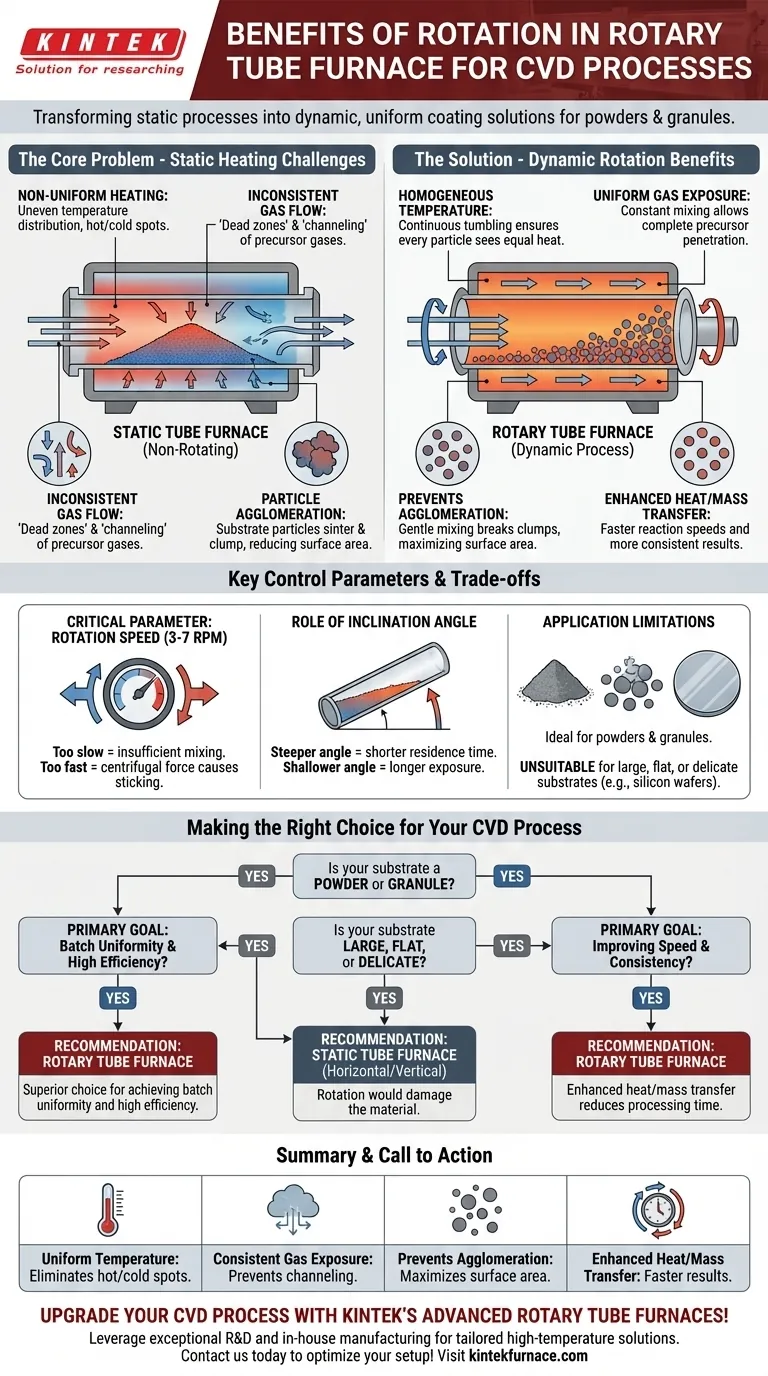
In short, the rotation mechanism in a rotary tube furnace benefits Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) by transforming a static process into a dynamic one. This continuous motion ensures that substrate materials, especially powders, are uniformly exposed to heat and precursor gases, which is essential for creating high-quality, consistent coatings.
The fundamental advantage of rotation is that it solves the core challenges of non-uniformity inherent in many CVD processes. By continuously mixing the substrate, it guarantees homogeneous temperature distribution, consistent gas exposure, and prevents particle agglomeration, leading to more efficient and repeatable results.

The Core Problem in CVD: Overcoming Non-Uniformity
To appreciate the benefit of rotation, one must first understand the common issues that arise in a static (non-rotating) furnace during a CVD process, particularly when working with powders or small parts.
The Challenge of Static Heating
In a stationary tube, heat is not transferred evenly. The material at the bottom of the tube receives more direct conductive heat from the furnace wall, while the material on top is heated primarily through convection and radiation, creating significant temperature gradients.
