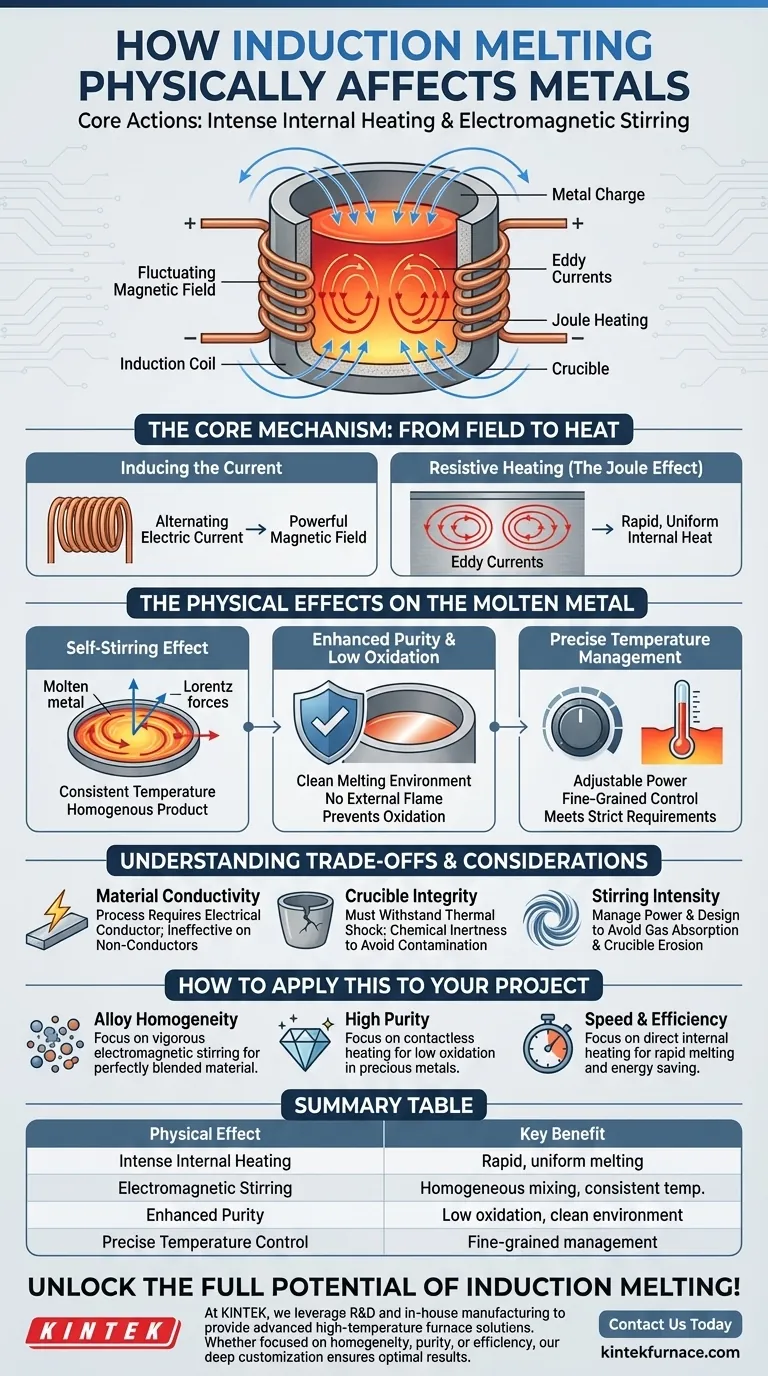
At its core, induction melting physically affects metals through two primary actions: intense internal heating and electromagnetic stirring. The process uses a fluctuating magnetic field to induce electric currents directly within the metal, causing it to heat from the inside out, while the same magnetic forces simultaneously stir the resulting molten pool.
Induction melting is not simply a method to liquefy metal; it is a highly controlled process that uses electromagnetic principles to achieve a rapid, clean, and homogenous melt without direct contact from a heat source.
