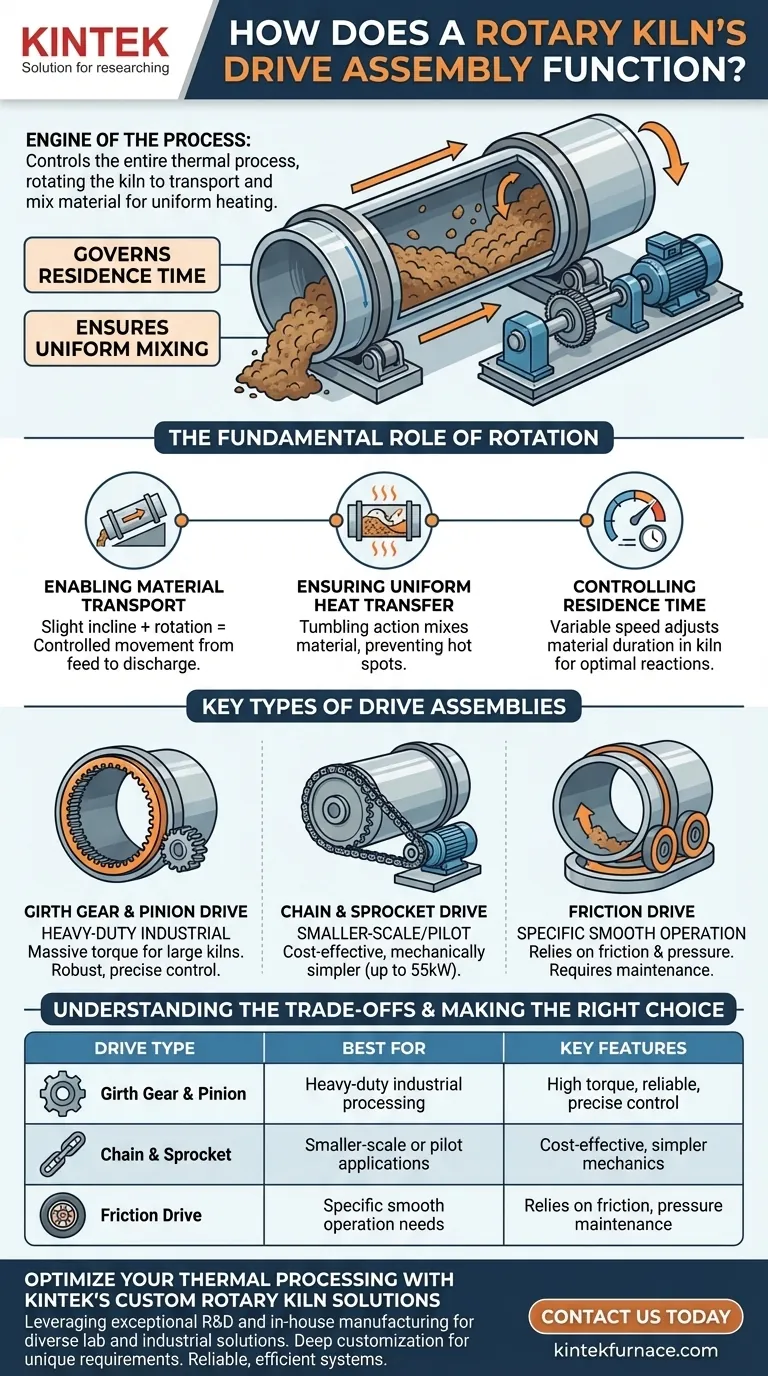
At its core, a rotary kiln's drive assembly is the engine that controls the entire thermal process. It uses a motor connected to a transmission system—most commonly a large gear, but sometimes chains or friction wheels—to slowly and consistently rotate the kiln's cylindrical drum. This controlled rotation is the fundamental mechanism that transports material through the heated chamber and tumbles it to ensure uniform heating, which is essential for inducing the desired chemical reaction or physical change.
The drive assembly is more than just a motor; it is a precision control system. Its primary function is to govern the residence time and mixing of material inside the kiln, making the choice of drive type a critical engineering decision tied directly to the scale and requirements of the process.
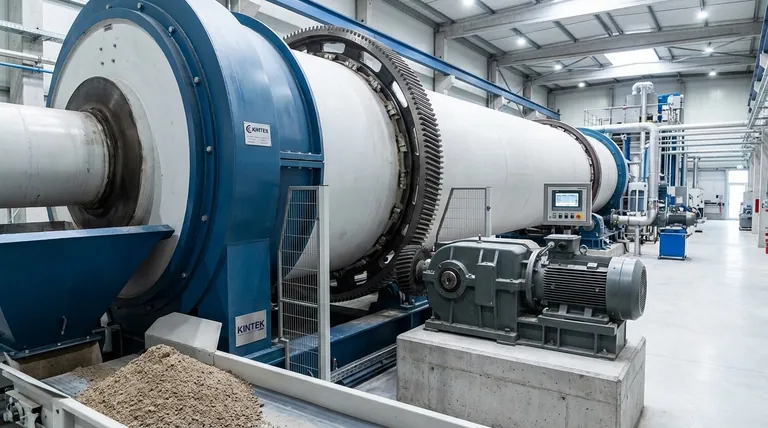

The Fundamental Role of Rotation in Kiln Processing
The drive assembly doesn't just spin the kiln; it enables the core principles of its operation. The speed and consistency of the rotation directly impact product quality and efficiency.
