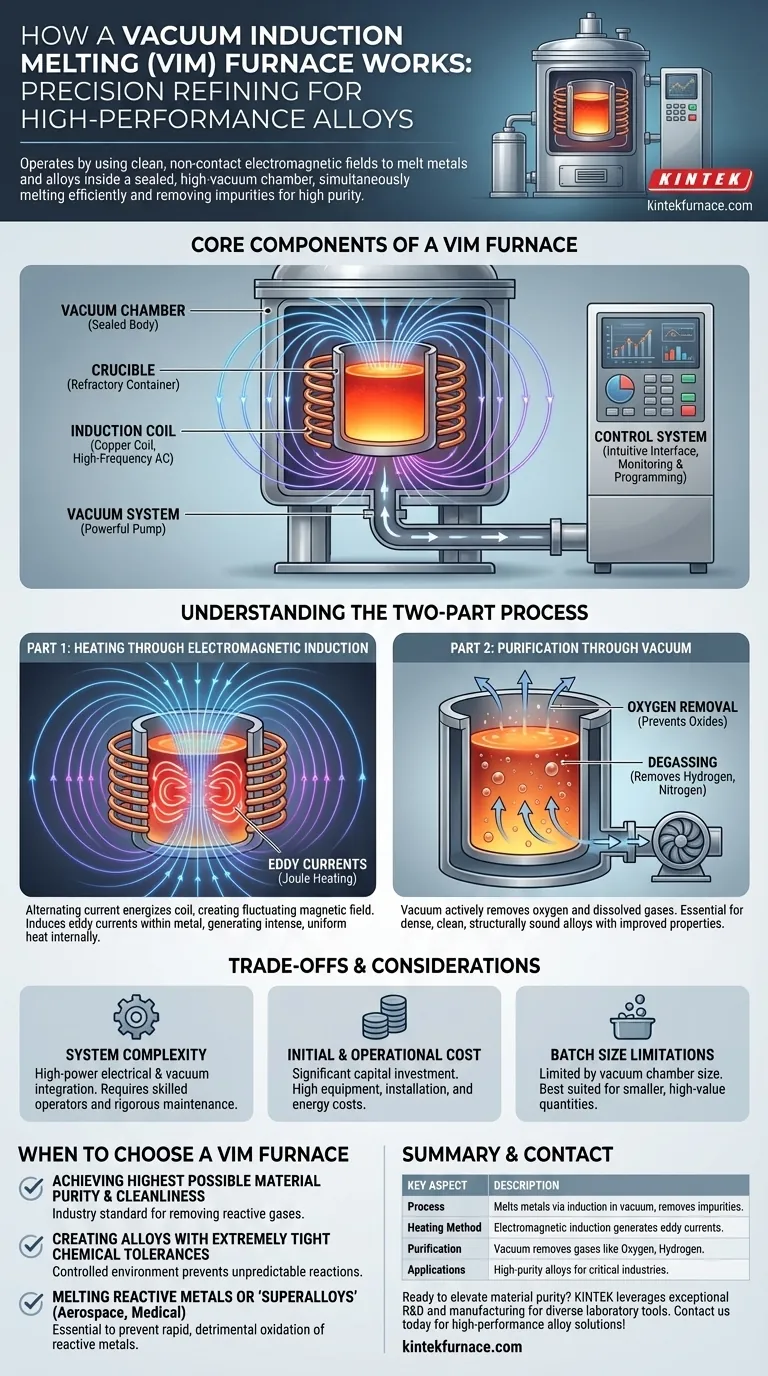
In essence, a vacuum induction melting (VIM) furnace operates by using clean, non-contact electromagnetic fields to melt metals and alloys inside a sealed, high-vacuum chamber. This dual-action process accomplishes two critical goals simultaneously: it melts the material efficiently and removes dissolved gases and impurities by exposing the liquid metal to the vacuum. The result is a final product with exceptionally high purity and tightly controlled chemical composition.
A VIM furnace is not just a tool for melting metal; it is a precision instrument for refining it. By combining the physics of induction heating with the chemistry of a vacuum, it eliminates atmospheric contamination to produce the ultra-clean, high-performance alloys demanded by the most critical industries.
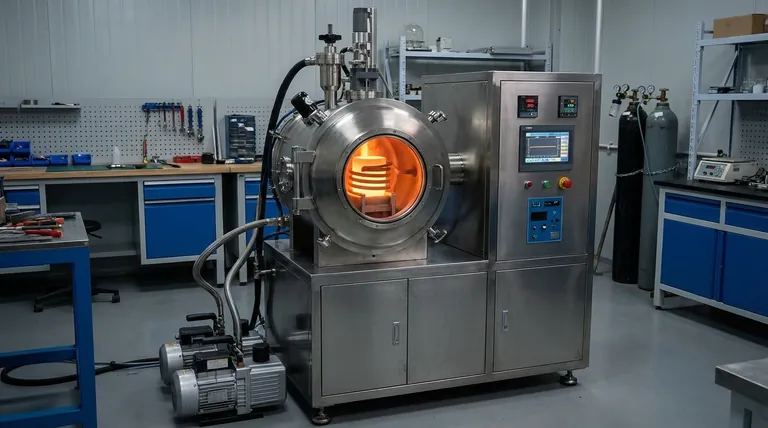

The Core Components of a VIM Furnace
To understand how a VIM furnace works, it is essential to first understand its key components, each playing a distinct and vital role in the process.
