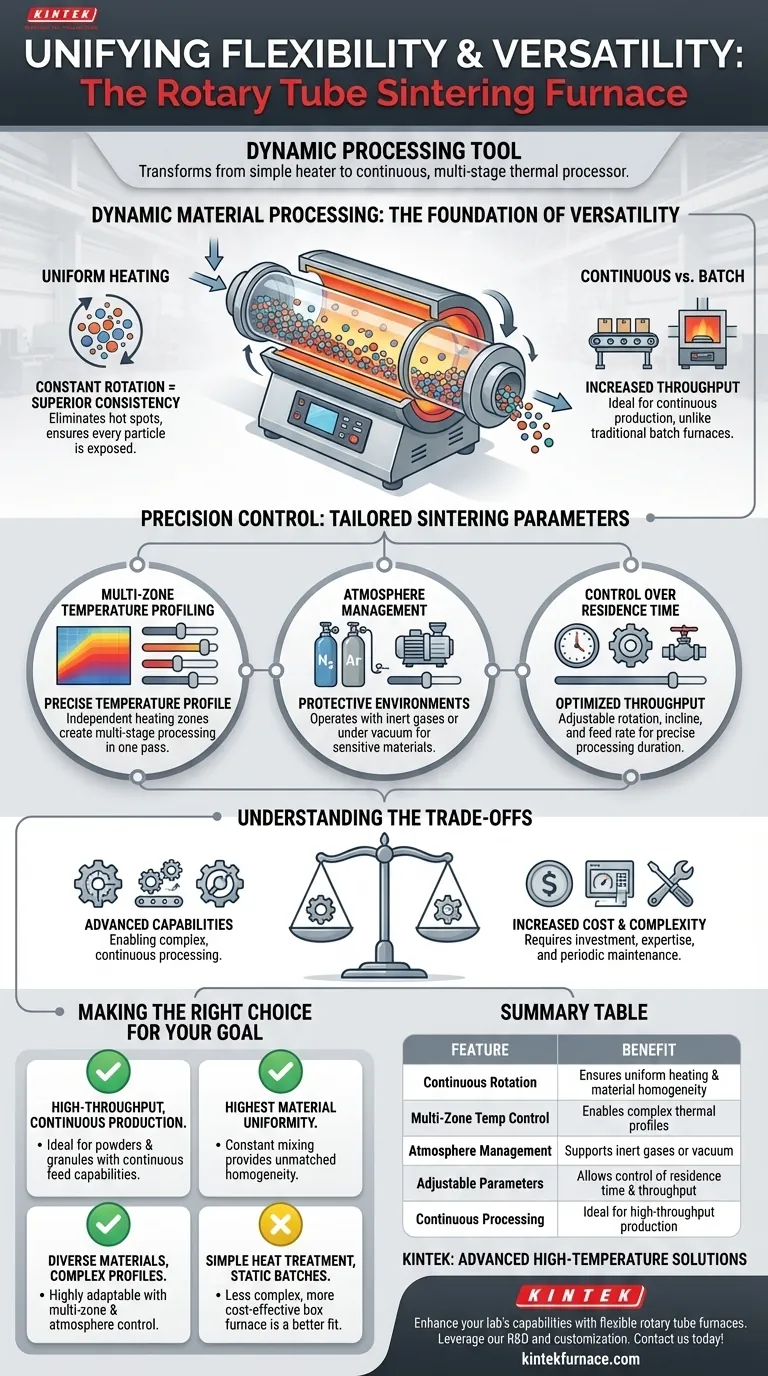
The flexibility of a rotary tube sintering furnace stems from its unique combination of dynamic material handling and precise environmental control. Unlike static furnaces, its ability to continuously rotate the processing tube provides unmatched heating uniformity, while features like multi-zone temperature control, atmosphere management, and customizable physical parameters allow it to adapt to a vast range of materials and production scales.
The core value of a rotary tube furnace isn't just one feature, but how its integrated systems for rotation, temperature, and atmosphere control work together. This transforms it from a simple heater into a dynamic processing tool capable of handling continuous production and complex, multi-stage thermal profiles that are impossible in static systems.

The Foundation of Versatility: Dynamic Material Processing
The fundamental difference between a rotary furnace and other types is its motion. This single characteristic unlocks significant processing advantages.
Uniform Heating Through Continuous Rotation
The constant tumbling of material inside the rotating tube is the primary source of its high-quality output. This motion ensures every particle is exposed to the heat source evenly.
