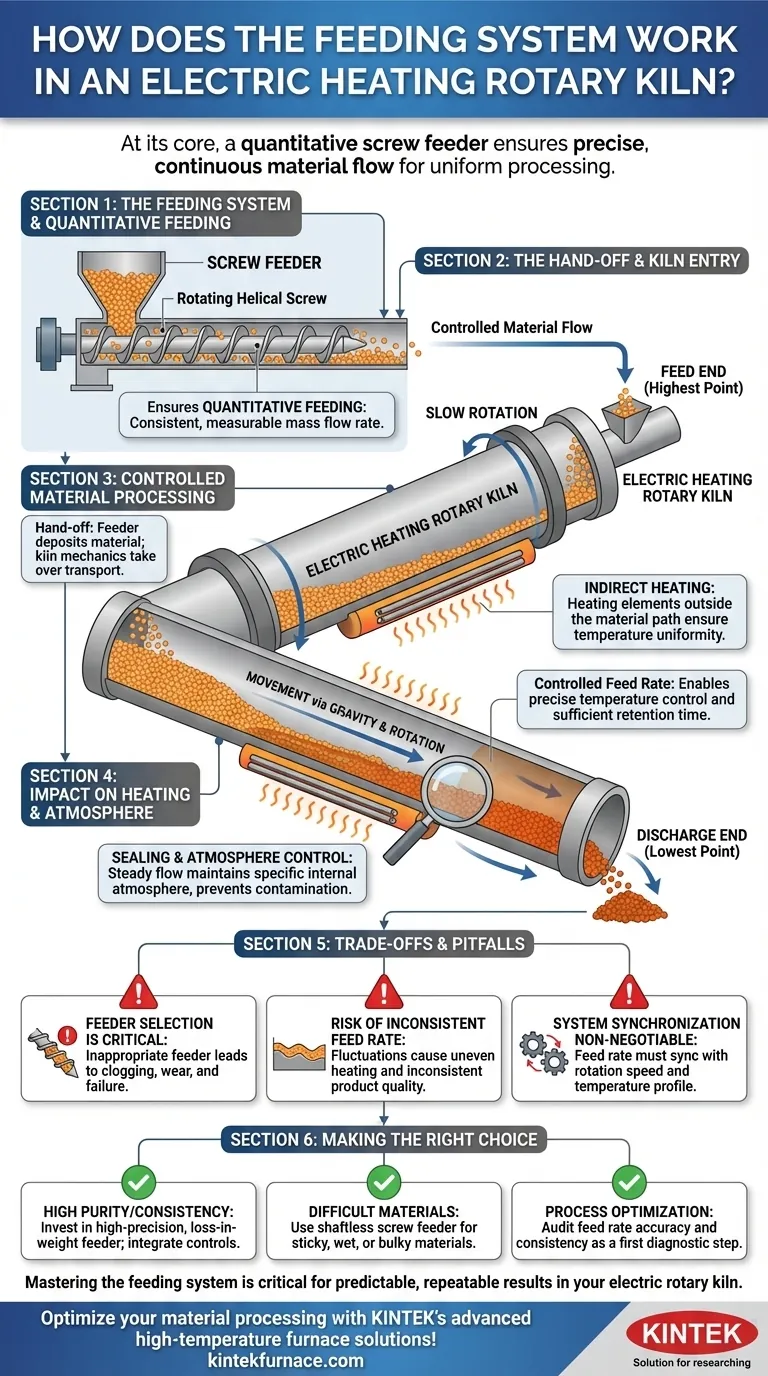
At its core, the feeding system in an electric heating rotary kiln uses a quantitative device, typically a screw feeder, to introduce a precise and continuous flow of material into the high end of the inclined kiln. This controlled entry is the critical first step that ensures the material moves predictably through the various heating zones, allowing for uniform temperature exposure and consistent processing.
The feeding system's primary function is not simply to add material, but to establish a stable, predictable flow rate. This initial control is the foundation upon which the kiln's entire process of uniform heating, controlled reaction time, and consistent product quality is built.

The Role of the Feeding System in the Overall Process
The feeding system is the starting point of a highly controlled and sequential operation. Its performance directly dictates the effectiveness of every subsequent stage within the rotary kiln.
Quantitative Feeding: The Screw Feeder
The most common feeding mechanism is a screw feeder. This device uses a rotating helical screw blade within a tube to move a specific volume of material with each rotation.
