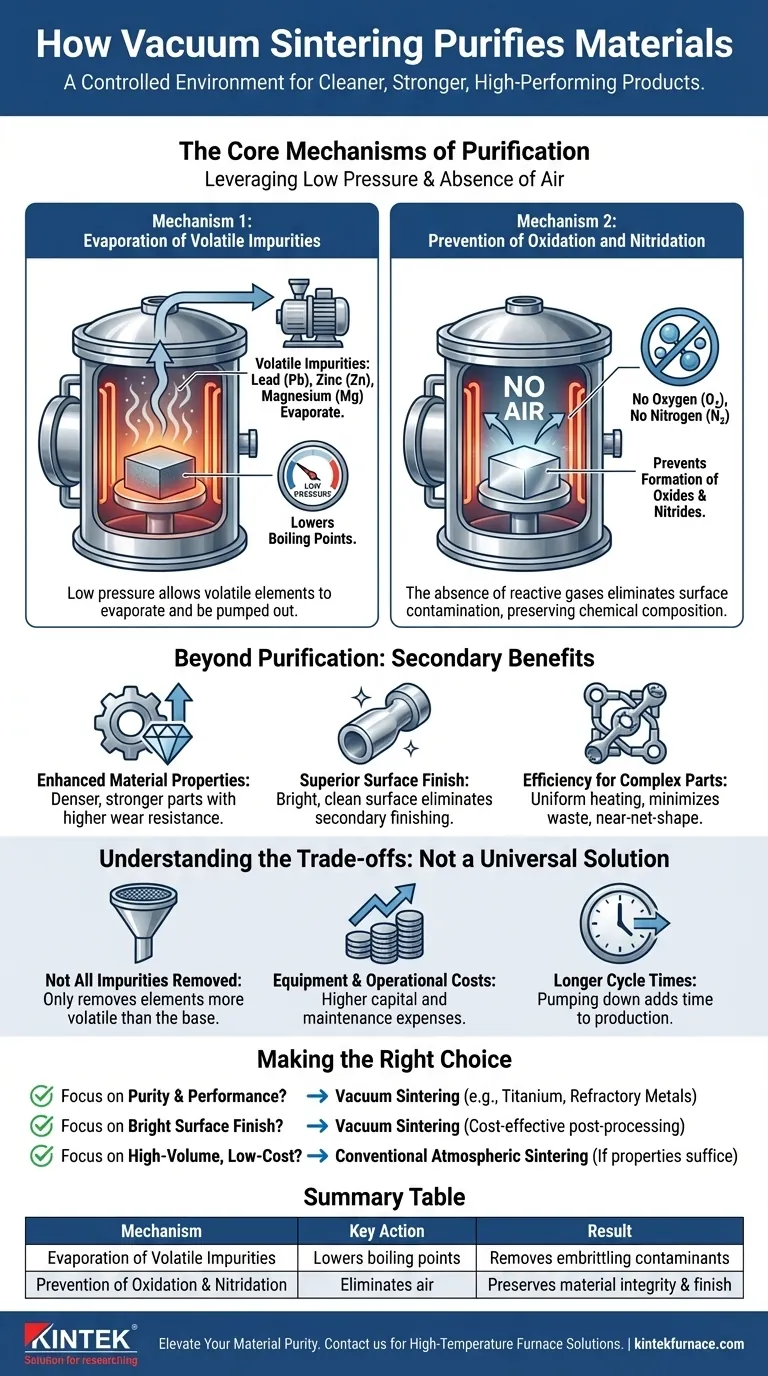
In short, vacuum sintering purifies materials through two primary actions. By operating under extremely low pressure, it allows volatile impurities like lead, zinc, and magnesium to evaporate out of the base material. Simultaneously, the absence of air prevents the formation of new impurities, such as oxides and nitrides, that would otherwise compromise the material's integrity and performance.
The power of vacuum sintering lies not in adding a purifying agent, but in creating a controlled environment. This environment actively removes unwanted elements and prevents contamination, resulting in a fundamentally cleaner, stronger, and higher-performing final product.
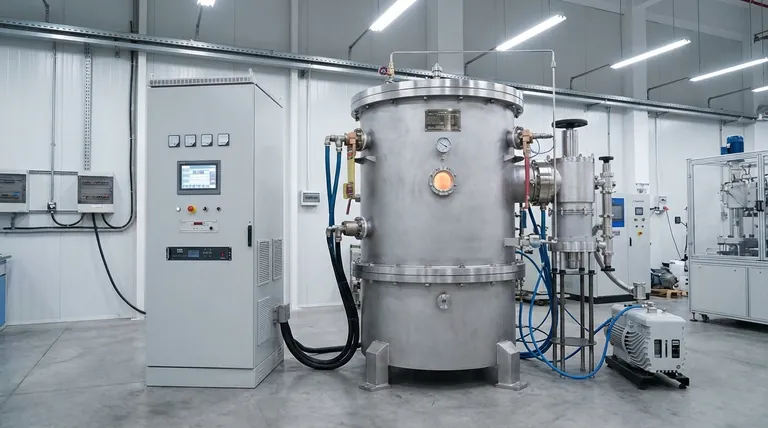

The Core Mechanisms of Purification
To understand the value of vacuum sintering, you must first understand the physics at play. The process leverages the vacuum environment in two distinct ways to achieve a purer material.
