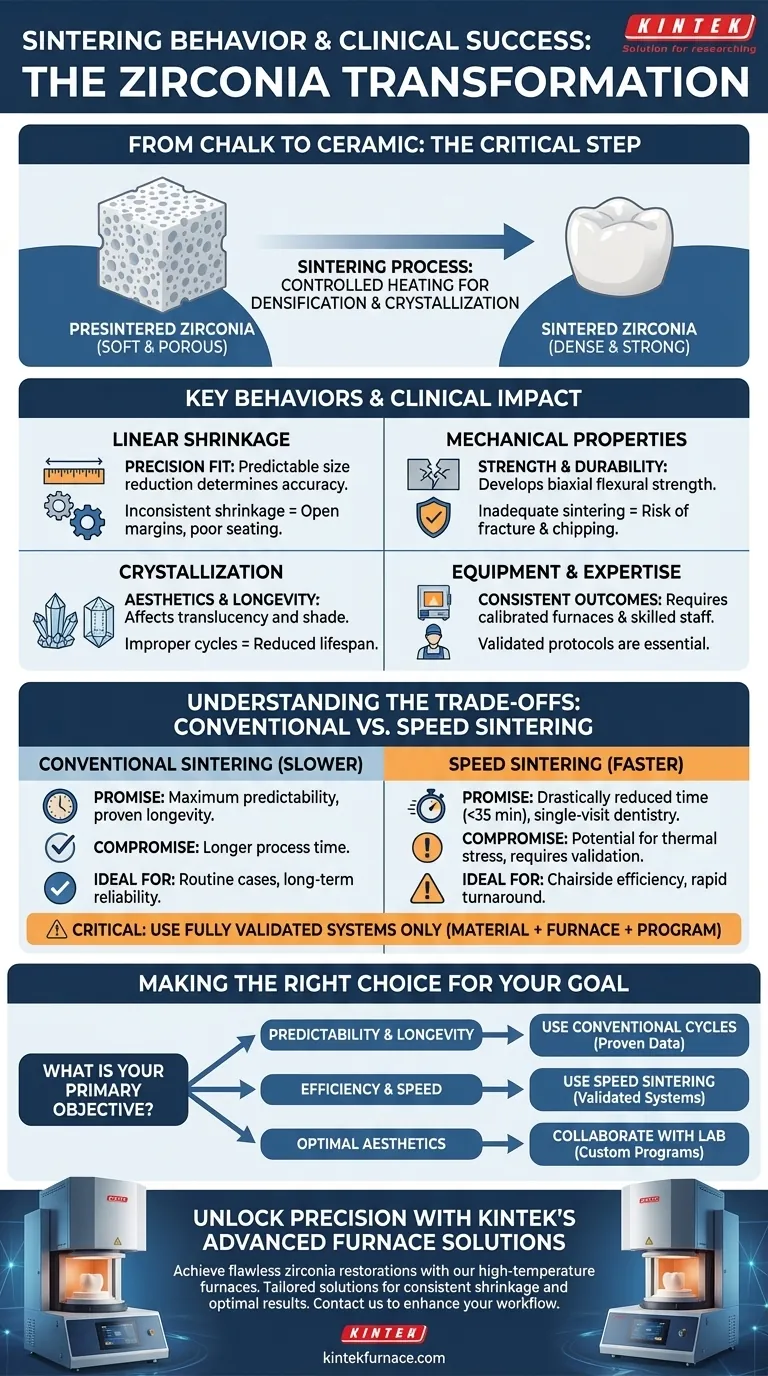
At its core, the sintering behavior of a presintered zirconia block is the single most critical manufacturing step that determines the final success of a dental restoration. This controlled heating process dictates the restoration's ultimate fit, strength, and durability by transforming the soft, oversized "chalky" material into a dense, high-strength ceramic that matches the intended design.
The central challenge in zirconia fabrication is not merely heating the material, but precisely managing its transformation. Sintering behavior—specifically its shrinkage and crystallization—directly translates to the clinical quality of the final restoration, where even minor deviations can compromise fit and longevity.

The Fundamental Transformation: From Chalk to Ceramic
What is a Presintered Block?
A presintered zirconia block is an enlarged, porous version of the final restoration. It is milled in this soft state because it is easy to shape with high precision.
The material is intentionally oversized by a specific, known percentage to compensate for the shrinkage that will occur during sintering.
The Sintering Process
Sintering is a high-temperature process that triggers two critical events: densification and crystallization.
During densification, the porous material becomes solid and compact, shrinking in size. Simultaneously, the material's microstructure crystallizes, giving the zirconia its exceptional strength and fracture resistance.