This eliminates hot spots and temperature gradients common in static furnaces, where material at the bottom and center may be under-heated. The result is superior process consistency and material homogeneity.
Enabling Continuous vs. Batch Processing
The furnace can be set at an incline, and the rotation speed can be precisely controlled. This allows material to be fed into one end and gradually travel to the other for discharge.
This capability makes the rotary furnace ideal for continuous or semi-continuous production, dramatically increasing throughput compared to the one-at-a-time nature of traditional batch furnaces.
Precision Control Over Sintering Parameters
Beyond physical motion, a rotary furnace provides granular control over every critical aspect of the thermal process, allowing it to be tailored to specific material requirements.
Multi-Zone Temperature Profiling
High-end models are equipped with multiple, independently controlled heating zones along the length of the tube. This allows for the creation of a precise temperature profile.
A material can be pre-heated in the first zone, sintered at a peak temperature in the middle zones, and then cooled in a controlled manner in the final zones, all within a single pass. This is crucial for complex materials that require multi-stage processing.
Sophisticated Atmosphere Management
Sintering often requires a specific environment to prevent oxidation or promote certain reactions. Rotary furnaces are designed to operate with a variety of atmospheres.
They can be purged with protective inert gases like nitrogen or argon, or they can operate under vacuum. This adaptability makes them suitable for processing sensitive metals, ceramics, and chemical compounds.
Control Over Residence Time and Throughput
Flexibility extends to the rate of production. The combination of the tube's inclination angle, its rotation rate, and the material feed rate gives an operator precise control over how long the material spends in the furnace—its residence time.
This allows the process to be optimized for different particle sizes, densities, and thermal requirements, ensuring complete and efficient sintering whether for small R&D batches or large-scale production.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly versatile, the rotary tube furnace is not universally superior. Its advanced capabilities introduce specific considerations.
The Cost of Customization
The features that provide flexibility—multiple heating zones, advanced automation, vacuum compatibility, and robust rotating mechanisms—increase the furnace's initial cost and complexity compared to a simpler box or static tube furnace.
Operational Complexity
With more variables to control (rotation speed, inclination angle, feed rate, multi-zone temperatures), optimizing a process requires more technical expertise. Achieving the perfect recipe for a new material can involve a steeper learning curve.
Maintenance Considerations
The rotating mechanism, including the seals required for atmosphere control, introduces moving parts that are not present in a static furnace. These components require periodic inspection and maintenance to ensure long-term reliability and performance.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right furnace depends entirely on your specific processing needs and operational scale.
- If your primary focus is high-throughput, continuous production of powders or granules: The rotary furnace is the ideal choice due to its continuous feed and discharge capabilities.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest material uniformity: The constant mixing action of the rotary furnace provides a level of homogeneity that is difficult to match in static systems.
- If your primary focus is processing diverse materials requiring complex thermal profiles: The multi-zone temperature control and atmosphere management make it a highly adaptable tool for both R&D and production.
- If your primary focus is simple heat treatment of a single, solid object or small, static batches: A less complex and more cost-effective box or static tube furnace is likely a better fit.
Ultimately, the rotary tube furnace empowers you to move beyond simple batch heating and master dynamic, continuous thermal processing.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Continuous Rotation | Ensures uniform heating and material homogeneity |
| Multi-Zone Temperature Control | Enables complex thermal profiles for diverse materials |
| Atmosphere Management | Supports inert gases or vacuum for sensitive processes |
| Adjustable Parameters | Allows control of residence time and throughput |
| Continuous Processing | Ideal for high-throughput production of powders and granules |
Ready to enhance your lab's capabilities with a flexible rotary tube furnace? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Whether you're in R&D or production, we can help you achieve superior thermal processing. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can benefit your specific needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What types of materials can be processed in a rotary tube furnace? Discover Ideal Materials for High-Temp Processing
- What factors should be considered when selecting a tube for a rotary tube furnace? Ensure Optimal Performance and Longevity
- What is the purpose of the rotation mechanism in a rotary tube furnace? Achieve Uniform Heating and Enhanced Process Control
- What are the main structural components of a rotary furnace? Explore Key Parts for Efficient Material Processing
- What materials can be used to make the rotating tube assembly of these furnaces? Choose the Best for Your High-Temp Needs



















