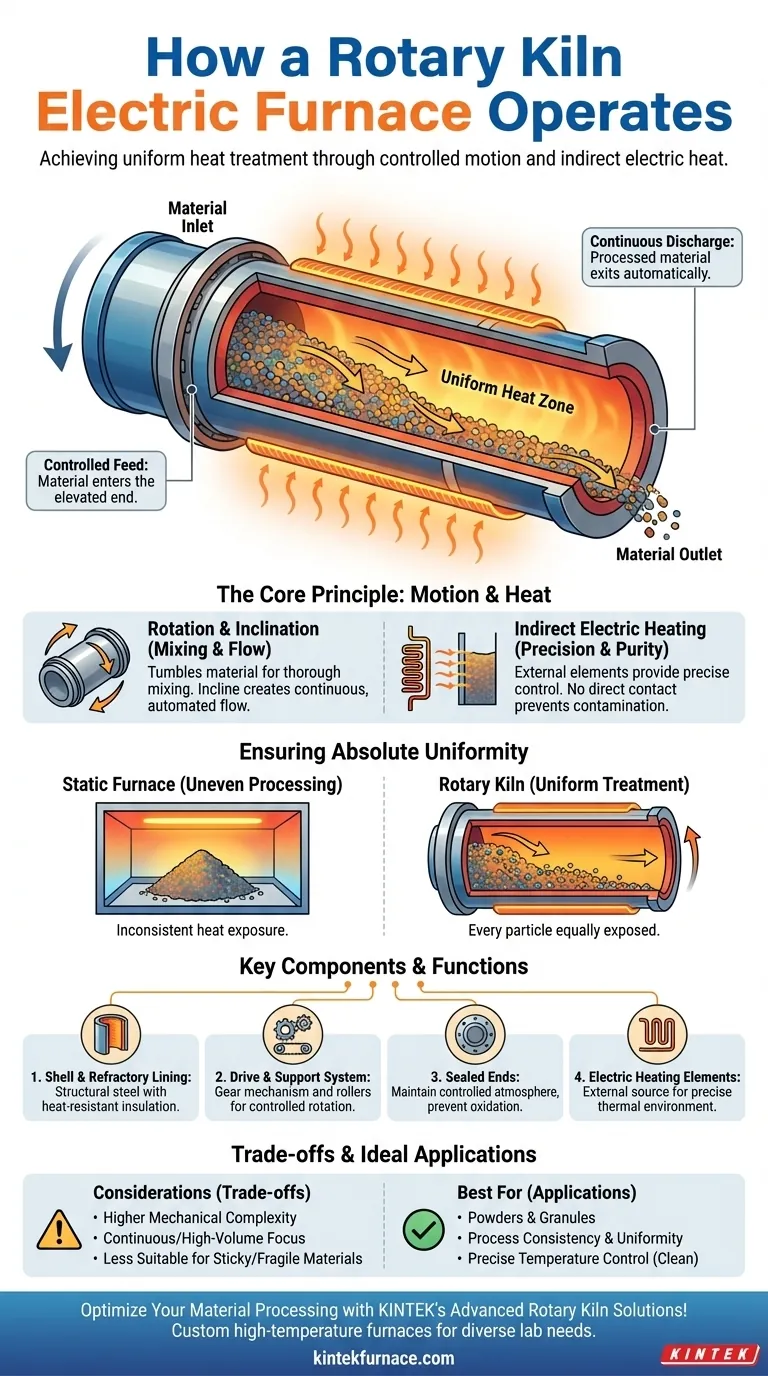
At its core, a rotary kiln electric furnace operates by using controlled rotation and a slight incline to tumble materials through a precisely heated cylinder. This design uses external electric heating elements to ensure every particle of the material is exposed to the same temperature, solving the common problem of uneven processing found in static furnaces.
The fundamental advantage of a rotary kiln electric furnace is its ability to deliver exceptionally uniform heat treatment. By combining continuous mixing with precise, indirect electric heat, it overcomes the inconsistencies inherent in static batch processing.

The Core Operating Principle: Motion and Heat
The effectiveness of this furnace comes from the interplay between its physical movement and its heating method. Each aspect is engineered to achieve a specific outcome.
The Role of Rotation and Inclination
The main body of the furnace is a long, cylindrical barrel, often called a retort or shell. This barrel is mounted on a slight horizontal angle.
