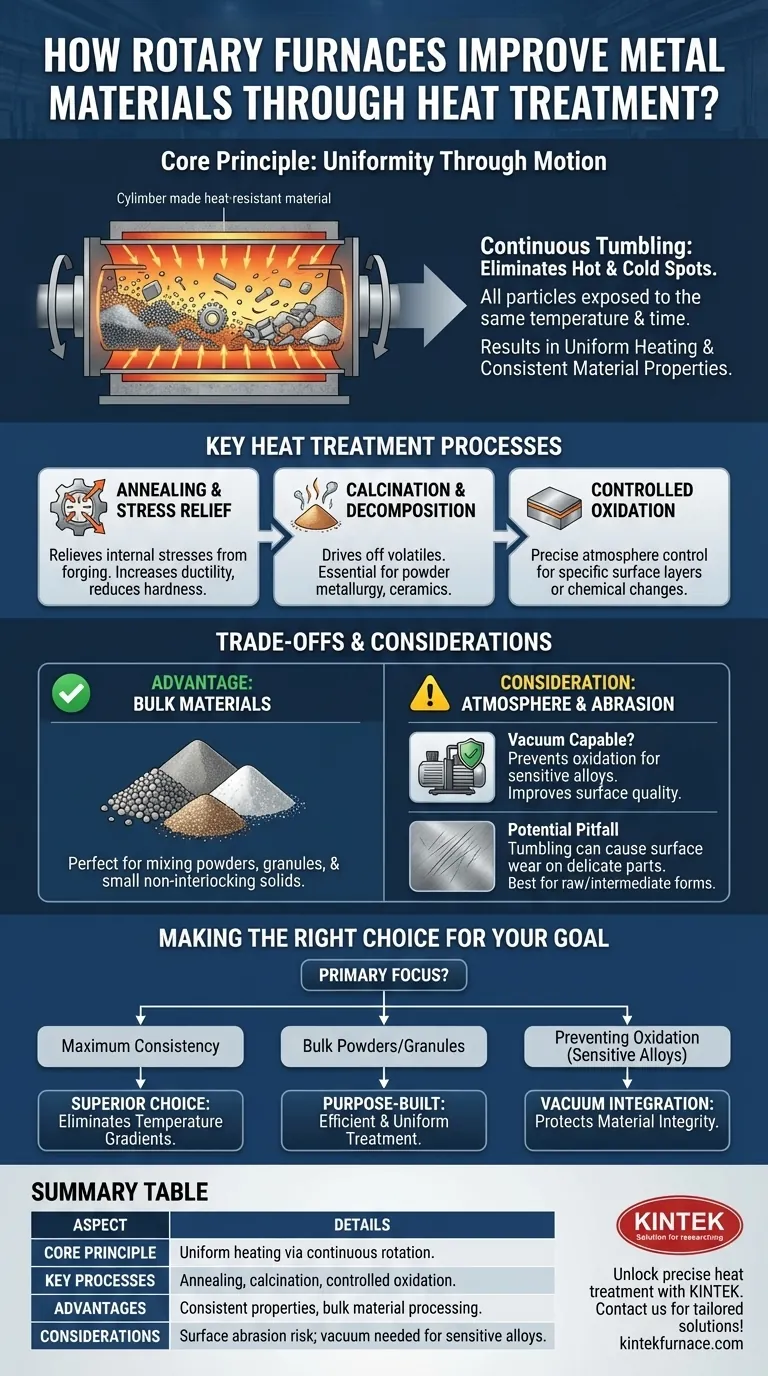
At their core, rotary furnaces improve metal materials through superior thermal uniformity. By continuously rotating and tumbling the material during heat treatment, these furnaces ensure that every particle or part is exposed to the same temperature for the same amount of time. This eliminates hot and cold spots, leading to highly consistent and predictable improvements in the material's final structure and performance.
The defining advantage of a rotary furnace is its ability to create homogenous material properties. The constant motion guarantees that processes like annealing or calcination are applied evenly throughout the entire batch, which is often impossible to achieve in a static furnace.
