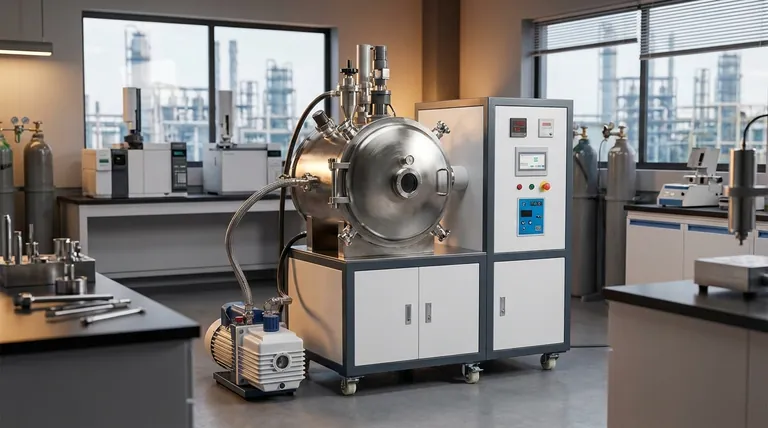
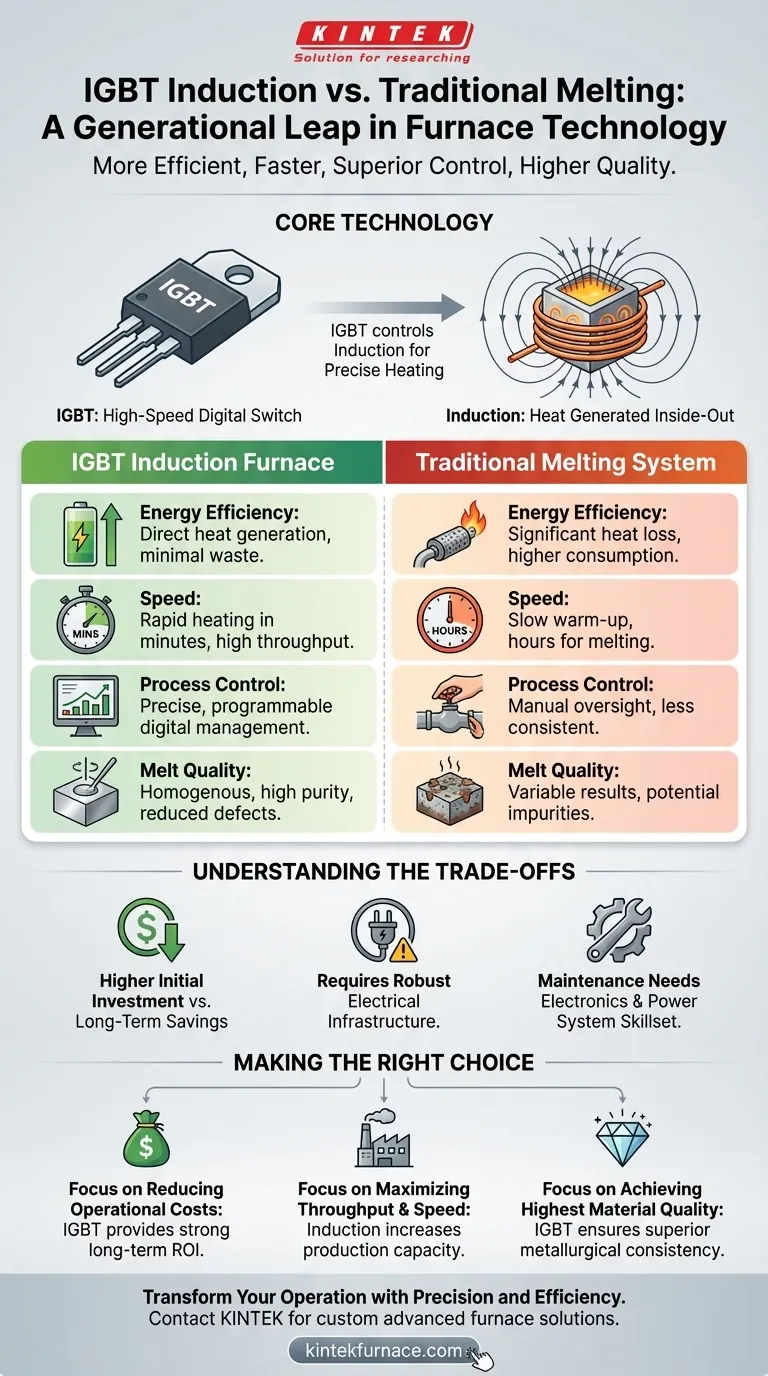
In a direct comparison, IGBT induction melting furnaces represent a generational leap forward from traditional melting systems. They are fundamentally more energy-efficient, offer significantly faster melt times, provide superior process control, and result in a higher quality final product. This is not an incremental improvement but a transformative shift in melting technology.
The core difference lies in how heat is generated. Traditional systems heat the metal from the outside-in, wasting significant energy, while IGBT induction furnaces use a precisely controlled electromagnetic field to generate heat directly inside the metal itself, unlocking major gains in efficiency, speed, and quality.

Understanding the Core Technology: The IGBT Advantage
To appreciate the difference, you must first understand the role of the Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor (IGBT) and the principle of induction. This combination is what makes modern furnaces so effective.
