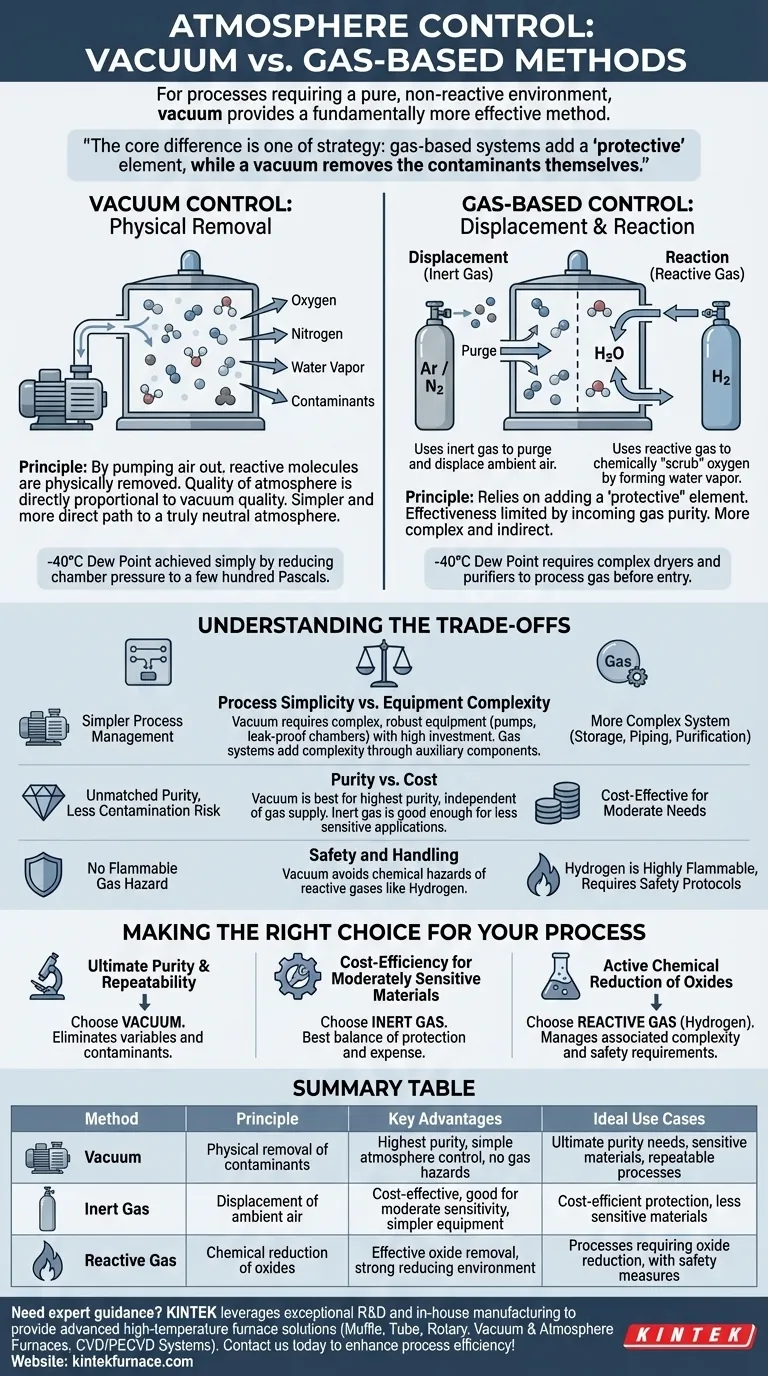
For processes requiring a pure, non-reactive environment, vacuum provides a fundamentally more effective method of atmosphere control than gas-based systems. While methods like using purified hydrogen can achieve low contamination levels, vacuum accomplishes this more simply by physically removing reactive molecules like oxygen and water vapor, rather than trying to displace or neutralize them.
The core difference is one of strategy: gas-based systems add a "protective" element to a contaminated environment, while a vacuum removes the contaminants themselves. This makes vacuum an inherently simpler and more direct path to achieving a truly neutral atmosphere.
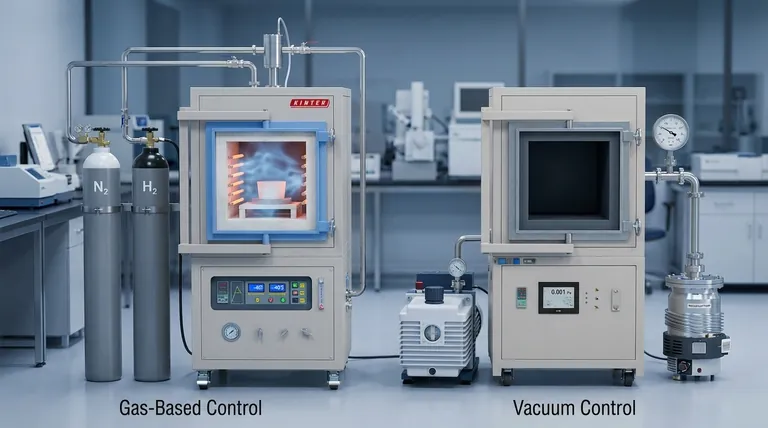

The Principle of Atmosphere Control
At its core, atmosphere control is about preventing unwanted chemical reactions—primarily oxidation—during high-temperature processes like smelting, sintering, or heat treating. The method chosen dictates how this protection is achieved.
