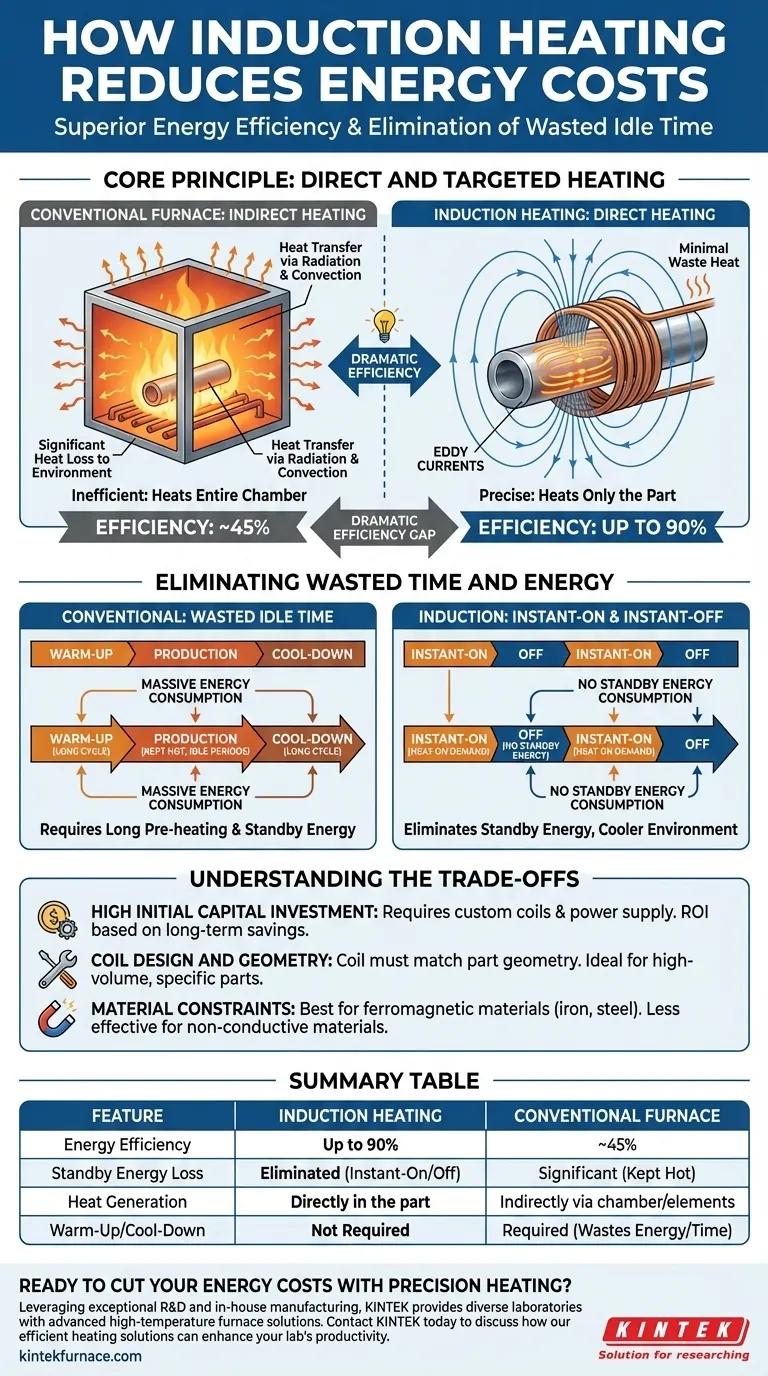
At its core, induction heating reduces energy costs through two primary mechanisms: superior energy efficiency and the elimination of wasted idle time. Unlike traditional furnaces that must heat an entire chamber, induction generates heat directly inside the workpiece, converting up to 90% of its energy into useful heat, compared to as low as 45% for many conventional methods.
The fundamental advantage of induction is precision. By heating only the part and only when needed, it minimizes the two largest sources of energy waste in industrial heating: heat loss to the environment and the energy consumed keeping a furnace hot during idle periods.
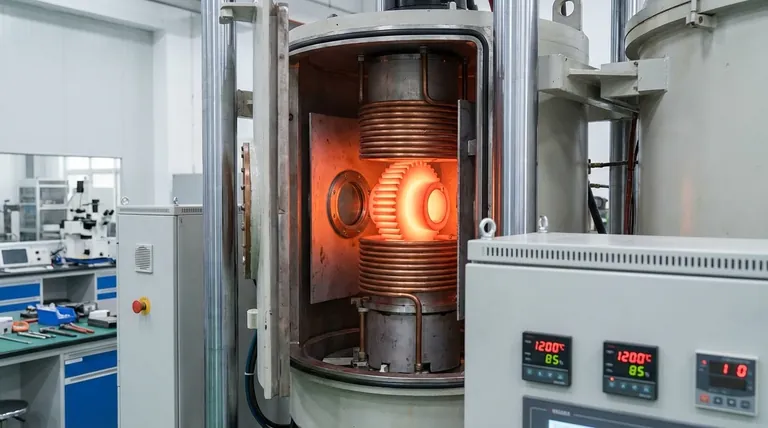

The Core Principle: Direct and Targeted Heating
To understand the cost savings, you must first understand how fundamentally different induction is from a conventional furnace. It's the difference between boiling water in a pot on a stove versus heating it with a microwave.
