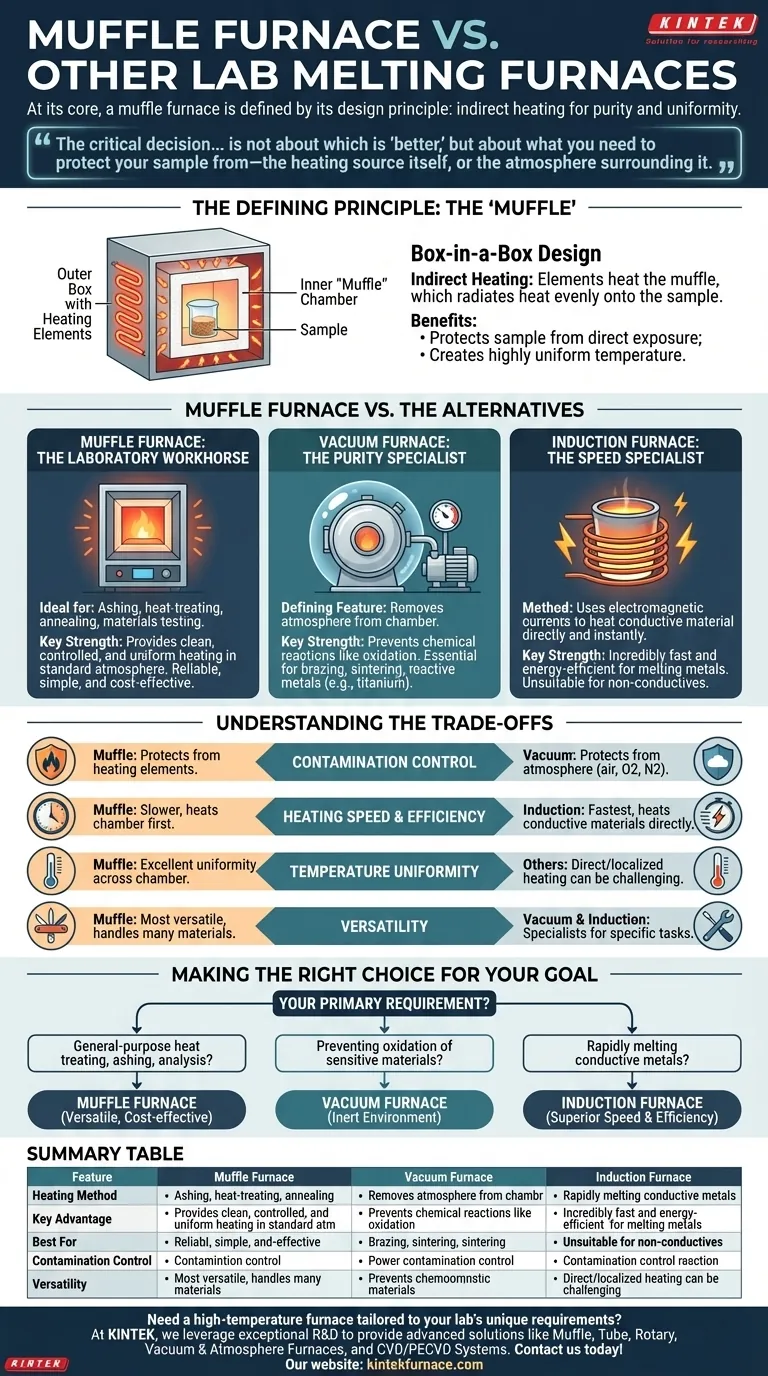
At its core, a muffle furnace is defined by its design principle: the sample is placed inside an insulated chamber (the "muffle") that is heated externally. This separates the material from the heating elements and any contaminants from combustion. In contrast, other furnaces may heat the material directly or control the atmosphere in a more specialized way, such as creating a vacuum.
The critical decision between a muffle furnace and its alternatives is not about which is "better," but about what you need to protect your sample from—the heating source itself, or the atmosphere surrounding it.
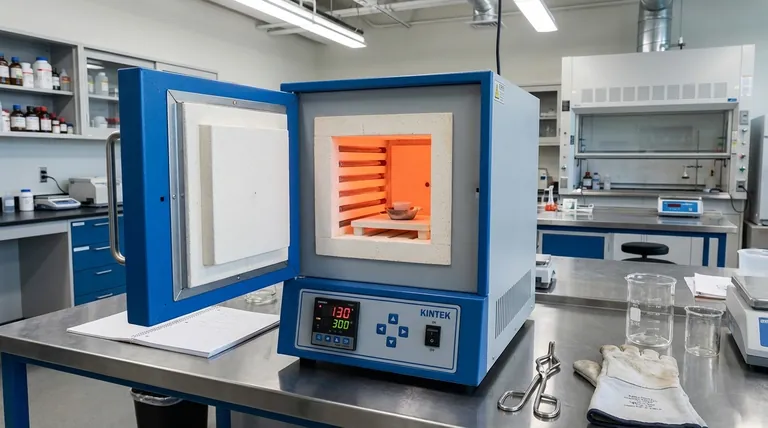

The Defining Principle: The "Muffle"
A muffle furnace is essentially a "box-in-a-box." The outer box contains the heating elements (coils or rods), and the inner box, or muffle, holds the sample.
