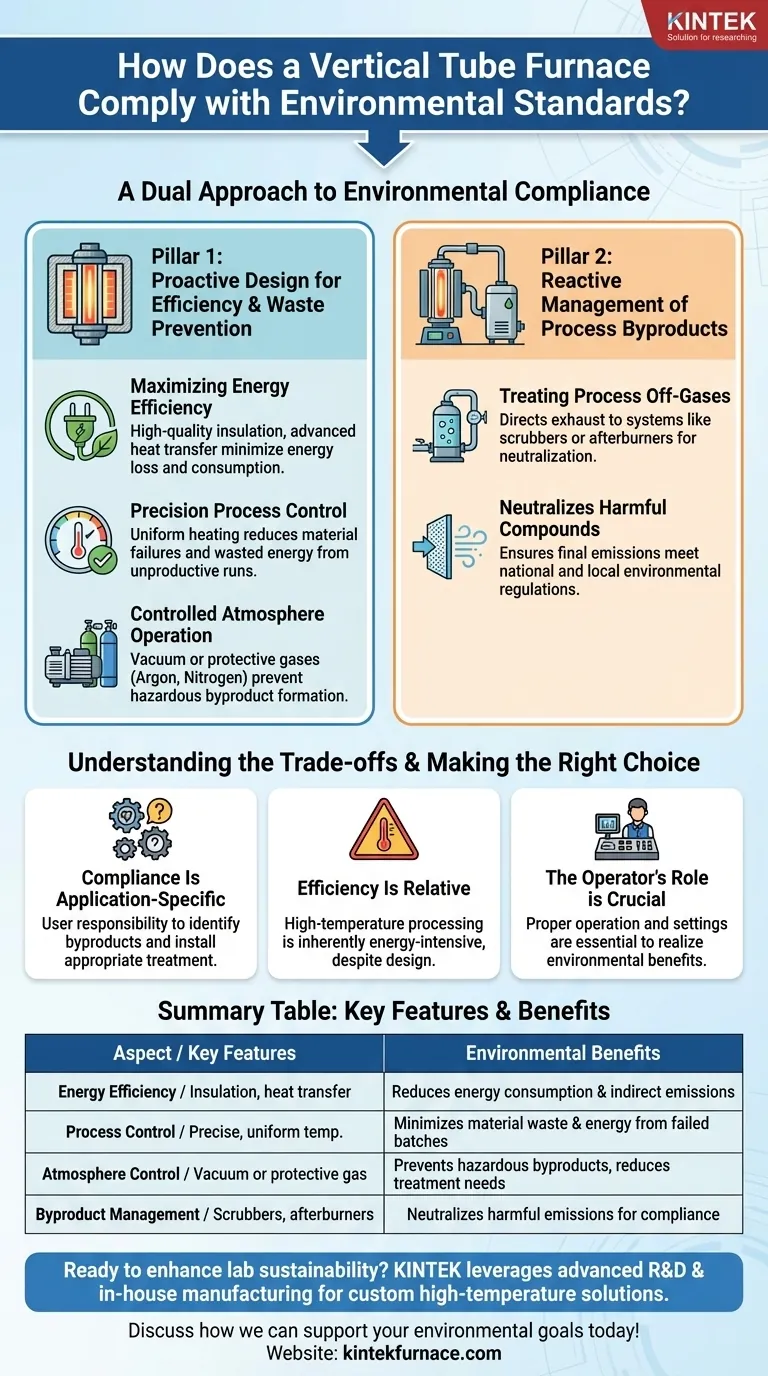
At its core, a vertical tube furnace complies with environmental standards through a combination of treating process byproducts and implementing design principles that minimize energy and material waste. This dual approach addresses both the direct emissions generated during operation and the indirect environmental impact associated with high energy consumption.
True environmental compliance in a vertical tube furnace is not just about filtering exhaust. It is an outcome of a holistic design focused on energy efficiency, precise process control, and proactive waste prevention from the start.

