In Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), precise temperature control is not merely a process parameter; it is the fundamental mechanism that dictates the outcome. It directly governs the reaction kinetics, influencing the uniformity, crystalline quality, and chemical purity of the deposited thin film. Without it, the process becomes unpredictable and unreliable.
The core challenge of CVD is managing a delicate balance between chemical reactions in the gas phase and on the substrate surface. Precise temperature control is the primary tool for managing this balance, directly translating thermal energy into predictable material properties.

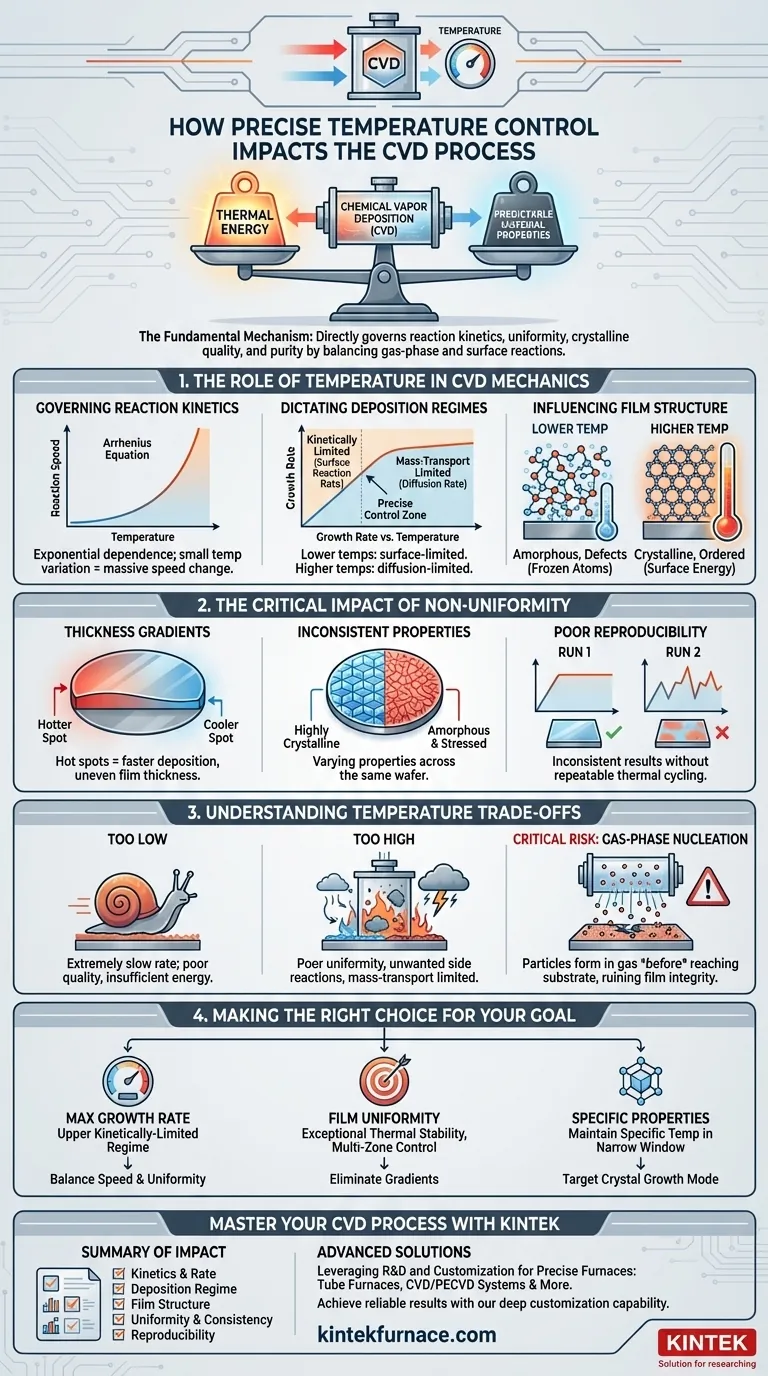
The Role of Temperature in CVD Mechanics
Temperature is the activation energy source for the entire CVD process. Every step, from breaking down precursor gases to forming atomic bonds on the substrate, is a thermally driven event.
Governing Reaction Kinetics
The rate of chemical reactions in CVD is exponentially dependent on temperature, a relationship described by the Arrhenius equation. A small variation in temperature can cause a massive change in reaction speed.
This means temperature directly controls how quickly precursor gas molecules decompose into their reactive components and how fast those components incorporate into the growing film.
