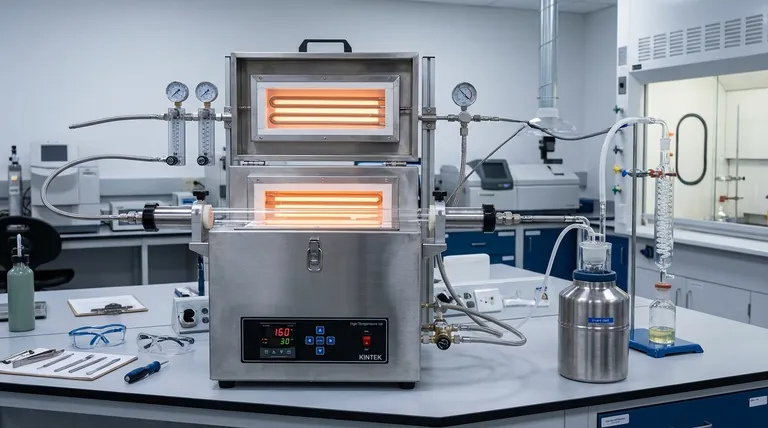
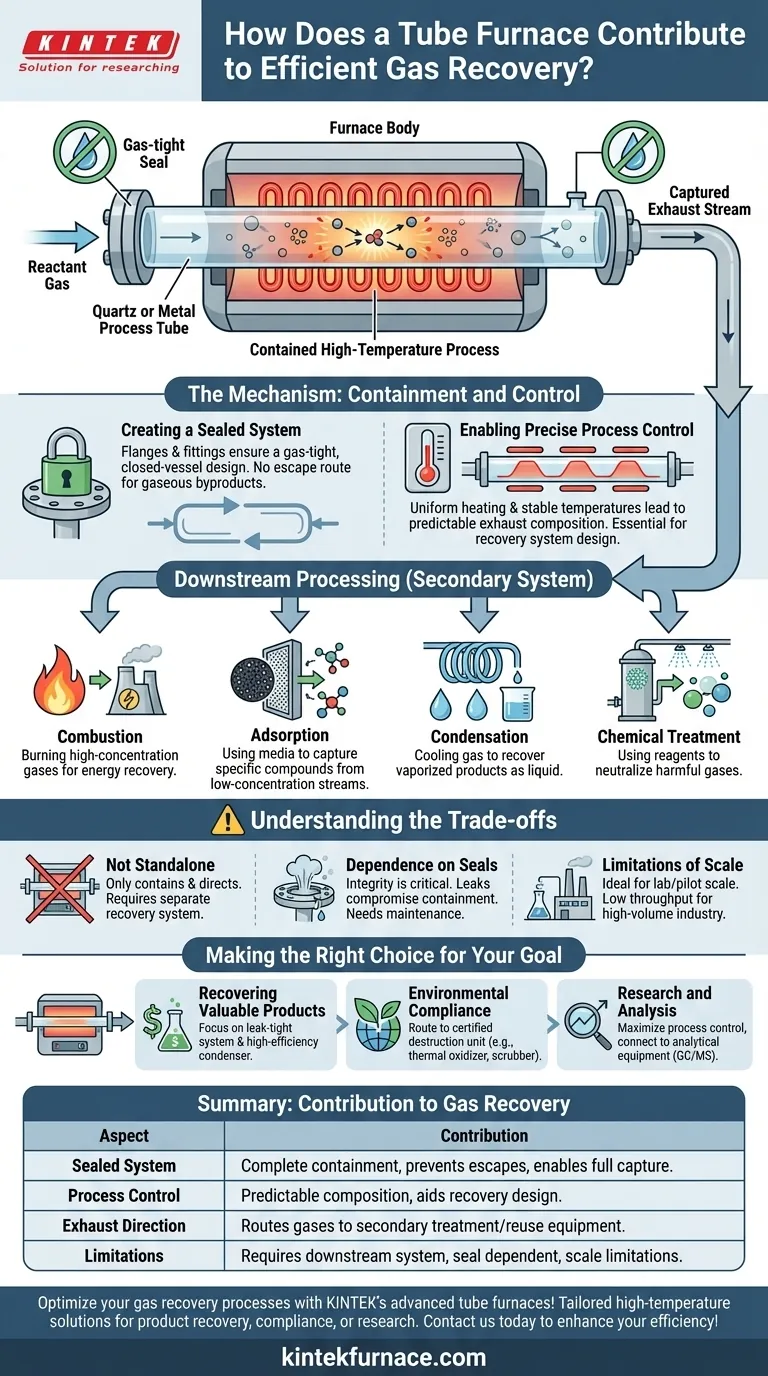
At its core, a tube furnace contributes to efficient gas recovery by creating a completely sealed and controlled environment for high-temperature processes. Unlike open or semi-open systems, this design ensures that all gaseous byproducts, such as cracked or flue gases, are fully contained within the process tube, preventing them from escaping into the atmosphere and allowing them to be captured for treatment or reuse.