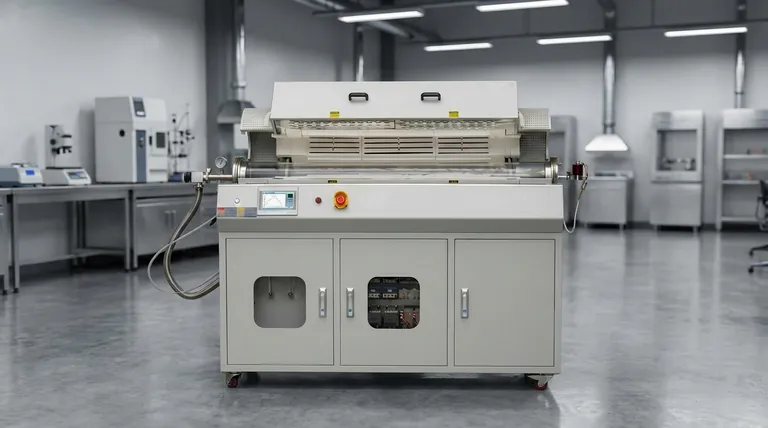

The Core Principle: Uniformity Through Motion
A rotary furnace is a cylindrical chamber that rotates along its horizontal axis. This simple mechanical action is the key to its effectiveness in heat treatment.
How Rotation Creates Uniform Heating
As the furnace rotates, the material inside is constantly lifted and tumbled. This action, often called mixing, continuously exposes new surfaces of the material to the heat source.
This prevents the outer layers of the material batch from insulating the inner core, a common problem in static furnaces.
Eliminating Temperature Gradients
The primary goal of this tumbling is to eliminate temperature gradients, which are differences in temperature between different parts of the material.
By ensuring the entire batch reaches and maintains the target temperature uniformly, the resulting metallurgical transformation is consistent. This leads directly to more reliable and predictable mechanical properties in the final product.
Key Heat Treatment Processes
The precise temperature control and uniform heating of rotary furnaces make them ideal for several critical industrial processes.
Annealing and Stress Relief
Annealing is a process that alters a metal's microstructure to increase its ductility and reduce its hardness, making it more workable.
The uniform heating and controlled cooling in a rotary furnace are perfect for relieving internal stresses that may have been introduced during forging or other manufacturing steps.
Calcination and Thermal Decomposition
Rotary furnaces are widely used for calcination, a high-temperature process that drives off volatile substances or induces a phase transition in a material.
This is essential in industries like powder metallurgy and the production of ceramics or refractory materials, where precise thermal decomposition is required.
Controlled Oxidation
While often undesirable, oxidation can be a controlled process used to create specific surface layers or chemical changes.
A rotary furnace allows for precise control over the atmosphere, enabling controlled oxidation when required for a specific material outcome.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
No single technology is a universal solution. Understanding the context where a rotary furnace excels—and where it might not—is crucial.
Advantage: Processing Bulk Materials
Rotary furnaces are exceptionally well-suited for processing materials in bulk forms like powders, granules, and small, non-interlocking solids. Their ability to mix these forms is a significant advantage over other furnace types.
Consideration: The Role of Atmosphere
Many high-performance metal treatments require a controlled atmosphere to prevent unwanted chemical reactions, especially oxidation at high temperatures.
When this is a priority, a vacuum can be integrated into the furnace design. Operating under a vacuum prevents oxidation, which dramatically improves the surface quality and mechanical performance of sensitive metals.
Potential Pitfall: Surface Abrasion
The tumbling action that ensures uniform heating can also cause surface wear or abrasion on delicate or finished parts.
For this reason, rotary furnaces are typically used for raw materials or intermediate products rather than finished components where surface integrity is paramount.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right heat treatment method depends entirely on your material and desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum material consistency: The rotary furnace's ability to eliminate temperature gradients makes it the superior choice for uniform properties.
- If your primary focus is processing bulk powders or granular materials: A rotary furnace is purpose-built for the efficient and uniform heat treatment of these material forms.
- If your primary focus is preventing surface oxidation on sensitive alloys: Ensure the rotary furnace is a vacuum-capable model to protect material integrity at high temperatures.
By matching the furnace's core strengths to your process objectives, you can unlock significant improvements in material quality and performance.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Core Principle | Uniform heating through continuous rotation and tumbling of materials. |
| Key Processes | Annealing, calcination, controlled oxidation for stress relief and decomposition. |
| Advantages | Eliminates temperature gradients, ensures consistent material properties, ideal for bulk powders and granules. |
| Considerations | May cause surface abrasion; vacuum integration prevents oxidation for sensitive alloys. |
Unlock precise heat treatment for your materials with KINTEK's advanced rotary furnaces. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with tailored solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures your unique experimental requirements are met for superior performance and efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can elevate your processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the main structural components of a rotary furnace? Explore Key Parts for Efficient Material Processing
- How do rotary tube furnaces achieve precise temperature control? Master Uniform Heating for Dynamic Processes
- What is the purpose of the rotation mechanism in a rotary tube furnace? Achieve Uniform Heating and Enhanced Process Control
- What are the common approaches to mixing in rotary furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Efficiency in Thermal Processing
- What types of materials are suitable for processing in rotary tube furnaces? Ideal for Free-Flowing Powders and Granules



