Dictating Deposition Regimes
The CVD process operates in distinct regimes based on temperature. At lower temperatures, the process is kinetically limited; the growth rate is limited only by how fast the chemical reactions can occur on the surface.
At higher temperatures, the process becomes mass-transport limited. Here, the surface reactions are so fast that the growth rate is limited by how quickly new reactant molecules can diffuse through the gas to reach the substrate. Precise control ensures you operate in the desired regime for your specific goal.
Influencing Film Structure
Temperature heavily influences the final microstructure of the film. Higher temperatures generally provide more surface energy for atoms to arrange themselves into a well-ordered, crystalline lattice.
Conversely, lower temperatures can "freeze" atoms in place before they find their ideal lattice sites, resulting in an amorphous or polycrystalline structure with smaller grains and more defects.
The Critical Impact of Non-Uniformity
Even small temperature variations across the surface of the substrate can have dramatic and detrimental effects on the final product.
Thickness Gradients
If one area of a substrate is just a few degrees hotter than another, the deposition rate will be significantly higher in that spot. This results in a film that is thicker on one side than the other, which is often a critical failure for semiconductor and optical applications.
Inconsistent Material Properties
A temperature gradient can also cause variations in material properties across the same wafer. One area might be highly crystalline and stressed, while another is amorphous and relaxed, leading to unpredictable device performance.
Poor Reproducibility
Without precise, repeatable thermal cycling from run to run, it is impossible to achieve consistent results. A process that works one day may fail the next if the temperature profile deviates even slightly, destroying manufacturing yield.
Understanding the Temperature Trade-offs
Choosing the right temperature is not about finding the highest or lowest setting; it's about operating within a specific "process window" and understanding the consequences of being outside it.
The "Too Low" Problem
Operating at a temperature that is too low results in an extremely slow deposition rate, making the process economically unviable. The resulting film quality may also be poor due to insufficient energy for proper atomic bonding and defect reduction.
The "Too High" Problem
Excessively high temperatures can trigger unwanted side reactions or cause the film to grow in the mass-transport limited regime. This often leads to poor uniformity as the reactants are consumed near the gas inlet before they can spread across the entire substrate.
The Risk of Gas-Phase Nucleation
A critical failure mode at very high temperatures is gas-phase nucleation. The precursor gases react and form particles in the hot gas before ever reaching the substrate. These particles then rain down onto the surface, creating defects and ruining the film's structural integrity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The ideal temperature is entirely dependent on the desired outcome. Precise control allows you to intentionally target these outcomes with confidence.
- If your primary focus is maximum growth rate: Operate at the upper end of the kinetically-limited regime, just before mass-transport limitations and poor uniformity become dominant issues.
- If your primary focus is film uniformity: Prioritize a furnace with exceptional thermal stability and multi-zone control to eliminate any temperature gradients across the substrate, even if it means sacrificing some deposition speed.
- If your primary focus is specific material properties (e.g., high crystallinity): You must precisely maintain the specific temperature that favors the desired crystal growth mode, which often exists within a very narrow process window.
Ultimately, mastering the thermal dynamics of your CVD system is the key to transforming it from an unpredictable reactor into a precise manufacturing tool.
Summary Table:
| Temperature Control Aspect | Impact on CVD Process |
|---|---|
| Reaction Kinetics | Governs deposition rate and precursor decomposition via Arrhenius equation |
| Deposition Regimes | Determines kinetically-limited vs. mass-transport-limited growth |
| Film Structure | Influences crystallinity, grain size, and defect levels |
| Uniformity | Prevents thickness gradients and inconsistent material properties |
| Reproducibility | Ensures consistent results across multiple runs |
Master your CVD process with KINTEK's advanced furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with precise high-temperature furnaces like Tube Furnaces, CVD/PECVD Systems, and more. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we meet your unique experimental needs for uniform, high-quality thin films. Contact us today to optimize your temperature control and achieve reliable results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Why are CVD tube furnace sintering systems indispensable for 2D material research and production? Unlock Atomic-Scale Precision
- Why are advanced materials and composites important? Unlock Next-Gen Performance in Aerospace, Auto, and More
- What is the working principle of a CVD tube furnace? Achieve Precise Thin Film Deposition for Your Lab
- What makes a CVD Tube Furnace essential for material science and nanotechnology? Unlock Precision in Material Synthesis
- Where is a CVD Tube Furnace commonly used? Essential for High-Tech Materials and Electronics



