The Vacuum Chamber
The entire process takes place within an airtight furnace body, typically constructed from stainless steel or other high-temperature-resistant materials. This chamber is engineered to withstand both the intense internal heat and the powerful external pressure created by the vacuum. Its primary function is to isolate the melt from the outside atmosphere.
The Induction Coil
This is the engine of the furnace. A copper coil, through which a high-frequency alternating current (AC) is passed, sits inside the vacuum chamber (or sometimes outside, in a "cold-wall" design). It generates the powerful magnetic field required for heating but never makes physical contact with the metal.
The Crucible
Located inside the induction coil, the crucible is the refractory container that holds the raw conductive material to be melted. It must be able to withstand extreme temperatures and be chemically inert to the molten metal to avoid introducing its own impurities.
The Vacuum System
A powerful vacuum pump system is connected to the chamber. Its job is to evacuate air and other gases from the chamber before and during the melting process. This creates the controlled, low-pressure environment that is the hallmark of VIM technology.
The Control System
Modern VIM furnaces are managed by a sophisticated control system. This system allows operators to program temperature profiles, monitor the process in real-time, and log critical data. An intuitive interface is crucial for managing the complex interplay between the vacuum, power, and temperature.
Understanding the Two-Part Process
The "magic" of a VIM furnace happens through the precise coordination of two fundamental physical processes: heating via induction and purification via vacuum.
Part 1: Heating Through Electromagnetic Induction
The process begins when an alternating current energizes the induction coil, creating a rapidly fluctuating magnetic field around the crucible.
When the conductive metal is inside this field, the magnetic forces induce powerful electrical currents within the material itself. These are known as eddy currents.
Due to the metal's natural electrical resistance, these eddy currents generate intense, uniform heat throughout the material—a phenomenon called Joule heating. For magnetic materials like iron and nickel, additional heat is generated as their internal magnetic domains rapidly realign with the changing field. This method is incredibly fast and efficient because the heat is generated inside the material, not applied to its surface.
Part 2: Purification Through Vacuum
Before and during heating, the vacuum system actively removes gases from the chamber. This achieves several critical objectives.
First, it removes oxygen, preventing the formation of oxides (impurities) that degrade the quality and performance of many alloys.
Second, the vacuum exposure helps draw out other dissolved gases from the molten metal, such as hydrogen and nitrogen. This "degassing" step is vital for creating dense, structurally sound metals free from porosity. The result is an alloy with superior cleanliness and improved mechanical properties.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While powerful, a VIM furnace is a specialized tool with specific trade-offs that make it suitable for some applications but not others.
System Complexity
The integration of high-power electrical systems, high-vacuum technology, and precise thermal controls makes a VIM furnace a complex piece of equipment. It requires skilled operators and a rigorous maintenance schedule.
Initial and Operational Cost
VIM furnaces represent a significant capital investment. The cost of the equipment, installation, and the energy required for operation is substantial, which is why its use is typically reserved for high-value materials.
Batch Size Limitations
The size of the vacuum chamber inherently limits the volume of metal that can be processed in a single cycle. VIM is therefore a batch process, best suited for producing smaller, high-value quantities rather than the mass tonnage seen in conventional steelmaking.
When to Choose a VIM Furnace
A VIM furnace is a specialized tool, and its use is dictated by the required material properties of the final product.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest possible material purity and cleanliness: The VIM process is the industry standard for removing reactive gases like oxygen and nitrogen from the melt.
- If your primary focus is creating alloys with extremely tight chemical tolerances: The VIM's controlled environment prevents unpredictable reactions and ensures the final composition precisely matches the design specification.
- If your primary focus is melting reactive metals or "superalloys" used in aerospace and medical applications: The vacuum is essential to prevent the rapid, detrimental oxidation that would occur when melting materials like titanium, nickel, or cobalt alloys in air.
Ultimately, adopting the VIM process empowers you to engineer materials at a fundamental chemical level, moving beyond simple melting to true metallurgical design.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Process | Melts metals using electromagnetic induction in a vacuum chamber to remove impurities. |
| Heating Method | Electromagnetic induction generates eddy currents for efficient, uniform heating. |
| Purification | Vacuum removes dissolved gases like oxygen and hydrogen, enhancing purity. |
| Applications | High-purity alloys for aerospace, medical, and other critical industries. |
| Key Components | Vacuum chamber, induction coil, crucible, vacuum system, control system. |
Ready to elevate your material purity with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide diverse laboratories with precision tools like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how our VIM furnaces can deliver ultra-clean, high-performance alloys for your critical applications!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the core functions of the High Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace? Optimize DD5 Superalloy Purification
- What are the common applications of Vacuum Induction Melting? Essential for High-Performance Metals and Alloys
- How has vacuum smelting impacted the development of superalloys? Unlock Higher Strength and Purity
- What role does a vacuum induction melting furnace play in Fe-5%Mn-C alloys? Ensure Chemical Integrity and High Purity
- What are some common applications of vacuum induction melting and casting (VIM&C)? Essential for Aerospace, Medical, and Nuclear Industries



