Enabling Material Transport
The kiln drum is set at a slight incline. The drive assembly's slow rotation, combined with this angle, gently tumbles the material, causing it to move steadily from the upper feed end to the lower discharge end.
Without this controlled movement, the material would either pass through too quickly or not at all, making continuous processing impossible.
Ensuring Uniform Heat Transfer
The primary goal of a kiln is to heat every particle of the material to a specific temperature. The tumbling action created by the drive constantly mixes the material bed.
This ensures all particles are evenly exposed to the heat source, whether it's a direct flame inside the kiln or external electric heaters. This prevents hot spots and guarantees a consistent, high-quality final product.
Controlling Residence Time
Residence time—the total duration a material spends inside the kiln—is arguably the most critical process variable. The drive's motor is almost always a variable-speed unit.
By adjusting the rotational speed, operators can precisely control the residence time. Slower rotation increases the time material spends in the kiln for reactions that require longer heating, while faster rotation increases throughput for quicker processes.
Key Types of Drive Assemblies
While the goal is the same, the mechanical method used to turn the kiln varies based on the size and demands of the application.
Girth Gear and Pinion Drive
This is the most common design for heavy-duty, industrial-scale kilns. A massive ring gear, called a girth gear, is mounted around the circumference of the kiln shell.
A small, high-torque pinion gear, driven by the motor and a gearbox, engages with the girth gear to rotate the entire drum. This system is robust and can deliver the immense torque needed for very large and heavy kilns.
Chain and Sprocket Drive
For smaller or lower-power kilns (typically those requiring 55 kW or less), a chain and sprocket system is a viable and cost-effective alternative.
Similar to a bicycle chain, a large sprocket is fixed to the kiln shell and is driven by a motor via a roller chain. This design is mechanically simpler but is not suitable for the high torque demands of large-scale operations.
Friction Drive
In some designs, a set of high-friction drive wheels are pressed against a smooth steel riding ring on the kiln shell. As the drive wheels turn, they rotate the kiln drum through friction.
This method can offer smooth operation but relies heavily on maintaining the correct pressure between the wheels and the kiln shell.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a drive assembly involves balancing power, cost, and maintenance requirements. There is no single "best" option; there is only the right option for the specific application.
Power and Scale
This is the primary deciding factor. The immense weight of a large industrial kiln filled with material requires the massive torque that only a gear and pinion system can reliably deliver.
For smaller pilot plants or applications with lighter loads, a chain drive provides sufficient power at a lower capital cost.
Maintenance and Reliability
Girth gear systems are designed for decades of continuous operation. They are enclosed and robust, but repairing a major component like the gear itself is a significant undertaking.
Chain drives are more exposed to the elements and may require more frequent tensioning and lubrication. However, replacing a chain or sprocket is typically a simpler and faster task.
Precision and Control
Modern gear drives, especially when paired with a Variable Frequency Drive (VFD) on the motor, offer exceptionally precise and responsive speed control. This is critical for processes where residence time must be managed to within seconds.
While chain drives also use variable-speed motors, the inherent mechanics can introduce slightly more slack or variation into the system compared to a tightly meshed gear.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The optimal drive assembly is not a one-size-fits-all solution; it is dictated by the scale and precision of your thermal processing operation.
- If your primary focus is heavy-duty, high-throughput industrial processing: A girth gear and pinion system is the industry standard for its ability to deliver the high torque and reliability required for large-scale kilns.
- If your primary focus is smaller-scale or pilot applications: A chain and sprocket drive offers a cost-effective and mechanically simpler solution perfectly suitable for lower power requirements.
- If your primary focus is absolute process control and consistency: A gear drive paired with a modern variable frequency motor provides the most precise and repeatable control over rotational speed and material residence time.
Ultimately, the drive assembly translates electrical power into process control, making it the critical component for achieving consistent and predictable results from your rotary kiln.
Summary Table:
| Drive Type | Best For | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Girth Gear & Pinion | Heavy-duty industrial processing | High torque, reliable, precise control |
| Chain & Sprocket | Smaller-scale or pilot applications | Cost-effective, simpler mechanics |
| Friction Drive | Specific smooth operation needs | Relies on friction, requires pressure maintenance |
Optimize Your Thermal Processing with KINTEK's Custom Rotary Kiln Solutions
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Rotary Furnaces, is complemented by strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Whether you need a robust girth gear drive for industrial scale or a cost-effective chain drive for pilot projects, we deliver reliable, efficient systems tailored to your goals.
Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can enhance your process control and productivity!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- What are some common processes carried out in rotary kilns? Unlock Efficient Material Transformation Solutions
- What benefits were gained from converting an indirectly heated rotary kiln to electric heating? Boost Efficiency and Cut Costs
- How are rotary kilns utilized in environmental protection? Transforming Waste into Resources
- What processes are suitable for indirect rotary kilns besides lithium processing? Unlock Versatile Thermal Solutions
- What temperature can electromagnetic rotary kilns reach? Up to 1100°C for High-Efficiency Heating
- What are the typical processes performed in rotary kilns? Unlock Efficient Material Transformation
- How does a rotary kiln electric furnace differ from a retort furnace? Choose the Right Furnace for Your Materials
- What are the maintenance benefits of indirectly fired rotary kilns? Lower Costs, Higher Uptime



















