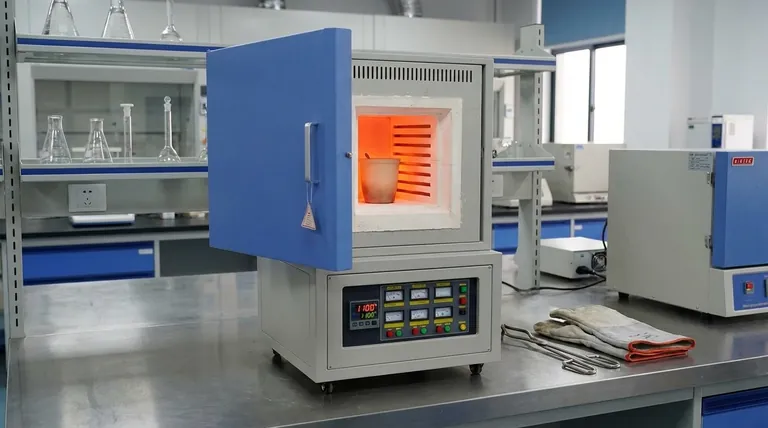
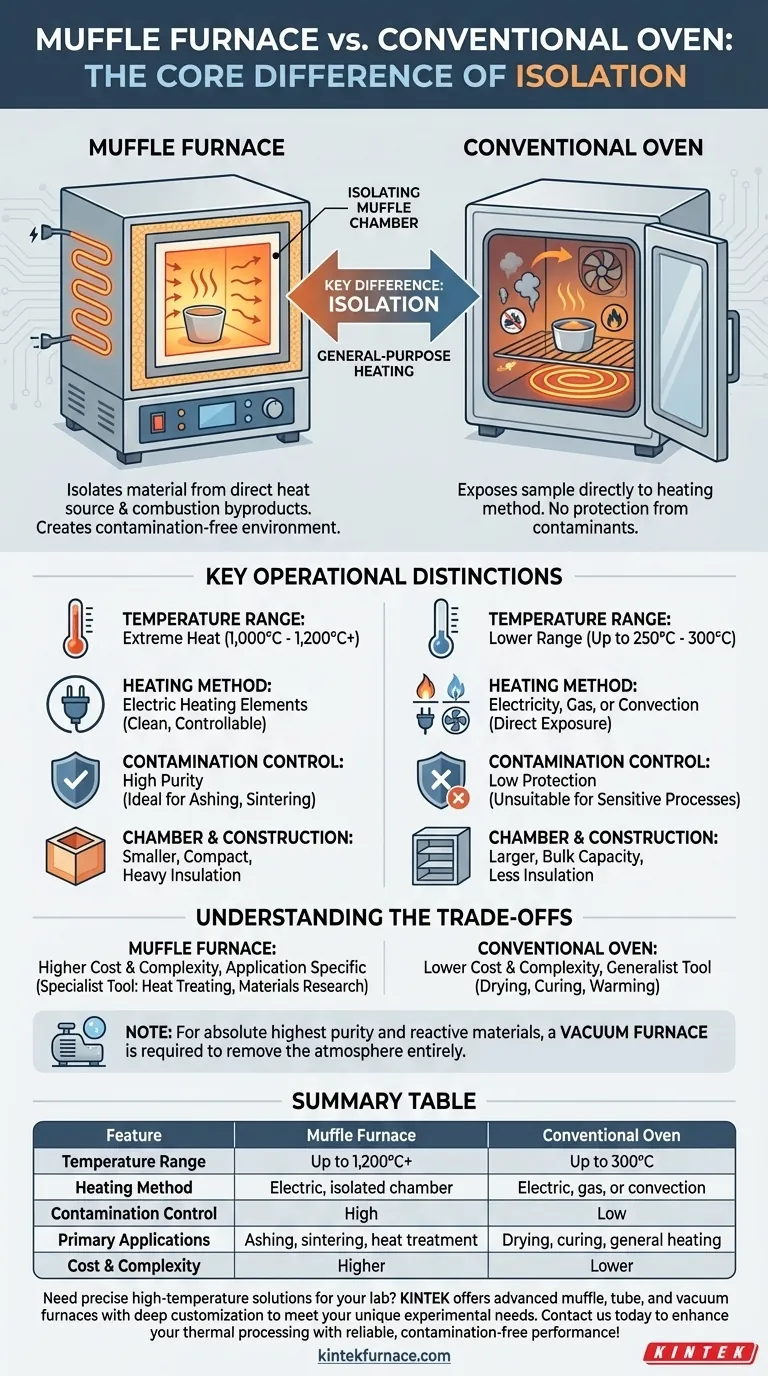
At its core, a muffle furnace differs from a conventional oven in one critical way: it isolates the material being heated from the direct heat source and any byproducts of combustion. A muffle furnace creates a highly controlled, contamination-free environment for specialized high-temperature tasks. In contrast, a conventional oven is a general-purpose tool for heating at lower temperatures where such isolation is not required.
