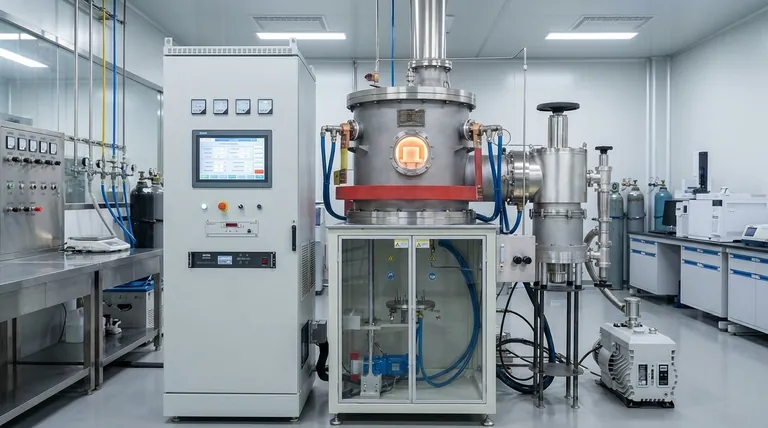
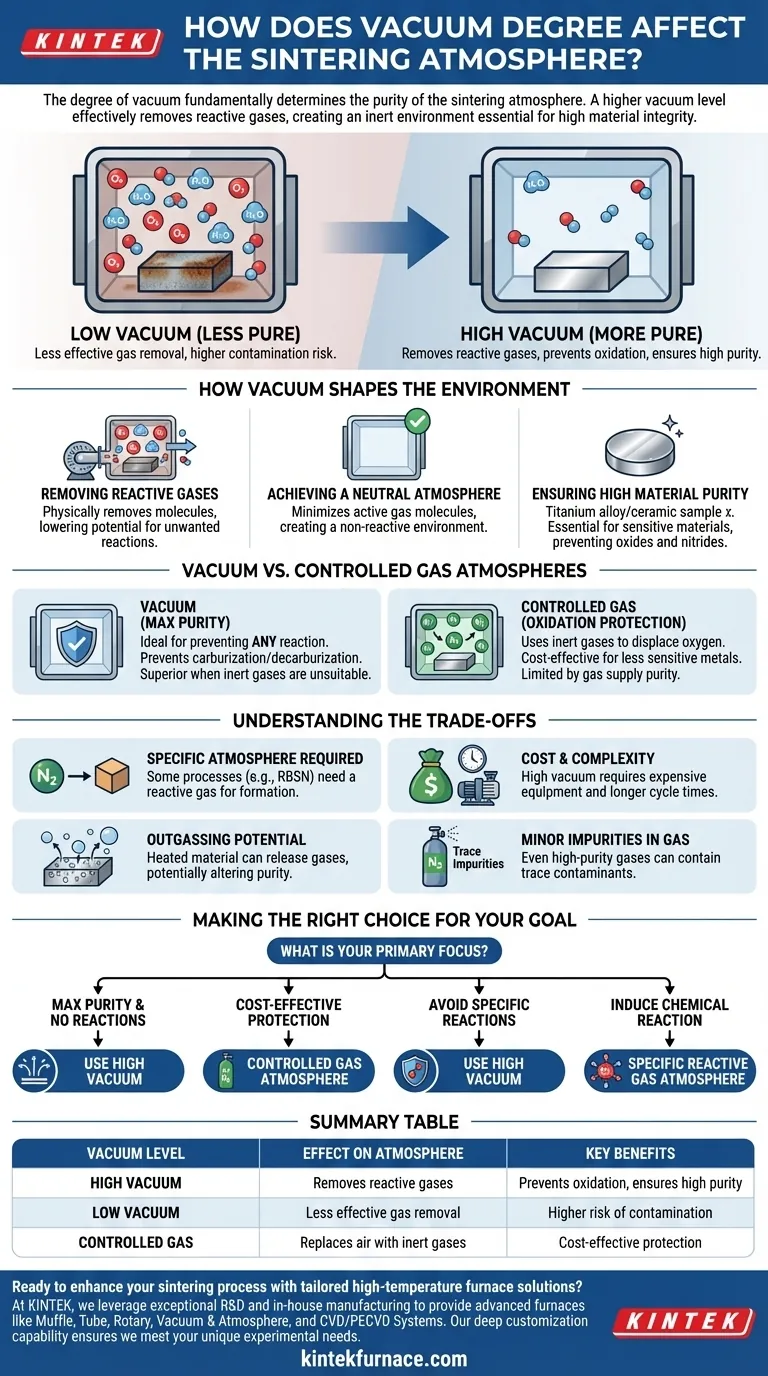
The degree of vacuum fundamentally determines the purity of the sintering atmosphere. A higher vacuum level more effectively removes reactive gases like oxygen and water vapor from the furnace chamber. This creates an environment that is significantly more inert, minimizing unwanted chemical reactions and protecting the integrity of the material being processed.
The level of vacuum is not merely about removing air; it is a strategic tool for controlling the chemical environment. A higher vacuum creates a purer, more neutral atmosphere, which is essential for preventing oxidation and achieving high material integrity, especially for sensitive alloys and ceramics.

