In short, the size of a crucible furnace is its most defining characteristic, directly determining its application, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness. While smaller furnaces are ideal for laboratories and small businesses, their inherent size limitations make them impractical for large-scale industrial operations that require high-volume metal processing.
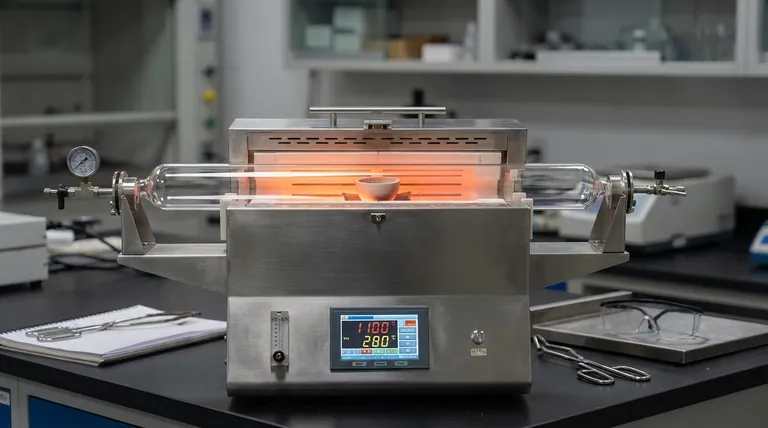
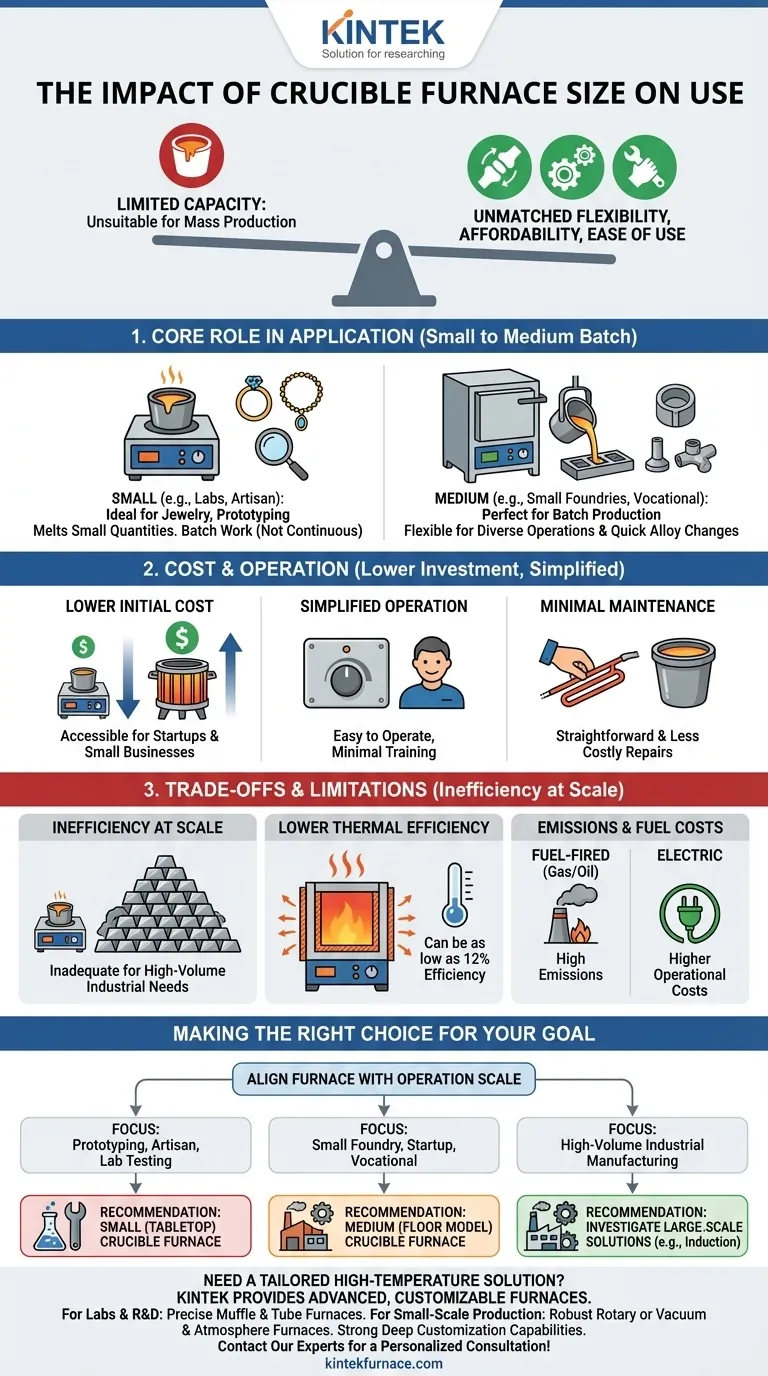
A crucible furnace's size dictates its core trade-off: its limited capacity makes it unsuitable for mass production, but this same characteristic provides unmatched flexibility, affordability, and ease of use for small-to-medium scale operations.