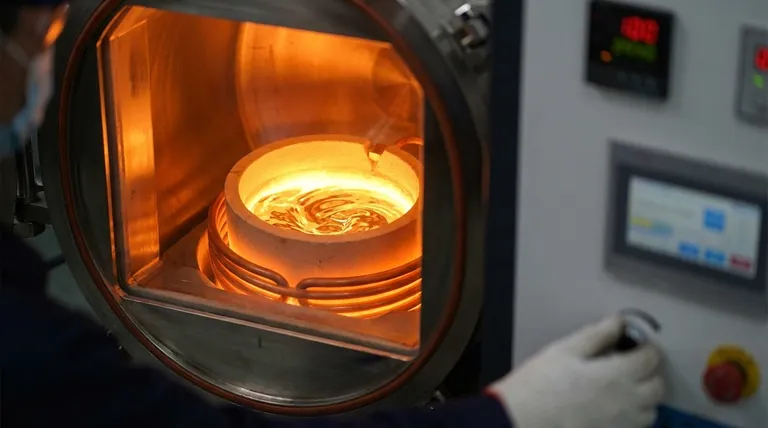

The Core Mechanism: From Field to Heat
The entire process begins with an induction coil, which is the engine of the furnace. Understanding how this coil translates electricity into molten metal is key.
Inducing the Current
An alternating electric current is passed through a copper coil, which generates a powerful and rapidly changing magnetic field around and within the crucible holding the metal charge.
Resistive Heating (The Joule Effect)
This magnetic field passes through the electrically conductive metal, inducing strong internal electrical currents known as eddy currents. The metal’s own natural resistance to the flow of these currents generates immense heat, a phenomenon known as Joule heating. This causes the metal's temperature to rise rapidly and uniformly, melting it from within.
The Physical Effects on the Molten Metal
Once the metal becomes molten, the electromagnetic forces continue to act upon it, producing several distinct and highly beneficial physical effects.
The Self-Stirring Effect
The induced currents interact with the powerful magnetic field, creating forces (Lorentz forces) that cause the molten metal to move and circulate vigorously within the crucible. This electromagnetic stirring is a defining characteristic of induction melting.
This constant motion ensures a consistent temperature throughout the melt and guarantees that any alloying elements are mixed thoroughly, resulting in a perfectly homogenous final product.
Enhanced Purity and Low Oxidation
Because the heat is generated inside the metal itself, there is no need for an external flame or combustion. This creates a much cleaner melting environment with very low oxygen levels, which significantly prevents oxidation and the formation of impurities. The metal never touches a heating element, only the inert crucible.
Precise Temperature Management
The power supplied to the induction coil can be adjusted with extreme precision. This gives operators fine-grained control over the heating rate and final temperature of the melt, which is critical for meeting the strict metallurgical requirements of sensitive alloys.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While powerful, the induction process is governed by specific principles that create limitations and require careful management.
Material Requirement: Conductivity
The fundamental principle of induction heating relies on the material being an electrical conductor. The process is highly inefficient or entirely ineffective on non-conductive materials like ceramics or certain types of slag.
Crucible Integrity
The crucible, typically made of graphite or ceramic, is a critical component. It must be able to withstand extreme thermal shock while also being chemically inert to the molten metal. A poorly chosen or compromised crucible can become a source of contamination, defeating one of the key benefits of the process.
Stirring Intensity
While the stirring effect is usually a major advantage, an overly vigorous stir can sometimes increase gas absorption from the atmosphere or accelerate crucible erosion in certain applications. Controlling the power frequency and coil design helps manage this effect.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Your specific goal will determine which physical aspect of induction melting is most valuable to you.
- If your primary focus is alloy homogeneity: The automatic and vigorous electromagnetic stirring is the most critical feature, as it guarantees a perfectly blended final material.
- If your primary focus is high purity: The clean, contactless heating in a controlled environment is the key benefit, minimizing oxidation and contamination for precious metals or superalloys.
- If your primary focus is speed and efficiency: The direct internal heating provides unparalleled speed and energy efficiency compared to traditional furnace methods that must heat a chamber first.
Ultimately, induction melting provides a level of control over a metal's physical state that is simply unattainable with most other methods.
Summary Table:
| Physical Effect | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Intense Internal Heating | Rapid, uniform melting from within via Joule heating |
| Electromagnetic Stirring | Ensures homogeneous mixing and consistent temperature |
| Enhanced Purity | Low oxidation and contamination in a contactless environment |
| Precise Temperature Control | Fine-grained management for sensitive alloys |
Unlock the full potential of induction melting for your laboratory! At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Whether you're focused on alloy homogeneity, high purity, or efficiency, our expertise ensures optimal results. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your metal melting processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the common applications of Vacuum Induction Melting? Essential for High-Performance Metals and Alloys
- What is vacuum induction melting technology and why is it important? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications
- What is the purpose of vacuum melting, casting and re-melting equipment? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications
- What are some common applications of vacuum induction melting and casting (VIM&C)? Essential for Aerospace, Medical, and Nuclear Industries
- How does vacuum melting technology contribute to sustainability? Boost Durability and Recycling Efficiency



