Mechanism 1: Evaporation of Volatile Impurities
Under normal atmospheric pressure, every material has a specific boiling point. A key principle of vacuum physics is that lowering the pressure also lowers a material's boiling point.
Vacuum sintering exploits this by creating an environment where impurities with high volatility (a tendency to evaporate) are encouraged to turn into a gas at temperatures well below the melting point of the primary material.
Elements such as lead (Pb), zinc (Zn), and magnesium (Mg) are common contaminants that are highly volatile. The vacuum effectively "sucks" these evaporated impurities out of the furnace, physically removing them from the final part.
Mechanism 2: Prevention of Oxidation and Nitridation
Many high-performance metals and alloys are highly reactive with gases present in the air, especially oxygen and nitrogen.
When heated in a conventional furnace, these materials will readily form oxides and nitrides on their surfaces. These compounds are impurities that create a brittle, weak layer, degrade mechanical properties, and result in a dull surface finish.
By removing the air, a vacuum furnace eliminates the reactants. This prevents oxidation and nitridation from occurring in the first place, preserving the material's inherent chemical composition and ensuring a bright, clean surface.
Beyond Purification: The Secondary Benefits
The purification effect of vacuum sintering directly leads to several critical improvements in the final component, which often justifies the investment in the technology.
Enhanced Material Properties
By removing embrittling impurities and preventing the formation of oxides, vacuum sintering produces parts that are denser, stronger, and have higher wear resistance. This is essential for components used in demanding applications.
Superior Surface Finish
Because no surface oxidation occurs, parts emerge from a vacuum furnace with a bright, smooth, and often metallic-looking finish. This can eliminate the need for secondary cleaning or finishing operations, reducing process steps and cost.
Efficiency for Complex Parts
For small or intricately shaped components made from powdered metal, vacuum sintering ensures uniform heating and consistent densification. This minimizes material waste and produces near-net-shape parts, reducing the need for costly post-sintering machining.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, vacuum sintering is not a universal solution. An objective assessment requires understanding its limitations.
Not All Impurities are Removed
This process is only effective for removing impurities that are more volatile than the base material. Elements with a very low vapor pressure (i.e., a very high boiling point) will not evaporate and will remain in the material.
Equipment and Operational Costs
Vacuum furnaces are more complex and carry a higher capital cost than standard atmospheric furnaces. They also require more sophisticated control systems and maintenance, leading to higher operational expenses.
Longer Cycle Times
The process of pumping down the furnace to achieve the required vacuum level adds time to the overall production cycle. For high-volume, low-margin parts, this can be a significant drawback compared to faster atmospheric processes.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right sintering process depends entirely on your project's specific requirements for purity, performance, and cost.
- If your primary focus is maximum purity and performance: Vacuum sintering is the superior choice, especially for reactive materials like titanium, refractory metals, or high-performance stainless steels.
- If your primary focus is producing parts with a bright, clean surface finish: The oxidation-prevention benefit makes vacuum sintering highly effective, potentially saving costs on post-processing.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, low-cost production of non-reactive materials: A conventional atmospheric sintering process may be a more cost-effective solution if the material properties it yields are sufficient for your application.
Ultimately, choosing vacuum sintering is a strategic decision to invest in a controlled process for an uncontaminated and superior final material.
Summary Table:
| Mechanism | Key Action | Result |
|---|---|---|
| Evaporation of Volatile Impurities | Lowers boiling points to remove elements like lead, zinc, and magnesium | Removes embrittling contaminants |
| Prevention of Oxidation and Nitridation | Eliminates air to stop oxide and nitride formation | Preserves material integrity and surface finish |
Ready to elevate your material purity and performance? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by strong deep customization capability to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how our vacuum sintering solutions can enhance your processes and deliver superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of setting a mid-temperature dwell stage? Eliminate Defects in Vacuum Sintering
- What is the role of sintering or vacuum induction furnaces in battery regeneration? Optimize Cathode Recovery
- Why must sintering equipment maintain a high vacuum for high-entropy carbides? Ensure Phase Purity and Peak Density
- What is the function of a vacuum sintering furnace in the SAGBD process? Optimize Magnetic Coercivity and Performance
- What processing conditions does a vacuum furnace provide for TiCp/Fe microspheres? Sintering at 900 °C



