A tube furnace itself does not recover gas; rather, it is a critical enabling technology. Its primary role is to contain a process, capture 100% of the gaseous exhaust, and provide a controlled stream that can be efficiently directed to a separate recovery or treatment system.

The Mechanism: Containment and Control
A tube furnace's effectiveness in gas management stems from its fundamental design, which prioritizes containment and precise process control. This allows for predictable and manageable exhaust streams.
Creating a Sealed System
A process is conducted inside a sealed tube, typically made of quartz, alumina, or metal alloy. Flanges and fittings at either end ensure the system is gas-tight.
This closed-vessel design means that any gases produced during the reaction—whether from thermal cracking, synthesis, or another process—have no escape route. They are forced to exit through a designated outlet port.
Enabling Precise Process Control
Modern tube furnaces feature multiple heating zones and high-quality insulation. This allows for extremely uniform and stable temperature profiles along the length of the tube.
This level of control ensures the chemical reactions are consistent, producing a predictable composition of exhaust gas. Knowing the exact makeup of the waste stream is essential for designing an effective recovery or neutralization system.
Directing Exhaust for Downstream Processing
The captured gas stream exiting the furnace can be piped directly to specialized secondary equipment. The furnace acts as the first step in a larger gas-handling workflow.
Depending on the goal, this downstream equipment could include systems for:
- Combustion: Burning high-concentration organic gases to recover energy.
- Adsorption: Using activated carbon or other media to capture specific compounds from a low-concentration stream.
- Condensation: Cooling the gas to recover vaporized products in liquid form.
- Chemical Treatment: Using scrubbers or reagents to neutralize acidic or harmful gases.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, a tube furnace is only one component of a complete gas recovery strategy. Understanding its limitations is key to successful implementation.
The Furnace Is Not a Standalone Solution
The most common misunderstanding is believing the furnace itself treats the gas. It only contains and directs it.
You must invest in a separate, appropriate downstream system to actually recover, treat, or analyze the exhaust. Without this, the furnace is simply a reactor that vents contained waste.
Dependence on System Integrity
The entire benefit hinges on the quality of the seals. Any leaks in the flanges, fittings, or the process tube itself will compromise containment, allowing gases to escape.
Operating at high temperatures or with corrosive gases can degrade seals and tube materials over time, requiring diligent inspection and maintenance to ensure the system remains gas-tight.
Limitations of Scale
Tube furnaces are ideal for laboratory research, pilot projects, and small-scale production where precise control is paramount.
For large-scale industrial gas recovery, the relatively low throughput of a tube furnace is a significant limitation. Different types of reactors are typically required for high-volume manufacturing environments.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To properly leverage a tube furnace for gas management, align your setup with your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is recovering valuable products: Your priority is a leak-tight system connected to a high-efficiency condenser or cold trap to liquefy and collect target compounds from the exhaust stream.
- If your primary focus is environmental compliance: Your main concern is routing the exhaust to a certified destruction unit, such as a thermal oxidizer (afterburner) or a chemical scrubber, to neutralize hazardous components.
- If your primary focus is research and analysis: You need a system with maximum process control and an outlet port connected to analytical equipment, like a gas chromatograph or mass spectrometer, to study the reaction byproducts.
Ultimately, viewing the tube furnace as a high-precision containment vessel is the key to designing an effective and efficient gas management strategy.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Contribution to Gas Recovery |
|---|---|
| Sealed System | Ensures complete containment of gases, preventing escapes and enabling full capture for downstream processing. |
| Process Control | Provides uniform heating and stable temperatures for predictable gas composition, aiding in recovery system design. |
| Exhaust Direction | Routes captured gases to secondary equipment like condensers or scrubbers for treatment or reuse. |
| Limitations | Requires separate recovery systems; dependent on seal integrity; best for lab-scale applications, not high-volume. |
Optimize your gas recovery processes with KINTEK's advanced tube furnaces! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with tailored high-temperature solutions, including Tube Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, whether for product recovery, environmental compliance, or research analysis. Contact us today to discuss how our reliable equipment can enhance your efficiency and outcomes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety



