The decision between a muffle furnace and a conventional oven is not about which is "better," but about which tool is correct for the job. A muffle furnace is for high-temperature precision and purity, while a conventional oven is for general-purpose heating and drying.

The Fundamental Design Difference: Isolation
The name "muffle furnace" comes from the "muffle," an insulating chamber that separates the workload from the heating elements. This design is the source of all its key capabilities.
How a Muffle Furnace Works
A muffle furnace contains an inner chamber made of high-temperature ceramic or alloy. The heating elements are positioned outside this chamber.
This design ensures that the sample is only exposed to radiant heat, not to the electrical elements or any potential contaminants they might release at extreme temperatures. Heavy insulation minimizes heat loss, allowing for stable and efficient operation at very high temperatures.
How a Conventional Oven Works
A conventional oven, whether for laboratory or industrial use, typically exposes the sample directly to the heating method.
This could involve direct radiation from gas burners or electric coils, or it may use a fan to circulate hot air (convection). This approach is perfect for tasks like drying or curing but offers no protection from atmospheric contaminants or byproducts from the heat source itself.
Key Operational Distinctions
The core design difference leads to significant variations in performance, application, and control. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for selecting the right equipment.
Temperature Range and Control
Muffle furnaces are built for extreme heat, commonly reaching temperatures of 1,000°C to 1,200°C or even higher. Their sophisticated controllers and thick insulation provide exceptionally precise and stable temperature management.
Conventional drying or lab ovens operate in a much lower range, typically up to 250°C or 300°C. Their temperature control is less precise, which is acceptable for their intended applications.
Heating Method and Environment
Muffle furnaces almost exclusively use electric heating elements. This method provides clean, controllable heat that is ideal for the isolated chamber design.
Ovens are more varied, employing electricity, gas, or convection. Gas-fired ovens, in particular, introduce combustion byproducts directly into the heating chamber.
Contamination Control
This is the primary reason to choose a muffle furnace. For applications like ashing (burning off organic material to determine inorganic content) or sintering (fusing powdered material), any contamination invalidates the results. The muffle design guarantees purity.
Conventional ovens offer no such protection, making them unsuitable for sensitive analytical or materials science processes.
Chamber Size and Construction
Muffle furnaces typically have smaller, compact chambers to ensure temperature uniformity and minimize energy use at high heat. The housing is robust, often made of stainless steel with thick, multi-layered fiber insulation.
Drying ovens often feature larger chambers designed to accommodate bulk materials or multiple large items at once, with less emphasis on heavy insulation.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a muffle furnace involves a commitment to specialized capability, which comes with clear trade-offs.
Cost and Complexity
Due to their specialized materials, advanced insulation, and precise temperature control systems, muffle furnaces are significantly more expensive than conventional ovens of a similar size. Their operation requires a greater understanding of thermal processing.
Application Specificity
A muffle furnace is a specialist tool. It excels at heat treating, ashing, materials research, and creating glass or enamel coatings. Using it for simple drying would be inefficient and unnecessary.
An oven is a generalist tool. It is perfectly suited for drying glassware, curing parts, and general warming applications where high heat and atmospheric purity are not concerns.
A Note on Vacuum Furnaces
For processes requiring the absolute highest level of purity, even a muffle furnace is insufficient. A vacuum furnace takes contamination control a step further by removing the atmosphere entirely. This is essential when working with highly reactive metals that would be damaged by oxygen, even in a clean muffle environment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your goal determines the correct tool. Evaluate your needs based on temperature, purity, and budget.
- If your primary focus is general drying, curing, or warming below 300°C: A conventional lab or drying oven is the correct, most cost-effective choice.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature analysis, material testing, or heat treatment that requires purity: A muffle furnace is the only suitable option to ensure accurate, repeatable results.
- If your primary focus is processing highly sensitive or reactive materials in an inert environment: Neither tool is correct; you require the superior contamination control of a vacuum furnace.
Ultimately, understanding the principle of sample isolation is the key to selecting the right thermal processing equipment for your specific task.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Muffle Furnace | Conventional Oven |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range | Up to 1,200°C+ | Up to 300°C |
| Heating Method | Electric, isolated chamber | Electric, gas, or convection |
| Contamination Control | High (isolated from heat source) | Low (exposed to byproducts) |
| Primary Applications | Ashing, sintering, heat treatment | Drying, curing, general heating |
| Cost and Complexity | Higher | Lower |
Need precise high-temperature solutions for your lab? KINTEK offers advanced muffle, tube, and vacuum furnaces with deep customization to meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to enhance your thermal processing with reliable, contamination-free performance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the primary function of a muffle furnace for BaTiO3? Master High-Temp Calcination for Ceramic Synthesis
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency



















