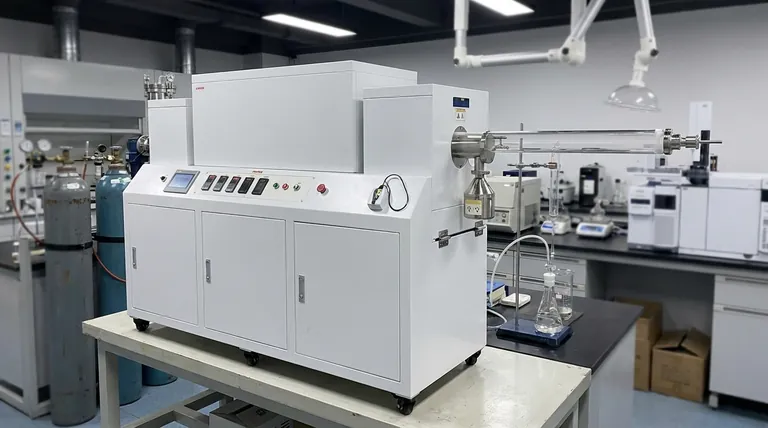
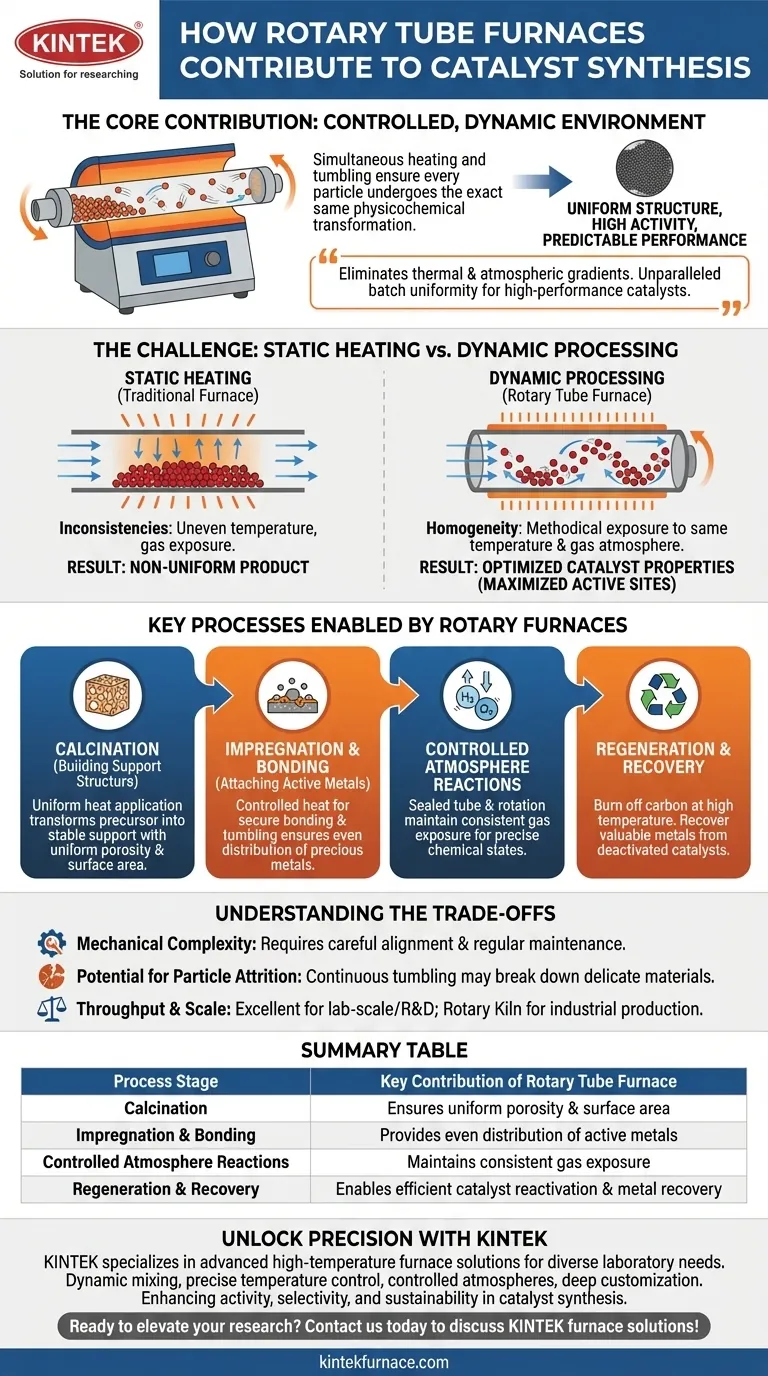
At its core, a rotary tube furnace contributes to catalyst synthesis by creating a highly controlled, dynamic environment where materials are simultaneously heated and tumbled. This continuous mixing ensures every particle undergoes the exact same physicochemical transformation, which is critical for producing catalysts with uniform structure, high activity, and predictable performance.
While many furnaces provide precise heat, the rotary tube furnace's defining advantage is its ability to eliminate thermal and atmospheric gradients. By constantly tumbling the material, it guarantees unparalleled batch uniformity, a non-negotiable requirement for high-performance catalysts.