Gas-Based Control: Displacement and Reaction
Controlled atmospheres using gas rely on two main strategies. The first is displacement, where an inert gas like argon or nitrogen is used to purge the furnace and physically push out the ambient air.
The second strategy uses a reactive or "reducing" gas like hydrogen. Hydrogen actively bonds with oxygen to form water vapor (H₂O), which is then vented. This chemically "scrubs" the oxygen from the environment.
Vacuum Control: Physical Removal
Vacuum control operates on a much simpler principle: physical removal. By pumping the air out of a sealed chamber, a vacuum system removes the molecules—oxygen, nitrogen, water vapor, and others—that could react with the material.
The quality of the atmosphere is then directly proportional to the quality of the vacuum. A higher vacuum means fewer residual gas molecules and therefore a purer, more neutral environment.
A Practical Comparison: The Dew Point Standard
A common metric for atmosphere quality is the dew point, which measures water vapor content. A lower dew point signifies a drier, less oxidative atmosphere.
The Challenge of a -40°C Dew Point
Achieving a dew point of -40°C is a benchmark for a high-purity atmosphere. In a gas-based system, this is a complex undertaking.
For a hydrogen atmosphere, the gas itself must be processed through sophisticated dryers and purifiers to remove residual moisture before it even enters the furnace. The system's effectiveness is limited by the purity of the incoming gas.
The Simplicity of Vacuum
A vacuum system achieves the equivalent of a -40°C dew point far more directly. This level of dryness is reached simply by reducing the chamber pressure to a few hundred Pascals.
At this pressure, the partial pressure of water vapor is so low that it has the same practical effect as a painstakingly dried gas. No complex gas purification is needed; the protection comes from the absence of molecules.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While vacuum offers superior control, the choice is not always straightforward and involves balancing performance with practical constraints.
Process Simplicity vs. Equipment Complexity
Vacuum simplifies atmosphere management but requires complex and robust equipment. High-quality vacuum pumps, leak-proof chambers, and precise seals are essential and demand significant capital investment and maintenance.
Gas systems may use simpler chambers but add complexity through gas storage, piping, purification systems, and flow regulators.
Purity vs. Cost
For the highest-purity applications, vacuum is unmatched. It minimizes the risk of contamination because it is not reliant on the purity of an external gas supply.
However, for less sensitive materials or processes, an inert gas flush with nitrogen or argon can be a significantly more cost-effective solution that provides "good enough" protection.
Safety and Handling
Hydrogen gas, while an excellent reducing agent, is highly flammable and requires extensive safety protocols and infrastructure. Vacuum systems, while operating at high pressures and temperatures, do not introduce this type of chemical hazard.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your decision should be driven by the specific requirements of your material and the goals of your process.
- If your primary focus is ultimate purity and process repeatability: Vacuum is the superior choice, as it most effectively eliminates the variables and contaminants present in gas-based systems.
- If your primary focus is cost-efficiency for moderately sensitive materials: An inert gas atmosphere, such as nitrogen or argon, often provides the best balance of protection and operational expense.
- If your process requires active chemical reduction of existing oxides: A hydrogen-based atmosphere is necessary, but you must be prepared to manage the associated complexity and safety requirements.
Choosing the right atmospheric control is a critical decision that directly impacts product quality, consistency, and cost.
Summary Table:
| Method | Principle | Key Advantages | Ideal Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vacuum | Physical removal of contaminants | Highest purity, simple atmosphere control, no gas hazards | Ultimate purity needs, sensitive materials, repeatable processes |
| Inert Gas (e.g., Nitrogen, Argon) | Displacement of ambient air | Cost-effective, good for moderate sensitivity, simpler equipment | Cost-efficient protection, less sensitive materials |
| Reactive Gas (e.g., Hydrogen) | Chemical reduction of oxides | Effective oxide removal, strong reducing environment | Processes requiring oxide reduction, with safety measures |
Need expert guidance on selecting the right atmosphere control for your lab? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your unique needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, with strong deep customization capabilities to ensure precise performance. Contact us today via our contact form to enhance your process efficiency and achieve superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
People Also Ask
- How does a mixed gas flow control system maintain stability during high-temperature nitriding? Precision Gas Ratios
- What are the primary inert gases used in vacuum furnaces? Optimize Your Heat Treatment Process
- How do argon and nitrogen protect samples in vacuum furnaces? Optimize Your Thermal Process with the Right Gas
- What is an atmosphere protection muffle furnace? Unlock Precise Heat Treatment in Controlled Environments
- What are the key features of an atmosphere box furnace? Unlock Precise Heat Processing in Controlled Environments



