How Vacuum Shapes the Sintering Environment
The primary purpose of using a vacuum or a controlled atmosphere in sintering is to prevent the hot material from reacting with ambient air, particularly oxygen. The vacuum degree dictates how effectively this is achieved.
Removing Reactive Gases
The most immediate effect of applying a vacuum is the physical removal of gas molecules from the chamber. This includes oxygen, nitrogen, and water vapor, all of which can cause detrimental oxidation and contamination at high sintering temperatures.
A higher vacuum means fewer residual gas molecules are present, drastically lowering the potential for these unwanted reactions to occur.
Achieving a Neutral Atmosphere
A perfect vacuum is a true void, creating the ultimate neutral, non-reactive environment. While a perfect vacuum isn't achievable, a high vacuum gets very close.
By minimizing the number of active gas molecules, a high vacuum creates an atmosphere that will not react with the material. This is crucial for parts where even trace amounts of oxidation or contamination can compromise performance.
Ensuring High Material Purity
For materials that are highly sensitive to contamination, such as titanium alloys, refractory metals, and advanced ceramics, a high vacuum is essential.
It prevents the formation of oxides and nitrides on the material's surface and within its grain structure, ensuring the final product meets stringent purity and performance specifications.
Vacuum vs. Controlled Gas Atmospheres
While vacuum sintering aims to remove all gases, atmosphere sintering involves replacing the air with a specific, controlled gas. The choice depends on the material and the process goals.
The Purity Advantage of Vacuum
Vacuum is the ideal choice when the goal is to prevent any atmospheric reaction. It is superior when even inert gases like argon or reducing gases like hydrogen are unsuitable.
For example, it prevents unwanted reactions like carburization or decarburization in certain steels, which could occur in the presence of other gases.
The Role of Controlled Gases
Atmosphere sintering uses gases like argon, nitrogen, or hydrogen to create a protective environment. These gases displace oxygen, effectively preventing oxidation.
This method is often used for less sensitive metals where the primary goal is oxidation prevention, and the potential for slight impurities from the gas supply is acceptable. Some processes even require a specific gas to induce a desired chemical reaction.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right atmosphere is a balance of technical requirements and practical constraints. A high vacuum is not always the best or most practical solution.
When a Specific Atmosphere is Required
Some sintering processes, such as reaction-bonded silicon nitride (RBSN), fundamentally depend on a reactive gas atmosphere (nitrogen) to form the desired final compound. In these cases, a vacuum would prevent the necessary chemical transformation.
The Cost and Complexity of High Vacuum
Achieving and maintaining a high vacuum requires more sophisticated and expensive equipment, including powerful pumps and robust furnace construction. Pump-down cycles can also be longer, increasing overall processing time and operational costs compared to atmosphere sintering.
Potential for Outgassing
Under vacuum, the material being heated can itself release trapped gases, a phenomenon known as outgassing. This can alter the purity of the vacuum atmosphere if not properly managed, potentially re-introducing contaminants that the vacuum was meant to remove.
Minor Impurities in Gas Atmospheres
While effective for oxidation protection, controlled gas atmospheres are limited by the purity of the gas supply. Even high-purity argon or nitrogen can contain trace amounts of oxygen or water, which may be unacceptable for the most sensitive applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your decision to use a high vacuum or a specific gas atmosphere should be driven by your material's sensitivity and the desired properties of the final product.
- If your primary focus is maximum purity and preventing all reactions: Use a high vacuum. It provides the most neutral and non-reactive environment, critical for sensitive materials like titanium, refractory metals, or medical-grade alloys.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective oxidation protection: A controlled gas atmosphere like argon or nitrogen is often sufficient for less sensitive metals and general-purpose applications.
- If your primary focus is to avoid specific gas-related reactions: Vacuum is the superior choice when common process gases could cause unwanted side effects, such as decarburization in steel or hydride formation in certain alloys.
- If your primary focus is to induce a chemical reaction: A specific reactive gas atmosphere (e.g., nitrogen for nitriding) is required, and vacuum is unsuitable.
By understanding the relationship between vacuum degree and atmospheric purity, you can precisely control your sintering process to achieve the required material integrity.
Summary Table:
| Vacuum Level | Effect on Atmosphere | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| High Vacuum | Removes reactive gases like oxygen and water vapor | Prevents oxidation, ensures high purity for sensitive materials |
| Low Vacuum | Less effective gas removal | Higher risk of contamination, suitable for less sensitive applications |
| Controlled Gas Atmosphere | Replaces air with inert gases like argon or nitrogen | Cost-effective oxidation protection, may introduce minor impurities |
Ready to enhance your sintering process with tailored high-temperature furnace solutions? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we meet your unique experimental needs, delivering precise temperature control and optimal atmosphere management for superior material integrity. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of setting a mid-temperature dwell stage? Eliminate Defects in Vacuum Sintering
- Why must sintering equipment maintain a high vacuum for high-entropy carbides? Ensure Phase Purity and Peak Density
- What is the function of a vacuum sintering furnace in the SAGBD process? Optimize Magnetic Coercivity and Performance
- What is the role of sintering or vacuum induction furnaces in battery regeneration? Optimize Cathode Recovery
- Why is a high-vacuum environment necessary for sintering Cu/Ti3SiC2/C/MWCNTs composites? Achieve Material Purity



