This temperature difference leads to inconsistent reaction rates across the material batch, resulting in a non-uniform product.
The Issue of Gas Flow Dynamics
Gaseous precursors flowing over a static bed of material may not penetrate the entire batch evenly. This can create "dead zones" where the reaction is starved of reactants and "channeling" where gas flows preferentially through certain paths, leading to uneven deposition.
The Problem of Particle Agglomeration
Without movement, substrate particles can easily sinter or stick together as they heat up. This clumping, known as agglomeration, reduces the total surface area available for the deposition reaction, dramatically lowering process efficiency and yielding an inconsistent product.
How Rotation Provides a Comprehensive Solution
The rotating action of the furnace tube directly counteracts each of these problems, creating a far more controlled and homogeneous reaction environment.
Achieving Homogeneous Temperature Distribution
By continuously tumbling the material, rotation ensures that every particle is periodically exposed to the hottest part of the tube wall. This constant mixing eliminates hot and cold spots, guaranteeing a uniform temperature throughout the entire substrate batch.
Ensuring Uniform Precursor Gas Exposure
Rotation constantly rearranges the particles, preventing gas channeling and ensuring that fresh precursor gases can reach the entire surface area of the material. This results in a much more consistent and complete coating formation.
Preventing Agglomeration and Improving Surface Area
The gentle mechanical mixing provided by the furnace's rotation actively breaks up any clumps that begin to form. This keeps the particles separate, maximizing the available surface area for the CVD reaction and leading to higher deposition efficiency.
Enhancing Heat and Mass Transfer
This dynamic environment significantly improves the efficiency of heat and mass transfer. Heat moves into the material more quickly, and reactant gases are transported to the surface more effectively, which can lead to faster processing times and more uniform results.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Control Parameters
While highly beneficial, a rotary system is not a universal solution. Its effectiveness depends on proper control and understanding its limitations.
The Importance of Rotation Speed
The speed of rotation, typically between 3 and 7 RPM, is a critical parameter. If the rotation is too slow, it will not provide sufficient mixing. If it is too fast, centrifugal force can cause particles to stick to the furnace walls, negating the benefits.
The Role of Inclination Angle
Many rotary furnaces can be tilted. This inclination angle controls the residence time of the material within the hot zone. A steeper angle results in a shorter residence time (ideal for continuous processing), while a shallower angle increases exposure time.
Key Application Limitations
Rotary tube furnaces are ideal for processing powders, granules, and other small, free-flowing parts. They are fundamentally unsuitable for depositing coatings onto large, flat, or delicate substrates (like silicon wafers), as the tumbling action would cause damage.
Making the Right Choice for Your CVD Process
Choosing the correct furnace type depends entirely on the physical form of your substrate and your primary process goal.
- If your primary focus is coating powders or granules: A rotary tube furnace is the superior choice for achieving batch uniformity and high efficiency.
- If your primary focus is improving process speed and consistency for particulates: The enhanced heat and mass transfer from rotation can significantly reduce processing times and improve product quality.
- If your primary focus is processing large, monolithic, or delicate substrates: A static horizontal or vertical tube furnace is the correct tool, as rotation would damage the material.
Ultimately, understanding your substrate's form factor is the key to selecting the right tool for a successful CVD process.
Summary Table:
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Uniform Temperature | Eliminates hot/cold spots by tumbling material for even heat distribution. |
| Consistent Gas Exposure | Prevents channeling and dead zones, ensuring complete precursor coverage. |
| Prevents Agglomeration | Breaks up clumps to maximize surface area and deposition efficiency. |
| Enhanced Heat/Mass Transfer | Improves reaction speed and uniformity for faster, reliable results. |
Upgrade your CVD process with KINTEK's advanced rotary tube furnaces! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with tailored high-temperature solutions. Our product line, including Rotary Furnaces, Muffle, Tube, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental needs for uniform powder coatings and enhanced efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your setup!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
People Also Ask
- What is the basic construction of a rotary tube furnace? Key Components for Uniform Heating
- What types of materials are suitable for processing in rotary tube furnaces? Ideal for Free-Flowing Powders and Granules
- What are the common approaches to mixing in rotary furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Efficiency in Thermal Processing
- What materials can be used to make the rotating tube assembly of these furnaces? Choose the Best for Your High-Temp Needs
- What is the purpose of the rotation mechanism in a rotary tube furnace? Achieve Uniform Heating and Enhanced Process Control



