This design ensures quantitative feeding—a consistent and measurable mass flow rate. Depending on the material's characteristics, such as particle size, flowability, and abrasiveness, different designs like single-screw, double-screw, or shaftless screw feeders are used.
The Hand-off to the Kiln Body
The feeder deposits the material at the feed end of the kiln, which is the highest point of the slightly inclined cylindrical drum. From this moment, the kiln's own mechanics take over the transport of the material.
How Feeding Enables Controlled Material Processing
A steady feed rate is essential for the controlled, continuous heat treatment that defines a rotary kiln's operation. It creates a predictable flow that allows the system's other components to function optimally.
The Principle of Inclination and Rotation
Once inside the kiln, the material moves from the high feed end toward the low discharge end due to two forces: gravity (from the kiln's slight slope) and the tumbling motion from the slow rotation of the drum.
A constant feed rate ensures a consistent "bed" of material moves steadily through the kiln, preventing piling up or gaps in the flow.
The Impact on Heating Uniformity
Electric rotary kilns use indirect heating, where heating elements (often silicon carbide rods) are positioned outside the material path, typically at the bottom of the kiln.
Because the feeding is consistent, the volume of material passing through each heating zone is predictable. This allows the temperature in each zone to be precisely controlled, ensuring every particle receives the same amount of thermal energy for the required retention time. The tumbling action further exposes all material surfaces to the radiant heat.
Sealing and Atmosphere Control
The controlled feed rate works in concert with the kiln's sealed design. By ensuring a steady flow, it becomes easier to maintain the specific internal atmosphere required for many chemical reactions, preventing unwanted contamination or oxidation.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Pitfalls
While effective, the success of the feeding system is contingent on proper design and operation. Missteps here can undermine the entire process.
Feeder Selection is Critical
The choice of screw feeder is not arbitrary. A material that is sticky or has poor flowability can easily clog a standard single-screw feeder. Using an inappropriate feeder, like one not designed for abrasive materials, will lead to premature wear, inconsistent flow, and process failure.
The Risk of Inconsistent Feed Rate
If the feed rate fluctuates, the material distribution inside the kiln becomes uneven. This leads directly to inconsistent product quality. Some material will be under-heated and under-reacted, while other material may be over-heated and degraded.
System Synchronization is Non-Negotiable
The feed rate must be perfectly synchronized with the kiln's rotation speed and the temperature profile of the heating zones. A change in one variable requires adjusting the others. Operating these systems independently without integration guarantees poor and unpredictable results.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The design and operation of your feeding system should be directly tied to your final processing objective.
- If your primary focus is high product purity and consistency: Invest in a high-precision, loss-in-weight screw feeder and ensure its controls are tightly integrated with the kiln's rotation and temperature systems.
- If your primary focus is processing difficult-to-handle materials: A shaftless screw feeder is often the superior choice for sticky, wet, or bulky materials as it is less prone to clogging and ensures a more reliable flow.
- If your primary focus is process optimization: Your first diagnostic step should always be to audit the feed rate. Validating its accuracy and consistency will often reveal the root cause of downstream inconsistencies.
Mastering the feeding system is the first and most critical step toward achieving predictable and repeatable results from your electric rotary kiln.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Details |
|---|---|
| Feeding Mechanism | Uses screw feeders (e.g., single, double, shaftless) for quantitative feeding. |
| Primary Function | Establishes stable, predictable flow rate for uniform material processing. |
| Impact on Process | Enables consistent heating, controlled reaction time, and atmosphere management. |
| Common Challenges | Feeder clogging, inconsistent flow, and poor synchronization with kiln systems. |
| Selection Criteria | Based on material properties like abrasiveness, flowability, and processing goals. |
Optimize your material processing with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with reliable equipment like Rotary Furnaces, designed for precise feeding and uniform heating. Our strong deep customization capability ensures tailored solutions to meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how our products can enhance your process efficiency and product quality!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
People Also Ask
- What are the uses of rotary kilns in the building materials industry besides cement clinker? Key Applications Explained
- What are some drying applications of electromagnetic rotary kilns? Discover Efficient, Precise Drying Solutions
- What are the main components in the construction of a rotary kiln? A Guide to the Core Systems
- How is bed depth controlled in a rotary kiln and why is it important? Optimize Heat Transfer and Efficiency
- What is the basic working principle of a rotary kiln? Master Industrial Thermal Processing Efficiency



