Why This Dictates Clinical Fit
The accuracy of this transformation is paramount. The dental lab's software calculates the enlargement factor based on the manufacturer's specified sintering shrinkage.
If the block does not shrink exactly as predicted, the final crown or bridge will not fit the patient's preparation, leading to clinical failure.
Key Behaviors and Their Clinical Impact
Linear Sintering Shrinkage
This is the most direct measure of a restoration's final accuracy. It is the percentage of size reduction the block undergoes during heating.
Inconsistent shrinkage, caused by poor material quality or improper furnace calibration, results in restorations that are too large or too small. This leads to open margins, poor contacts, or a restoration that simply won't seat.
Mechanical Properties
The final strength and durability of the restoration are developed during sintering. The process must be executed correctly to achieve the manufacturer's specified biaxial flexural strength.
Inadequate sintering can result in a weaker material that is more prone to fracture or chipping under the forces of chewing, compromising the long-term clinical success of the restoration.
Equipment and Expertise
The quality of the final restoration is not solely dependent on the material. It relies heavily on the sophistication of the sintering furnace and the expertise of the dental technician.
High-quality outcomes demand calibrated equipment and skilled staff who understand the specific protocols required for each type of zirconia to achieve customized, patient-specific results.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Conventional vs. Speed Sintering
The Promise of Speed Sintering
Speed sintering is an advanced protocol that drastically reduces fabrication time, often to under 35 minutes. This is achieved by using higher temperatures for shorter durations.
This innovation makes single-visit zirconia restorations possible, dramatically improving efficiency for both the dental practice and the patient.
The Potential Compromise
The primary concern with accelerated protocols is their potential impact on the material's properties. Rapid heating can introduce thermal stresses or lead to incomplete crystallization.
While many modern materials are engineered for speed sintering, it is critical to use a fully validated system. Mismatching a material with an unapproved fast cycle can compromise the final strength and aesthetics of the restoration.
Verifying Compatibility
Before adopting any sintering protocol, especially a rapid one, it is essential to confirm that the zirconia block, the furnace, and the specific heating cycle are all tested and approved for use together by the manufacturer. This ensures predictable shrinkage and optimal mechanical properties.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Achieving a successful zirconia restoration requires aligning the fabrication process with the clinical objective.
- If your primary focus is maximum predictability and proven longevity: Use conventional, slower sintering cycles with materials that have extensive long-term clinical data.
- If your primary focus is chairside efficiency and single-visit dentistry: Speed sintering is a powerful tool, but only when using a fully integrated system where the material, furnace, and program are validated to work together.
- If your primary focus is the highest aesthetic outcome: Collaborate with your lab on specific sintering programs, as adjustments to temperature and time can optimize the translucency and shade of certain zirconia types.
Ultimately, understanding the principles of sintering empowers you to make informed decisions that ensure consistent, high-quality patient outcomes.
Summary Table:
| Sintering Behavior | Clinical Impact | Key Factors |
|---|---|---|
| Linear Shrinkage | Determines restoration fit; deviations cause open margins or seating issues | Material quality, furnace calibration |
| Mechanical Properties | Affects strength and fracture resistance; inadequate sintering leads to chipping | Sintering protocol, temperature control |
| Crystallization | Influences durability and aesthetics; improper cycles reduce longevity | Heating rate, furnace type |
| Speed vs. Conventional | Speed sintering offers efficiency but risks strength; conventional ensures predictability | Protocol validation, material compatibility |
Unlock Precision in Your Dental Lab with KINTEK's Advanced Furnace Solutions
Are you striving for flawless zirconia restorations with perfect fit and unmatched strength? KINTEK specializes in high-temperature furnace technology tailored for dental laboratories. Our product line—including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems—is backed by exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing. With deep customization capabilities, we deliver solutions that precisely meet your unique sintering requirements, ensuring consistent shrinkage, optimal crystallization, and superior clinical outcomes.
Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can enhance your workflow and deliver reliable, high-quality dental restorations. Get in touch now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Vacuum Press Furnace
- Chairside Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Furnace with Transformer for Ceramic Restorations
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are some common mistakes when operating dental sintering furnaces? Avoid Costly Errors for Perfect Zirconia Restorations
- What factors determine the quality of sintered zirconia restorations? Master Material, Equipment, and Technique
- What factors should be considered when choosing a dental sintering furnace? Ensure Quality and Efficiency for Your Lab
- What is a dental sintering furnace and what is its purpose? Achieve High-Strength Dental Restorations
- Why is calibration important for dental sintering furnaces? Ensure Perfect Restorations and Avoid Costly Failures



