How Induction Generates Heat
Induction heating uses a powerful, high-frequency alternating current passed through a copper coil. This creates a dynamic magnetic field around the coil.
When a conductive part (like steel) is placed within this field, the field induces electrical currents, known as eddy currents, directly inside the material. The material's natural resistance to the flow of these currents generates precise, rapid, and localized heat.
Efficiency by Design
A traditional fuel-fired or electric resistance furnace operates by indirect heating. It first heats an internal chamber or heating elements, which then transfer that heat to the part via radiation and convection. This process is inherently inefficient.
A significant portion of the energy is wasted heating the furnace walls, the door, and the surrounding air. In contrast, induction's direct heating method converts nearly all the electrical energy drawn into actual heat within the part. This explains the dramatic efficiency gap, with induction achieving up to 90% efficiency compared to the 45% typical of a batch furnace.
Eliminating Wasted Time and Energy
Beyond pure conversion efficiency, induction's operational model creates significant secondary energy savings that compound over time.
No Warm-Up or Cool-Down Cycles
Conventional furnaces require long pre-heating cycles to reach operating temperature and must often be kept hot between shifts or batches to avoid repeating this process, consuming massive amounts of energy while producing nothing.
Induction systems are instant-on and instant-off. Heat is generated the moment the power is applied and stops the moment it is turned off. This "heat on demand" capability completely eliminates standby energy consumption.
Reduced Heat Loss to the Environment
Because the heat is generated inside the part, the induction coil itself remains cool. This results in very little waste heat being radiated into the surrounding workspace.
This not only saves the energy that would have been lost but also contributes to a cooler, safer, and more comfortable working environment, potentially reducing the load on factory HVAC systems.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly efficient, induction heating is not a universal solution. An objective assessment requires acknowledging its specific limitations.
High Initial Capital Investment
The upfront cost of an induction heating system, including the power supply and custom coils, is typically higher than that of a simple conventional furnace. The return on investment is calculated through long-term energy and operational savings.
Coil Design and Geometry
The efficiency of an induction system is highly dependent on the coil design. The coil must be carefully engineered to match the geometry of the part being heated.
This makes induction ideal for dedicated, high-volume production of specific parts but less flexible than a batch furnace for heating a wide variety of shapes and sizes on the fly without changing the coil.
Material Constraints
Induction works best on electrically conductive materials, particularly ferromagnetic metals like iron and steel. It is less effective or entirely unsuitable for non-conductive materials like ceramics or many polymers without the use of a conductive susceptor.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
The decision to adopt induction heating must be based on a clear analysis of your production goals and operational realities.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, repeatable production: Induction offers unparalleled speed, consistency, and energy efficiency per part.
- If your primary focus is reducing long-term operational costs: The significant reduction in energy consumption from induction often provides a clear and compelling return on the initial investment.
- If your primary focus is flexible heating for diverse, low-volume parts: The need for part-specific coils may make a conventional batch furnace a more practical choice.
Ultimately, understanding these principles empowers you to see past the initial cost and evaluate induction based on its total impact on your process efficiency and bottom line.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Induction Heating | Conventional Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Efficiency | Up to 90% | Typically ~45% |
| Standby Energy Loss | Eliminated (Instant-On/Off) | Significant (Kept Hot) |
| Heat Generation | Directly in the part | Indirectly via chamber/elements |
| Warm-Up/Cool-Down | Not Required | Required (Wastes Energy/Time) |
Ready to cut your energy costs with precision heating?
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, and Rotary Furnaces, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements.
Contact KINTEL today to discuss how our efficient heating solutions can enhance your lab's productivity and significantly reduce your operational expenses.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What other types of furnaces are related to hot pressing? Explore Key Thermal Processing Technologies
- How does the use of vacuum in hot-pressing affect the material processing? Achieve Denser, Purer, and Stronger Materials
- What role does Vacuum Hot Press technology play in the automotive industry? Boost EV Batteries, Safety, and Efficiency
- What is the process of hot pressing? A Guide to Achieving Superior Material Density
- What are the advantages of ceramic/metal composites produced using a vacuum press? Achieve Superior Strength and Durability



















