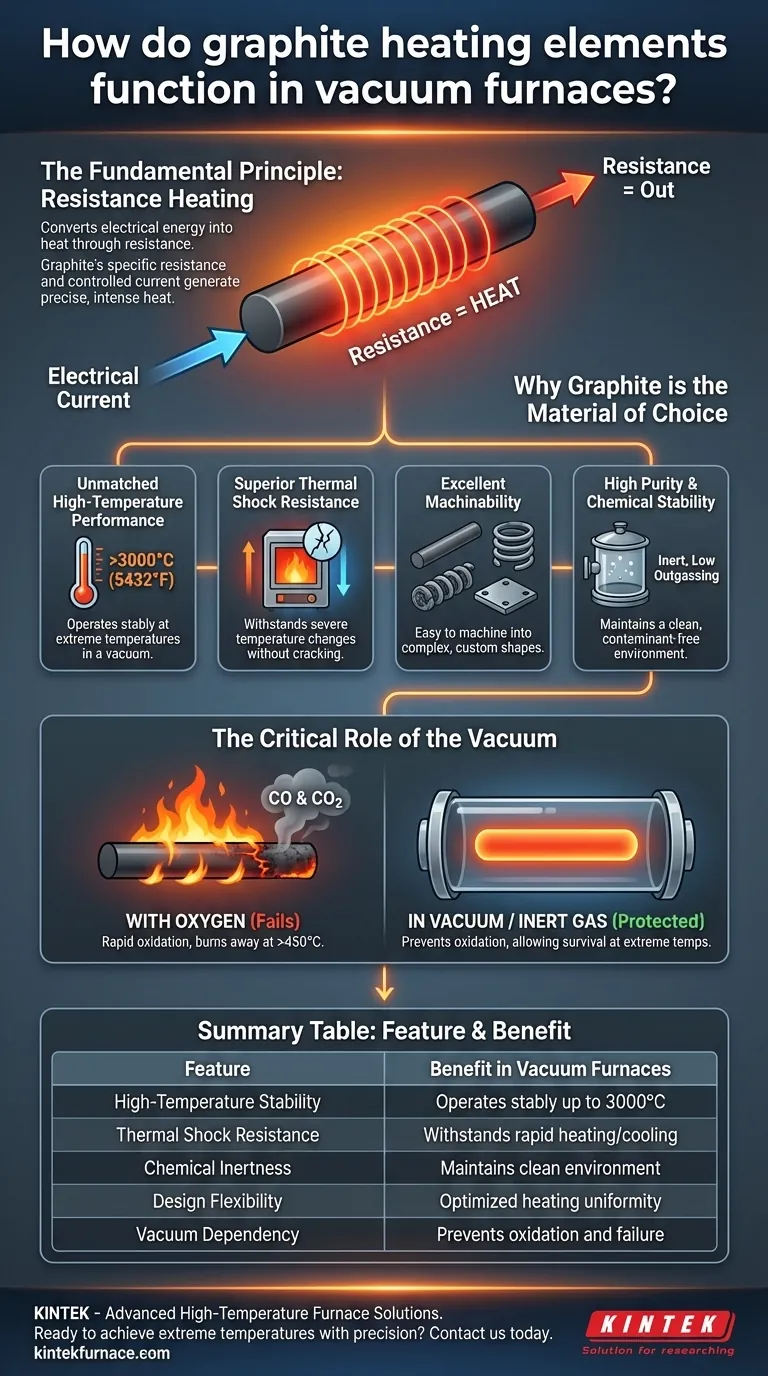
At its core, a graphite heating element in a vacuum furnace functions by converting electrical energy into heat through the principle of resistance heating. When a high electrical current is passed through the graphite, its inherent resistance causes it to glow and radiate immense amounts of heat. The vacuum environment is not incidental; it is absolutely critical, as it protects the graphite from oxidizing and disintegrating at the extreme temperatures it is designed to achieve.
The use of graphite is a deliberate engineering choice for high-temperature vacuum applications. Its unique combination of thermal stability, chemical inertness, and structural integrity makes it superior to most metals, but only when protected from oxygen by a vacuum or an inert gas.
The Fundamental Principle: Resistance Heating
A graphite element operates on the same basic principle as the glowing wires in a toaster, but engineered for much more demanding conditions.