Indirect Heating for Purity and Uniformity
The heating elements heat the muffle, which then radiates heat evenly onto the sample. This indirect approach is the furnace's key feature.
This design provides two primary benefits: it protects the sample from direct exposure to the heating elements, and it creates a highly uniform temperature environment, which is crucial for repeatable processes.
Muffle Furnace vs. The Alternatives
Choosing the right furnace requires understanding the specific environment each one creates. A muffle furnace is a versatile generalist, but specialized tasks often demand specialized tools.
Muffle Furnace: The Laboratory Workhorse
Muffle furnaces are ideal for a wide range of applications like ashing, heat-treating, annealing, and materials testing.
Their strength lies in providing a clean, controlled, and uniform heating environment in a standard atmosphere. They are reliable, relatively simple, and cost-effective for most common high-temperature lab work.
Vacuum Furnace: The Purity Specialist
The defining feature of a vacuum furnace is its ability to remove the atmosphere from the heating chamber.
This is not just about cleanliness; it's about preventing chemical reactions. Processes like brazing, sintering, or heat-treating reactive metals (e.g., titanium) would fail due to oxidation in a standard atmosphere. A vacuum furnace eliminates that risk entirely.
Induction Furnace: The Speed Specialist
An induction furnace does not use conventional heating elements. Instead, it uses powerful electromagnetic currents to heat a conductive material directly and instantly from within.
This method is incredibly fast and energy-efficient for melting metals and other conductive materials. However, it is highly specialized and unsuitable for non-conductive samples (like ceramics) or processes that require slow, uniform temperature ramps, like annealing.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No single furnace excels in every category. The optimal choice always involves balancing performance, cost, and the specific demands of your application.
Contamination Control
This is the most critical trade-off. A muffle furnace protects the sample from contamination by the heating elements. A vacuum furnace protects the sample from contamination by the atmosphere (air, oxygen, nitrogen).
Heating Speed and Efficiency
Induction furnaces are the fastest and most efficient for their specific task of heating conductive materials. Muffle furnaces are inherently slower, as they must first heat the entire insulated chamber before the sample reaches temperature.
Temperature Uniformity
Muffle furnaces excel at providing excellent temperature uniformity across the entire chamber, which is critical for consistent material processing. The direct and sometimes localized heating of other furnace types can make uniformity more challenging to achieve.
Versatility
The muffle furnace is the most versatile option, capable of handling many different materials and processes. Vacuum and induction furnaces are specialists, designed to perform a narrow range of tasks with exceptional performance.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your final decision should be guided by the primary requirement of your process.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose heat treating, ashing, or materials analysis: The muffle furnace is the most versatile and cost-effective choice.
- If your primary focus is preventing oxidation of sensitive materials: A vacuum furnace is the only tool that can provide the necessary inert environment.
- If your primary focus is rapidly melting conductive metals with maximum energy efficiency: An induction furnace is the superior and specialized instrument for the job.
By matching the furnace's core capability to your specific scientific or industrial goal, you ensure a precise, repeatable, and successful outcome.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Muffle Furnace | Vacuum Furnace | Induction Furnace |
|---|---|---|---|
| Heating Method | Indirect via muffle | Direct in vacuum | Direct via electromagnetic induction |
| Key Advantage | Uniform heating, sample purity from elements | Prevents oxidation, ideal for reactive materials | Fast, energy-efficient for conductive materials |
| Best For | Ashing, annealing, general heat treatment | Brazing, sintering, sensitive metals | Rapid melting of metals |
| Contamination Control | Protects from heating elements | Protects from atmosphere | Limited, depends on material conductivity |
| Versatility | High, handles various materials and processes | Low, specialized for inert environments | Low, only for conductive samples |
Need a high-temperature furnace tailored to your lab's unique requirements? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we can precisely meet your experimental needs, whether for general heat treatment, oxidation prevention, or rapid melting. Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can enhance your lab's efficiency and results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the study of biochar regeneration and reuse? Unlock Sustainable Water Treatment
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals



