The Core Role of Size in Application
The physical size of a crucible furnace is not just a specification; it is the primary factor that defines its best-fit use case in the industry.
Ideal for Small to Medium Batch Processing
Crucible furnaces excel at melting small to medium quantities of metal, from tabletop units for jewelry to floor models for small foundries.
Their design is fundamentally centered around containing metal within a pot (the crucible), which naturally limits the volume that can be processed in a single cycle. This makes them perfect for batch work, not continuous, high-throughput production.
Flexibility for Diverse Operations
The smaller capacity is an advantage for operations that require flexibility. It's much easier and faster to switch between melting different alloys in a crucible furnace without significant downtime or risk of cross-contamination.
This makes them highly valuable for laboratories, vocational schools, and businesses that handle varied, smaller jobs rather than a single, massive production run.
How Size Influences Cost and Operation
The scale of a crucible furnace has a direct and significant impact on its financial and operational accessibility.
Lower Initial Investment
Compared to massive industrial furnaces like induction or arc furnaces, crucible furnaces have a significantly lower initial cost.
Their simpler construction and smaller footprint reduce manufacturing and installation expenses, making them an attractive and accessible option for startups and small businesses with limited capital.
Simplified Operation and Maintenance
The relatively simple design associated with their smaller scale means crucible furnaces are easy to operate, requiring minimal specialized training.
Maintenance is also more straightforward and less costly. Replacing a crucible or a heating element is a much less involved process than overhauling a multi-ton industrial furnace, reducing downtime and operational costs.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While their size offers clear benefits for specific applications, it also introduces critical limitations that must be considered.
The Primary Constraint: Inefficiency at Scale
The most significant limitation is the inability to handle large-scale industrial applications. A business that needs to melt tons of metal per hour will find a crucible furnace entirely inadequate due to its batch volume restrictions.
Lower Thermal Efficiency
Crucible furnaces are generally less energy-efficient than other furnace types, with some traditional models having thermal efficiency as low as 12%.
Heat is applied to the outside of the crucible, and a significant amount of energy is lost heating the furnace chamber and the surrounding environment. This inefficiency becomes more pronounced and costly as the furnace size increases.
Emissions and Fuel Costs
Traditional fuel-fired (e.g., gas or oil) crucible furnaces can produce high levels of emissions, which may be a concern for environmentally sensitive operations.
While electric crucible furnaces nearly eliminate emissions, they can have higher operational costs depending on local electricity prices. This creates a trade-off between environmental impact and ongoing fuel expenses.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the right equipment, you must align the furnace's capabilities with the scale of your operation.
- If your primary focus is prototyping, artisan work, or lab testing: The small size, low initial cost, and flexibility of a tabletop or small-scale crucible furnace are ideal.
- If your primary focus is running a small foundry or startup: A medium-capacity crucible furnace provides a cost-effective entry point for producing castings without a massive capital investment.
- If your primary focus is high-volume industrial manufacturing: The inherent size and efficiency limitations make crucible furnaces unsuitable; you must investigate larger-scale solutions like induction furnaces.
Ultimately, understanding that a crucible furnace is a specialized tool for small-to-medium batch work is the key to leveraging its strengths effectively.
Summary Table:
| Furnace Size | Ideal Application | Key Advantage | Primary Limitation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Small (Tabletop) | Jewelry, Prototyping, Labs | Maximum Flexibility & Low Cost | Very Low Batch Volume |
| Medium (Floor Model) | Small Foundries, Vocational Schools | Cost-Effective for Batch Work | Lower Thermal Efficiency |
| Large / Industrial | Not Recommended | N/A | Impractical for Mass Production |
Need a High-Temperature Furnace Solution Tailored to Your Scale?
Whether you're running a research lab, a vocational school, or a small foundry, choosing the right furnace is critical for your productivity and budget. The team at KINTEK understands that one size does not fit all.
We provide advanced, customizable furnace solutions to meet your unique operational needs:
- For Labs & R&D: Our precise Muffle and Tube Furnaces offer the control and flexibility required for prototyping and testing.
- For Small-Scale Production: Our robust Rotary or Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces deliver the reliability needed for consistent batch processing.
Leveraging exceptional in-house R&D and manufacturing, we go beyond standard products to offer strong deep customization capabilities, ensuring your furnace precisely matches your capacity, material, and process requirements.
Let's find the perfect furnace for your application. Contact our experts today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety



















