for Ti-6Al-4V sintering? Protect Your Alloys from Embrittlement



