A Two-Pronged Approach to Environmental Compliance
A furnace's environmental performance hinges on two distinct strategies: proactively minimizing waste through efficient design and reactively managing any byproducts that are created.
Pillar 1: Proactive Design for Efficiency and Waste Prevention
Modern furnace design prioritizes efficiency, which directly translates to a smaller environmental footprint.
Maximizing Energy Efficiency
High-quality insulation and advanced heat transfer mechanisms are critical. By minimizing heat loss to the surrounding environment, the furnace consumes significantly less energy to reach and maintain the target temperature.
This reduction in energy consumption is a cornerstone of "green production," lowering both operational costs and the indirect emissions associated with power generation.
Precision Process Control
Vertical tube furnaces offer exceptionally precise and uniform temperature control. This consistency is not just for process quality; it's a key environmental feature.
Uniform heating eliminates hot and cold spots, which reduces the likelihood of failed or inconsistent batches. Fewer failures mean less wasted raw material and less energy consumed on unproductive runs.
Controlled Atmosphere Operation
The ability to operate under a vacuum or a specific protective gas (like argon or nitrogen) is a powerful environmental tool.
By removing reactive gases like oxygen, you can prevent the formation of unwanted oxides or other hazardous byproducts. This proactive approach to process chemistry can eliminate or drastically reduce the need for downstream gas treatment.
Pillar 2: Reactive Management of Process Byproducts
Even in a highly controlled process, some byproducts may be unavoidable depending on the materials being heated.
Treating Process Off-Gases
The most direct compliance mechanism is the treatment of waste gases, often called off-gases. The furnace is designed to have its exhaust directed into a secondary system.
This system, such as a chemical scrubber or an afterburner, neutralizes or captures harmful compounds before they are released, ensuring the final emissions meet national and local environmental regulations.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While designed for compliance, the furnace's environmental performance is not automatic. It depends heavily on proper configuration and an understanding of its operational realities.
Compliance Is Application-Specific
The furnace itself does not generate emissions; the process does. The type of off-gas treatment required is entirely dependent on the materials you are heating and the reactions that occur.
The user is responsible for identifying potential byproducts from their specific application and installing the appropriate gas treatment system to manage them.
Efficiency Is Relative
Even the most energy-efficient furnace consumes a substantial amount of power to achieve high temperatures. While design features minimize this consumption, high-temperature processing is inherently energy-intensive.
The Operator's Role is Crucial
The environmental benefits of precision control and efficiency are only realized when the furnace is operated correctly. Improper settings or protocols can easily negate the furnace's inherent design advantages, leading to wasted energy and materials.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To ensure compliance, you must align the furnace's capabilities with your specific environmental and operational priorities.
- If your primary focus is regulatory emissions compliance: Ensure you pair the furnace with an off-gas treatment system (e.g., scrubber, afterburner) certified to handle the specific byproducts of your process.
- If your primary focus is minimizing overall environmental footprint: Prioritize a model with superior insulation, multi-zone temperature control, and the capability for controlled-atmosphere operation to reduce energy and material waste at the source.
- If your primary focus is cost-efficiency: Leverage the furnace's precise temperature and atmosphere controls to maximize yield and reduce failures, which directly lowers energy and material costs per batch.
By understanding these principles, you can configure a vertical tube furnace to meet not only regulatory standards but also the highest goals of sustainable and efficient operation.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Features | Environmental Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Efficiency | High-quality insulation, advanced heat transfer | Reduces energy consumption and indirect emissions |
| Process Control | Precise, uniform temperature control | Minimizes material waste and energy use from failed batches |
| Atmosphere Control | Vacuum or protective gas operation | Prevents hazardous byproducts, reduces need for gas treatment |
| Byproduct Management | Integration with scrubbers or afterburners | Neutralizes harmful emissions to meet regulations |
Ready to enhance your lab's sustainability with a custom vertical tube furnace? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental needs, helping you achieve superior energy efficiency, compliance, and cost savings. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your environmental goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety



