The Challenge: Why Uniformity Governs Catalyst Performance
To understand the furnace's role, we must first understand the goal of catalyst synthesis. The effectiveness of a catalyst is dictated by its physical and chemical properties at a microscopic level.
The Goal: Maximizing Active Sites
A catalyst's performance, defined by its activity (reaction speed) and selectivity (producing the desired product), depends on its structure. This includes the surface area, pore size, and the precise distribution of active metal sites on a carrier material.
The Problem with Static Heating
In a traditional, static furnace, a bed of powdered material remains still. This leads to significant inconsistencies.
Particles on the top may be exposed to a different gas atmosphere than those at the bottom, while particles near the furnace walls get hotter than those in the center. This creates a non-uniform product where only a fraction of the catalyst performs as intended.
The Solution: Dynamic, Homogeneous Processing
A rotary tube furnace solves this by continuously tumbling the material. This motion ensures every single particle is methodically exposed to the same temperature and the same controlled gas atmosphere. This homogeneity is the key to creating a catalyst batch where every particle has the desired properties.
Key Catalyst Processes Enabled by Rotary Furnaces
The dynamic environment of a rotary furnace is essential for several distinct stages in the catalyst lifecycle, from creation to regeneration.
Calcination: Building the Support Structure
Calcination is a high-temperature thermal treatment that transforms a catalyst precursor into a stable, porous support structure. The rotation ensures that heat is applied evenly, resulting in uniform porosity and surface area, which are foundational for the final catalyst's performance.
Impregnation and Bonding: Attaching the Active Metals
In many catalysts, precious metals (like platinum or palladium) are bonded to a high-surface-area carrier (like alumina). A rotary furnace provides the controlled heat needed to securely bond these active metals, while the tumbling motion guarantees an even distribution across the entire carrier surface.
Controlled Atmosphere Reactions
Catalyst synthesis often requires specific gas environments, such as a reducing atmosphere (using hydrogen) or an oxidizing atmosphere (using oxygen), to achieve the correct chemical state of the active metals. The furnace's sealed tube and rotation ensure that all material reacts completely and uniformly with the process gas.
Regeneration and Recovery
Beyond initial synthesis, rotary furnaces are critical for sustainability. They are used to regenerate spent catalysts by carefully burning off accumulated carbon ("coke") at high temperatures. They also enable the recovery of valuable metals from deactivated catalysts, reducing waste and cost.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the rotary tube furnace is not a universal solution. Its advantages come with specific considerations.
Mechanical Complexity
The rotating mechanism, seals, and motor add a layer of mechanical complexity and maintenance compared to a simpler, static tube furnace. These systems require careful alignment and regular upkeep.
Potential for Particle Attrition
For very delicate or friable materials, the continuous tumbling motion can cause attrition, where particles break down into finer dust. This can alter the material's properties and may not be suitable for all precursors.
Throughput and Scale
Rotary tube furnaces are excellent for lab-scale research and development due to their precision. For massive industrial-scale production, a much larger version called a rotary kiln is used. The suitability for intermediate-scale production depends heavily on the specific process requirements.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right thermal processing tool depends entirely on your end objective.
- If your primary focus is developing novel catalysts with maximum uniformity: The dynamic mixing and precise atmospheric control of a rotary tube furnace are essential for achieving high activity and selectivity.
- If your primary focus is large-scale, continuous industrial production: A rotary kiln, which operates on the same principles, is the industry standard for processes like bulk calcination.
- If your primary focus is sustainability and catalyst lifecycle management: A rotary furnace is a uniquely effective tool for regenerating spent catalysts and recovering valuable metals.
By understanding these principles, you can leverage the unique capabilities of a rotary tube furnace to control material transformations with exceptional precision.
Summary Table:
| Process Stage | Key Contribution of Rotary Tube Furnace |
|---|---|
| Calcination | Ensures uniform porosity and surface area for stable catalyst support |
| Impregnation and Bonding | Provides even distribution of active metals on carrier materials |
| Controlled Atmosphere Reactions | Maintains consistent gas exposure for precise chemical states |
| Regeneration and Recovery | Enables efficient catalyst reactivation and metal recovery |
Unlock Precision in Your Catalyst Synthesis with KINTEK
Are you striving for unparalleled uniformity and performance in your catalyst development? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored for diverse laboratory needs. Our rotary tube furnaces, part of a comprehensive product line including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, are engineered with exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to deliver dynamic mixing, precise temperature control, and controlled atmospheres. With strong deep customization capabilities, we ensure our solutions precisely meet your unique experimental requirements, enhancing activity, selectivity, and sustainability in catalyst synthesis.
Ready to elevate your research? Contact us today to discuss how KINTEK can support your goals with reliable, customized furnace technology!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the benefits of continuous sample movement in rotary tube furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Efficiency
- How is the structure of a rotary tube furnace characterized? Discover Its Key Components and Benefits
- What other fields utilize rotary tube furnaces? Discover Versatile Heating Solutions for Multiple Industries
- What are the key features of rotary tube furnaces regarding heat treatment? Achieve Uniform Heating and High Throughput
- What are some applications of rotary tube furnaces? Ideal for Continuous High-Temperature Material Processing



