As the barrel rotates slowly, it gently tumbles the material inside. This motion ensures thorough mixing, preventing any part of the load from remaining unexposed at the bottom of the pile.
Simultaneously, the slight incline causes the material to gradually advance from the higher entry point (inlet) to the lower exit point (outlet), creating a continuous and automated process.
The Advantage of Electric Heating
This furnace uses an indirect heating method. The electric heating elements are positioned outside the rotating barrel.
Heat is transferred through the barrel's wall to the material inside. This separation of the heat source from the material prevents contamination and allows for extremely precise temperature control.
Unlike direct-fired gas kilns where combustion gases interact with the material, external electric heat provides a clean and highly uniform thermal environment.
Ensuring Absolute Uniformity
In a traditional static furnace, material sits in a pile or on trays. The outer and top layers are exposed to more heat, while the interior remains cooler, leading to inconsistent results.
A rotary kiln eliminates this problem entirely. The constant tumbling action ensures that every particle is uniformly exposed to the heated inner surface of the barrel, guaranteeing a consistent physical or chemical transformation throughout the entire batch.
Key Components and Their Function
Several critical parts work together to make the furnace operate effectively.
The Shell and Refractory Lining
The shell is the outer steel cylinder that provides the furnace's structure. Inside, it is protected by a refractory lining, a heat-resistant material that insulates the shell and endures the high process temperatures.
The Drive and Support System
A drive gear mechanism engages with the shell to produce the slow, controlled rotation. The entire rotating assembly is supported by heavy-duty support tyres and rollers, which bear the weight and ensure smooth movement.
Sealed Ends for Atmosphere Control
The inlet and outlet ends of the furnace are typically sealed. This is crucial for maintaining a specific controlled atmosphere inside the kiln, which is often required for processing sensitive materials and preventing unwanted chemical reactions like oxidation.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, this design has specific considerations that make it suitable for certain applications over others.
Mechanical Complexity
The rotating mechanism, including the drive gear, rollers, and seals, introduces more moving parts compared to a simple static furnace. This can result in higher initial costs and more demanding maintenance requirements over the furnace's lifespan.
Throughput vs. Application
Rotary kilns are engineered for continuous or semi-continuous processing, making them ideal for high-volume production. They may be less practical for very small, single-batch research or for processes that require frequent and rapid changes in material type.
Material Suitability
The tumbling action is perfect for powders, granules, and small, free-flowing solids. However, it may not be suitable for materials that are very sticky, prone to agglomeration, or extremely fragile.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Selecting the right furnace technology depends entirely on your material and your desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is process consistency and uniformity: The rotary kiln's continuous mixing action is fundamentally superior to static furnace designs for achieving homogenous results.
- If your primary focus is precise temperature control for sensitive materials: The indirect, external electric heating offers a level of cleanliness and accuracy that is difficult to achieve with direct-fired kilns.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, continuous throughput: The inclined, rotating design is engineered specifically for moving material from inlet to outlet automatically, maximizing production efficiency.
Understanding these operational principles empowers you to select the ideal heating technology to meet your specific material processing goals.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Details |
|---|---|
| Operation | Uses controlled rotation and incline to tumble materials through a heated cylinder for uniform exposure. |
| Heating Method | Indirect electric heating with external elements for precise temperature control and no contamination. |
| Key Components | Shell with refractory lining, drive system, support rollers, and sealed ends for atmosphere control. |
| Best For | Powders, granules, high-volume continuous processing requiring consistency and cleanliness. |
| Trade-offs | Higher mechanical complexity and maintenance; less suitable for sticky or fragile materials. |
Optimize your material processing with KINTEK's advanced rotary kiln solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnace options like Rotary Furnaces, Muffle, Tube, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can enhance your efficiency and results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are some applications of rotary tube furnaces? Ideal for Continuous High-Temperature Material Processing
- How is the structure of a rotary tube furnace characterized? Discover Its Key Components and Benefits
- Why is efficient heat transfer important in rotary tube furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Throughput
- How do rotary tube furnaces support real-time monitoring and continuous processing? Boost Efficiency with Continuous Flow & Live Observation
- What are the benefits of continuous sample movement in rotary tube furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Efficiency



