How Current Generates Heat
When electricity flows through any material, it encounters resistance. This opposition to the electrical flow generates heat. By designing elements with a specific resistance and passing a controlled current through them, we can produce precise and intense heat.
The Role of Material Properties
Graphite has an electrical resistance that is low enough to conduct large currents efficiently but high enough to generate significant heat. This property, combined with its other unique characteristics, makes it an ideal material for this purpose.
Why Graphite is the Material of Choice
Graphite is not used by accident. It is selected because its properties solve multiple challenges associated with high-temperature vacuum processing.
Unmatched High-Temperature Performance
Graphite can operate stably at temperatures up to 3000°C (5432°F) in a vacuum. Most metals would have melted or vaporized long before reaching these temperatures, making graphite one of the few viable options for extreme heat applications.
Superior Thermal Shock Resistance
Furnaces often need to heat up and cool down rapidly. Graphite has an exceptionally low coefficient of thermal expansion and high thermal conductivity, allowing it to withstand severe temperature changes without cracking or breaking.
Excellent Machinability and Design Flexibility
Despite its strength at high temperatures, graphite is relatively soft and easy to machine at room temperature. This allows for the creation of complex and efficient heating element shapes, such as rods, tubes, or large radiating plates, tailored to specific furnace designs.
High Purity and Chemical Stability
In a vacuum, graphite is chemically inert and has a very low vapor pressure. This means it does not easily react with the materials being processed or release impurities (outgas) that could contaminate the clean vacuum environment.
Understanding the Trade-offs: The Critical Role of the Vacuum
The primary limitation of graphite is also its defining operational requirement. Without the correct atmosphere, a graphite heating element will fail catastrophically.
The Existential Threat of Oxidation
In the presence of oxygen, hot graphite will rapidly oxidize—in simple terms, it will burn away into CO and CO2 gas. This process begins at temperatures as low as 450°C and accelerates dramatically as heat increases.
The Necessity of a Vacuum or Inert Gas
A vacuum furnace removes the oxygen, eliminating the threat of oxidation. Alternatively, the furnace can be backfilled with an inert gas like Argon or Nitrogen. This protective atmosphere is what allows the graphite to survive and perform at extreme temperatures.
Comparison with Other Materials
While materials like molybdenum and silicon carbide are also used as heating elements, graphite generally offers a higher maximum operating temperature and superior resistance to thermal shock, making it the preferred choice for the most demanding applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Understanding these principles allows you to align your furnace technology with your processing goals.
- If your primary focus is reaching extreme temperatures (above 2000°C): Graphite is the industry standard, offering unparalleled stability where most other materials fail.
- If your primary focus is process purity and repeatability: Graphite's chemical inertness and low outgassing ensure a clean environment and consistent results from one cycle to the next.
- If your primary focus is rapid thermal cycling: Graphite's exceptional thermal shock resistance provides a long service life and reliability in processes requiring fast heating and cooling.
By leveraging graphite's unique properties within a controlled atmosphere, engineers can achieve consistent and powerful high-temperature processing.

Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit in Vacuum Furnaces |
|---|---|
| High-Temperature Stability | Operates stably up to 3000°C (5432°F) |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Withstands rapid heating and cooling cycles without cracking |
| Chemical Inertness | Maintains a clean, contaminant-free process environment |
| Design Flexibility | Can be machined into complex shapes for optimal heating uniformity |
| Vacuum Dependency | Requires a vacuum or inert gas to prevent oxidation and failure |
Ready to achieve extreme temperatures with precision and reliability?
At KINTEK, we leverage our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental and production requirements.
Contact us today to discuss how our graphite heating element technology can enhance your high-temperature processing. Let our experts help you build a solution tailored for your success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Disilicide MoSi2 Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does graphite contribute to energy efficiency in vacuum furnaces? Achieve Faster, More Uniform Heating
- What is the significance of vacuum in relation to graphite components in furnaces? Prevent Oxidation for Extreme Temperatures
- What is the mechanism and effect of post-annealing NiTi thin films in a vacuum furnace? Unlock Superelasticity
- Why are vacuum furnaces used for the re-quenching of samples after a boriding treatment? Master Core Toughness
- What is the primary function of a vacuum graphite furnace? Achieve Extreme-Temperature Material Purity



