The Role of the IGBT: A High-Speed Digital Switch
An IGBT is an advanced semiconductor device that functions as an extremely fast and precise electrical switch. It combines the high-current handling of a bipolar transistor with the simple gate control of a MOSFET.
In an induction furnace, the IGBT precisely regulates the high-frequency power delivered to the induction coil. This allows for unparalleled, real-time control over the energy input, which directly translates to exact temperature control throughout the melting process.
How Induction Generates Heat
Induction furnaces do not use combustible fuels or external heating elements that make physical contact with the material. Instead, a powerful alternating current flows through a copper coil, creating a strong magnetic field.
When conductive metal is placed within this field, the field induces powerful electrical currents (eddy currents) within the metal itself. The metal's natural resistance to these currents generates intense, rapid heat, causing it to melt from the inside out.
A Head-to-Head Comparison: IGBT vs. Traditional Systems
When evaluated across key performance indicators, the advantages of an IGBT-powered induction system become clear.
Energy Efficiency and Operational Cost
IGBT induction is vastly more energy-efficient. Because heat is generated directly within the target metal, very little energy is wasted heating the furnace structure or the surrounding atmosphere.
Traditional fuel-fired furnaces, by contrast, suffer from significant heat loss through exhaust gases and thermal radiation, resulting in much higher energy consumption per ton of metal melted.
Speed and Throughput
The melting speed of an induction furnace is measured in minutes, not hours. This rapid heating cycle dramatically increases operational throughput and allows for more agile production scheduling compared to the slow warm-up and melting times of conventional systems.
Process Control and Consistency
This is a critical differentiator. The IGBT allows for fully automatic, programmable melting cycles with precise temperature management. This digital control ensures that every batch is melted under the exact same conditions, leading to highly uniform and repeatable results.
Traditional systems often rely on manual oversight, making it difficult to achieve the same level of consistency from one melt to the next.
Melt Quality and Metallurgical Purity
The magnetic field in an induction furnace creates a natural electromagnetic stirring action. This constant motion ensures a homogenous and uniform mixture of the molten metal, which is crucial for alloys.
This stirring helps impurities and slag (scum) rise to the surface for easier removal. The result is a cleaner, brighter final casting with significantly reduced defects like porosity or shrinkage.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While the benefits are substantial, a responsible technical evaluation must also consider the practical implications and potential challenges.
The Initial Investment
Modern IGBT induction systems typically carry a higher initial capital cost compared to some traditional furnace types. This investment must be weighed against the long-term savings in energy, materials, and labor.
Electrical Infrastructure Demands
High-power induction furnaces require a robust and stable electrical supply. Facilities may need to upgrade their power infrastructure to support the load, which can be a significant secondary cost.
Maintenance and Skillset
While overall maintenance is often lower due to fewer moving parts and no burners to service, troubleshooting the power electronics requires a different skillset. Your maintenance team will need training in electronics and power systems, not just traditional mechanical repair.
Making the Right Choice for Your Operation
The decision to adopt IGBT induction technology should be driven by your specific operational goals.
- If your primary focus is reducing operational costs: The superior energy efficiency and lower maintenance needs of an IGBT furnace provide a clear path to a strong long-term return on investment.
- If your primary focus is maximizing throughput and speed: The rapid "minutes-not-hours" melting cycle of an induction system is unmatched and will directly increase your plant's production capacity.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest material quality: The precise process control and electromagnetic stirring of an IGBT furnace deliver superior metallurgical consistency, purity, and final product integrity.
Ultimately, investing in an IGBT induction furnace is an investment in precise control, which drives fundamental improvements across your entire melting operation.
Summary Table:
| Feature | IGBT Induction Furnace | Traditional Melting System |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Method | Inside-out via electromagnetic field | Outside-in via fuel/element |
| Energy Efficiency | High (direct heat generation) | Lower (significant heat loss) |
| Melting Speed | Minutes (rapid heating) | Hours (slow warm-up) |
| Process Control | Precise, programmable digital control | Often manual, less consistent |
| Melt Quality | High purity with electromagnetic stirring | Variable, potential for impurities |
| Initial Cost | Higher upfront investment | Typically lower |
| Operational Cost | Lower long-term (energy/maintenance) | Higher (fuel, maintenance) |
Ready to Transform Your Melting Operation with Precision and Efficiency?
At KINTEK, we leverage our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing capabilities to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your unique needs. Our expertise in IGBT induction melting technology ensures you achieve superior energy efficiency, faster throughput, and unparalleled process control for a higher quality final product.
Whether you operate a foundry, a metallurgical lab, or a specialized manufacturing facility, our team is ready to design a custom solution that maximizes your return on investment.
Contact KINTEK today for a personalized consultation and discover how our advanced melting systems can revolutionize your production process.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- How has vacuum smelting impacted the development of superalloys? Unlock Higher Strength and Purity
- Why is a Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace essential? Unlock Purity for Aerospace and Semiconductors
- What role does a vacuum induction melting furnace play in Fe-5%Mn-C alloys? Ensure Chemical Integrity and High Purity
- How does the Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) process work? Achieve Superior Metal Purity and Control
- What are the common applications of Vacuum Induction Melting? Essential for High-Performance Metals and Alloys



















